Eggplant is a demanding crop. The plant is native to Southeast Asia and tropical regions of India. A culture accustomed to a warm climate makes many demands on its growth. If they are disturbed, problems will arise, first of all, the foliage will turn yellow. In this article we will tell you why eggplant leaves turn yellow and what to do to return them to a healthy green color and wait for the “little blue” harvest.
Causes of yellowing leaves of “blue” leaves 2. How to solve problems with yellowing leaves 2.1. How to arrange watering of plants 2.2. How to treat plants when diseases occur 2.3. How to solve a problem due to a pest attack 2.4. What to do if you choose the wrong soil 2.5. How to help plants with root damage 3. What to do if the lower plates suffer 3.1. How to improve the nutrition of the “little ones” in order to get rid of the disease 3.2. How to help a crop when the temperature regime is violated 3.3. Dealing with the problem of poor light conditions
Photo by ru.depositphotos: Identify the cause of the disease and begin treatment.
Inappropriate soil
Eggplant grows well and fully develops in loose and nutritious soil. You need to take care of its compliance with these requirements in advance, preferably in the fall.
It is not permissible to plant plants in heavy, dense soil. But they won’t like too light, sandy soil either. If the beds in your greenhouse are filled with such a substrate, the eggplant will begin to turn yellow and will not be able to develop properly.
To loosen heavy soils, it is recommended to add sand, peat, and sawdust. To compact sand compounds, it is worth adding a mixture of garden turf and clay.
Bad soil
In a greenhouse where eggplants are grown, yellow leaves appear due to infertile soil layer. Plants are quite demanding of soil; they need soil with a loose structure. Loam with a neutral reaction is best suited. The soil needs to be fertilized. I feed the soil with humus. The soil needs organic fertilizers.
The reason is in the soil
Transplant stress
Eggplant seedlings grown at home have difficulty getting used to a change in environment. If you have not taken care of the gradual adaptation of the plants to the microclimate of the greenhouse, immediately after planting they will begin to turn yellow and shed their leaves.
To prevent this, seedlings need to be hardened off, starting 2 weeks before the transplant procedure. Boxes with plants are taken out for a “walk” in the greenhouse. Of course, if the temperature in it rose to +18 - +20 degrees. At first, the stay in new conditions is 15–20 minutes. Day after day, the “walk” time is increased.
Possible causes of yellowing leaves
When growing seedlings, problems sometimes arise: seedlings fall and growth slows down . Eggplant seedlings may turn yellow. Deviations in development must be treated carefully, otherwise you will not be able to get a harvest. Yellowing is caused by the following reasons:
- insufficient content of macro- or microelements in the soil;
- violation of the watering regime;
- lack of nitrogen;
- development of diseases caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi;
- planting unhardened seedlings in the ground;
- the appearance of pests;
- violation of the fertilizer application regime.
This is useful to know, read: - Eggplant planting seedlings lunar calendar 2021
The upper leaves of seedlings turn yellow when the vegetable crop lacks microelements. The lower ones change color from a lack of macroelements and light.
Reference! There is no need to worry if the seedlings’ cotyledons begin to lighten when the first pairs of true leaves have formed. The death of old vegetative organs is a natural physiological process that accompanies the maturation of a culture.
Lack of lighting
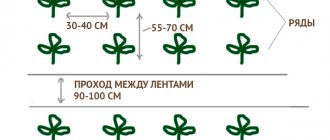
Plants planted too close and poorly formed experience a lack of sunlight. Eggplant bushes are powerful and spreading, so the norm for planting them is 3 plants per 1 sq./m.
For some varieties of eggplant, there are special planting standards. Recommended spacing information can be found on the seed packet.
An important condition for growing eggplants in a greenhouse is the correct and timely formation of the bush. Excess shoots thicken the plantings, depriving parts of the plants of sunlight. As a result, photosynthesis processes in the leaves are disrupted and they begin to turn yellow.
When grown in greenhouses, it is recommended to form eggplants into 1 or 2 stems. The first removal of excess shoots is carried out 3 - 4 weeks after planting the plants in the ground. By this time, the seedlings have already formed a powerful root system and are fully adapted to the microclimate of the greenhouse.
To form a bush, remove all side shoots up to the first fork. To provide nutrition to the first ovary, leave 1 leaf on the bottom of the stem. Of the shoots formed above the forks, 1 or 2 of the most developed and powerful ones are left. Next, the newly growing stepsons are removed weekly, preventing them from outgrowing.
In the process of forming eggplant bushes, together with the stepsons, remove dried leaves that are beginning to rot. They not only thicken the bushes, depriving parts of the plants of light, but are also a source of infection.
Useful materials
Read other articles about growing and caring for eggplant seedlings:
- Different growing methods: in peat tablets, in a snail and even on toilet paper.
- All the features of sowing according to the lunar calendar.
- Golden rules for growing from seeds.
- Peculiarities of cultivation in various regions of Russia: in the Urals, Siberia and the Moscow region.
- Read more about preparing seeds before planting.
Root damage
Most often, the tender roots of eggplants are damaged when planting seedlings in a greenhouse. To prevent this from happening, seedlings should be grown in separate containers and moved to the main place by transshipment without destroying the earthen ball.
The ideal option is to grow seedlings in peat pots. In this case, the roots are preserved as much as possible, since planting is carried out without removing the plants from the soil.
The tender roots of eggplants can be damaged if loosened too vigorously. They are located close to the soil surface, so it can only be processed to a depth of no more than 5 cm.
On the way to the harvest
Finding the cause of a change in the condition of seedlings, making a correct diagnosis and providing emergency assistance to a withering plant is a big step towards a rich harvest. Daily observation of young plants and fulfillment of their simple but necessary requirements will help you in this important task.
NOTE! Find out what diseases eggplants are susceptible to: what to do if the seedlings fall, stretch out or completely die? Causes of white spots and leaf curling. And also what pests can attack young seedlings?
Violation of the irrigation scheme
Eggplants are harmed by overdrying and waterlogging of the soil. In the first case, the suction roots die, in the second they rot. The result of this is the same: the above-ground part lacks nutrition and begins to dry out.
The optimal watering regime for eggplants is 2 times a week. When flowers appear and the ovary forms - 3 times every 10 days. Water consumption – 5 liters per bush.
Expert opinion
Istomina Karina Bogdanovna
Agronomist with knowledge and skills in growing vegetables
When watering, water should not get on the stems and leaves. Drops linger on their fleecy surface for a long time, which can cause rotting or fungal diseases.
What to do if the leaves of peppers and eggplants curl and turn yellow
If pest control measures are not taken, the plant will soon die.
Curling leaves indicate a much more serious problem than simple yellowing. It usually occurs in three cases: a lack of macro- and microelements, pest activity and uneven leaf growth. Basically, leaf curling occurs in seedlings and requires your immediate intervention.
- Place the plant in a sunny place . This method is recommended when leaves curl due to accelerated growth. The midrib of the leaf is stretched, but the leaf blade does not have time to form, which is why it becomes deformed. Usually the plant itself restores the required proportions, but if you need quick results, expose the container to light or move it to a warm room.
- Apply the required fertilizer complex . First of all, wood ash. Scatter it so that under each bush there is a layer approximately 3 mm thick. Immediately after this, water the plants with plenty of water. You can also use potassium nitrate (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). Apply 0.5 liters of the composition under each bush.
- Spray against pests . Typically, leaves curl because mite or aphid larvae have settled in the soil. Use onion tincture against them. Add a glass of onion peel to 1 liter of water. Leave the resulting mixture for 24 hours, and then spray the plants evenly every five days. You can also shed the soil with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Temperature changes
Heat-loving eggplants react painfully to cold at night and heat during the day. At temperatures above + 27 degrees, the foliage begins to dry out, and the ovary often falls off. Regular ventilation of the greenhouse helps to cope with the problem.
But do not forget to close all doors and windows at night. If the temperature in the greenhouse regularly drops to +15, the eggplants will begin to get sick, stop forming fruits and may even die.
Why do the leaves of peppers and eggplants turn yellow in a greenhouse?
When planting vegetables in greenhouse soil, you will also need to add a complex of microelements and fertilizers
Yellowing of leaves is often observed in plants even in such a seemingly protected place as a greenhouse. It is possible to understand what led to yellowing only by assessing the totality of parameters. And here's what you should pay attention to:
- humidity level in a greenhouse or greenhouse . Peppers and eggplants are quite delicate crops that react sharply to lower humidity levels. The optimal humidity level for peppers is 70-75%, and for eggplants – 65-70%;
- soil composition . If the required amount of fertilizer is not available in the greenhouse soil, then peppers and eggplants actively signal this by changing color. Most often they lack iron, which in turn leads to the development of chlorosis;
- temperature regime . It is believed that plants in a greenhouse are more protected from temperature changes. However, poor-quality assembly of the structure, early planting of seedlings, frequent ventilation and a greenhouse opened at night can lead to yellowing of the foliage. Even short-term frosts can damage the fragile structure of the leaves;
- the presence of fungal or bacterial infections . More often than others, greenhouse plants are affected by black leg, fusarium, verticillium, septoria, gray mold, late blight, etc. The first symptom of almost all of these diseases is yellowing of the leaves;
- parasite invasion . Greenhouse crops are no less susceptible to pest attacks than those growing in open ground. Aphids, nematodes, thrips, slugs, mole crickets - this is just an approximate list of those who want to feast on fresh greens.
Incorrect feeding
A lack or excess of nutrients is equally harmful to eggplant bushes.
They almost immediately signal an imbalance of substances by their appearance:
- Pale green leaves with a yellowish tint, stunted growth, and lack of formation of new leaf blades indicate a lack of nitrogen.
- Increased growth of green mass, poorly formed ovaries, and yellow leaf blades indicate an excess of organic matter in the soil.
- Yellowing of the leaves along the edges and their curling indicates a lack of potassium. More often, microelement deficiency manifests itself at the time of fruit filling.
- The leaves have turned yellow at the edges, the growth of the entire plant has slowed down - there is not enough potassium. The leaves rise upward, the plant sheds flowers, the fruits do not develop - phosphorus is needed.
It is quite easy to cope with nutritional deficiencies with the right supplements.
Fertilizer application scheme at different stages of plant development:
After the pick . This is the first application of nutrition, which is carried out at the stage of growing seedlings. If seedlings are grown without picking, fertilizers - nitrogen and potassium - are applied when two true leaves appear.- 8-10 days before transplantation - nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus.
- 2-3 weeks after disembarkation , not earlier. Plant roots that are not sufficiently adapted to the new environment are unable to fully absorb nutrients. Fertilize with nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus.
- During flowering and ovary formation, fertilize only with phosphorus and potassium. Nitrogen is completely excluded from fertilizing at this time.
Overfeeding with nitrogen is more difficult to cope with. Abundant watering for several days helps flush out excess substances from the soil.
Yellowing and dying of a small number of leaves is a natural process. Most often, an adult bush tries to get rid of old leaves located on the lower part of the stem. This does not harm the general condition of the plant, so there is no need to take any action.
The ovaries turn yellow
Eggplant ovaries turn yellow and fall off mainly when there is a lack of moisture in the soil, when there is a sharp change in air temperature, when the sun is too bright in combination with dry air (dry winds), and when there is a lack of nitrogen and microelements in the soil.
The fight against this phenomenon consists of overcoming these negative factors, organizing shading, protection from the wind, and organizing drip irrigation throughout the dry unfavorable season. Can be used to shade and protect from dry winds shelters made of non-woven, light-colored materials that allow moisture to pass through, so that drip irrigation evenly moistens the area occupied by eggplants.
Diseases
Yellow, limp leaves are a characteristic sign of some fungal or viral diseases.
Fusarium
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus of the genus Fusarium, which penetrates plant tissue through wounds in the roots. The source of infection can be soil, seed and seedlings. Typically, the peak of the disease occurs during the flowering period. First, the lower leaves turn yellow, then the fungus affects the entire above-ground part. Spores grow most actively in acidic soil. To treat fusarium, bushes are treated with Maxim, Fitosporin-M, Agat-25K, Vitaros.
Mosaic
A viral disease that appears as a yellowish pattern on the leaves. The causative agent of the disease is a virus that enters plants from the legs of insects and dirty garden tools. Often colonies of pathogens live in the soil, and infection occurs at the time of picking or transplanting. Mosaic is an incurable disease. Therefore, the main measure to combat it is timely prevention.
Alternaria blight
The first sign of this disease is numerous yellow-brown spots on the leaves. The fungus develops when heat is combined with high humidity. The fungus is carried by insects or enters plants from plant debris. Alternaria (gray rot) is treated with Antrakol, Horus, Trichodermin, Fitosporin.
Late blight
A fungal disease that develops in damp, cool weather. Often the development of a disease in a greenhouse is provoked by a violation of crop rotation. For treatment, the bushes are sprayed with copper-containing preparations: Hom, Oksikhom, Profit Gold.
Chlorosis
The reason for the development of this disease is a lack of nutrients: iron, zinc, magnesium and sulfur.
You can determine which element the plant lacks by the following symptoms:
A characteristic sign of a lack of iron and magnesium is yellowing of the leaf blade between the veins. The veins themselves remain bright green.- If the plant lacks sulfur, first the veins turn white or yellow, then the entire leaf.
- With zinc chlorosis, the lower row of leaves becomes covered with yellow spots.
The method of treating chlorosis is feeding with special preparations:
- Ferrovit, Micro Fe, Ferrylene are preparations based on iron chelate and compensate for the deficiency of this element;
- Magnesium sulfate, Calimagnesia - drugs for the treatment of magnesium chlorosis;
- For sulfur chlorosis, fertilize with potassium sulfate, Azophoska with sulfur, ammonium nitrate, urea;
- To treat zinc chlorosis, zinc sulfate and zinc oxide are used;
- Calcium chlorosis is eliminated by feeding with infusion of ash.
Keep weeds out of the greenhouse. They absorb large amounts of nutrients and thereby greatly deplete the soil.
The seedlings are sick
It’s one thing when part of the lower leaves of an already “adult”, strong plant turns yellow or falls off. But it’s different when small sprouts in pots begin to wither. So in a day or two, and they will all die! Why did the “guys” suddenly decide that she had come very much?
Bad soil
Too much moisture. This crop cannot be called drought-resistant: eggplants prefer frequent and abundant watering. But if they constantly grow in puddles (especially with acidic moisture), a dangerous process of rotting may begin in the root system.
This trouble has already happened to your plant if the leaves began to turn yellow not from the bottom, but from the top. Simply stopping watering for a couple of days is not enough - the soil is already contaminated with bacteria and/or fungi, so it must be ruthlessly replaced. Yes, and it would be useful to treat the pots with a solution of potassium permanganate. To prevent this situation from happening again, choose containers for sprouts with holes inside, from which excess moisture flows out onto the tray.
It is important to remember that when watering, moisture should only get into the soil and not collect in the leaves! Otherwise, they will again begin to rot. Nitrogen deficiency
This microelement is a favorite delicacy of “young” eggplants. When there is no nitrogen, the leaves begin to turn yellow and dry out - this time the process starts from the bottom. The roots remain healthy. In this case, it is easy to treat the babies by adding the necessary fertilizer to the soil.
Lack of nitrogen. This microelement is a favorite delicacy of “young” eggplants. When there is no nitrogen, the leaves begin to turn yellow and dry out - this time the process starts from the bottom. The roots remain healthy. In this case, it is simple to treat the babies by adding the necessary fertilizer to the soil.
The sun has overdone it
“Blue” is a crop that will not grow and will not produce a harvest if there is little light. But if the sprouts are constantly exposed to direct sunlight, they will get a banal burn.
What does this kind of sun sickness look like? Yellow dots or areas appear on the top of the leaves.
Protect your pets: at midday, make them a small “umbrella” from sheets of paper or napkins. And the rest of the time, let them continue to bask in the sun's rays.
Fungal diseases
If influenza is a common human disease, then the “little blue ones” most often suffer from fusarium. They become infected from soil that may contain a fungus called Fusaria, just like eggplants, which love warm, moist environments. Of course, not everyone can become infected, but only weakened sprouts - that is, if the watering is normal, there is enough nitrogen and there are no “wounds” on the sprouts or roots, they can avoid infection. If something goes wrong, the matter may be aggravated by fusarium.
Your seedlings suffer from this particular fungal disease if:
- the leaves have turned yellow, and the lower ones (cotyledons) are completely curled and dry;
- the stem is no longer green, but brown;
- the roots also suffer, becoming covered with a pink coating;
- If healthy, green plants stretch upward, then sick ones hardly grow.
It is difficult to cure diseased plants. In your case, it is more important to remove any still green shoots from the common bed or tub. They should be transplanted into fresh soil, not forgetting to treat them with fungicides.
And so that the next generation of eggplants does not encounter this disease, the soil and seeds are disinfected.
The second most popular disease of the little blue ones is verticellosis. It is caused by fungi.
- the leaves turn yellow, and the unhealthy color begins to spread across the leaf from the veins;
- the lower leaves curl and wither, as if they were dipped in boiling water;
- If you cut the stem, it turns out that it is brown inside.
Here, again, it is worth ruthlessly tearing out the yellowed sprouts. And do not throw it away (so that the disease does not start “walking” around the site), but burn it. Send the contaminated soil into the fire as well. In the meantime, transfer the seedlings that have not turned yellow to clean soil, carrying out prophylaxis with fungicides.
Pests
Tender leaves and shoots of eggplants are a tasty morsel for insect pests. They feed on plant sap, causing the leaves to wilt and then dry out completely.
Most often, greenhouse eggplants suffer from the invasion of the following parasites:
Whitefly
Spider mite
Aphid
- Whitefly . Adults and larvae are harmful to plants. Whitefly butterflies lay their eggs on the undersides of leaves, so they are not so easy to spot. Fungal diseases develop in damaged leaves, they turn yellow and die. Sometimes traces of insect activity are confused with chlorosis, lack of nutrients, “overdrying” of seedlings and other ailments. The most effective measure to combat whiteflies is to hang bright yellow traps with a sticky surface in the greenhouse.
- Spider mite . A characteristic sign of an attack by this pest is a thin web entangling the leaves and stems. Favorable conditions for tick reproduction are dry air and elevated temperatures. Therefore, regularly ventilate the greenhouse and maintain a humidity level of at least 60%. In case of severe infection, treat the bushes with insectoacaricides: Fitoverm, Neoron, Sunmite.
- Aphid . One of the most dangerous and common enemies of eggplants. The insect settles on all parts of plants and sucks the juices out of them. The bushes wither, the leaves become deformed, turn yellow, and become covered with a sticky coating. The fight against aphids is made difficult by the long period of eggplant fruit formation. As soon as buds appear on the plant, insecticides cannot be used, otherwise harmful substances will penetrate into the ovary. In this case, the fruits will become tasteless and even dangerous to eat. Therefore, to kill insects, use an infusion of ash, a soap solution, and a decoction of chamomile.
Expert opinion
Istomina Karina Bogdanovna
Agronomist with knowledge and skills in growing vegetables
To prevent infection by pests that cause yellowing of leaves, you can plant calendula, tansy, petunia, chamomile, and marigolds in a greenhouse. They repel the Colorado potato beetle, ants, caterpillars, rodents, and also prevent the development of nematodes.
Agricultural technology of culture
To obtain a bountiful harvest, you should properly care for your eggplant. Like every living plant, it has its own character and loves certain conditions.
Main characteristics:
- an annual plant, with large oblong-shaped fruits, thick skin and fleshy interior and small seeds;
- color depends on the variety: from white to blue-black;
- weight from 200 g to 2 kg;
- growth begins slowly, accelerating sharply by the time the ovaries appear;
- flowering begins 79-90 days after shoots;
- A little more than a month passes from the moment of pollination to ripening;
- overripeness is expressed in dried pulp and bitterness that the seeds produce.
Lack of microelements
The relationship between yellowness and problems with feeding is shown in the table.
| Microelement | Manifestation | Treatment |
| Potassium | Extensive yellowing of leaves | Ventilate greenhouses, whiten roofs and dose nitrogen fertilizing |
| Phosphorus | Leaves with yellow veins grow at an acute angle relative to the stem | Feeding with a preparation with a high phosphorus content |
| Zinc | Yellow-brown dying spots begin on the lower leaves | Treatment of leaves with zinc phosphate |
| Bor | Leaves turn yellow and curl | Choose a complex fertilizer |
| Calcium | Brownish-red spots appear that look like burns | |
| Sulfur | Yellow leaves at the top of the plant |
Prevention measures
- Choose a suitable place to plant the crop.
- High humidity causes fungal infections - do not plant plants in lowlands and near rainwater drains, shady places and next to moisture-loving crops.
- In greenhouses, the soil is covered with non-woven material to avoid contact with bacteria.
- Provide good air circulation, but not draft.
- Disinfect seeds before planting.
- Timely collection of all plant and household waste.
- After harvesting, the greenhouse must be treated with a solution of slaked lime, including paths and walls.
- Instruments should also be treated with antimicrobial agents.
- The diseased plant must be removed as quickly as possible to avoid spreading the disease to healthy bushes.