Eggplant is a heat-loving crop, so it grows well in open ground in the southern regions of Russia. But in order to get a good harvest in mid-latitudes, it is necessary to grow it in a greenhouse or under a film cover, and also take into account some nuances.
By default, we accept the fact that you already have a well-built and equipped greenhouse, and have selected eggplant varieties zoned specifically for your area (for a greenhouse, experienced gardeners most often choose low-growing, early- and mid-ripening plants).
- 15 best varieties and hybrids of eggplant for the greenhouse
Don't know which eggplant varieties and hybrids are suitable for the greenhouse? We have prepared a short review for you.
Eggplant varieties for growing in a greenhouse
This method of cultivation allows you to expand the choice of varieties, including the most exotic ones. But since, in most cases, planting volumes are limited by the area of the greenhouse, it is better to choose tall, productive varieties that will allow you to get a large number of fruits from a small area.
If greenhouse cultivation is combined with garden plantings, then it is more rational for the greenhouse to leave late-ripening specimens. Early eggplants will have time to ripen in open ground.
When “populating” a greenhouse, it is also a forward-thinking decision to give preference to hybrids.
Bibo F1
The hybrid is early ripening, grows up to a meter. The fruits are white and have excellent taste and are free of bitterness. Weight reaches 500 g. Resistant to mosaic and fusarium rot. The harvested crop is well stored until heat treatment.
Boyarin F1
Early ripening hybrid. It is resistant to sudden temperature changes, but grows best in a greenhouse. The fruits are classic, dark purple, pear-shaped, weighing up to 450 g. It has spreading branches; when growing, special attention should be paid to pinching.
Alyonka
An early-ripening variety with cylindrical fruits of unusual green color, average weight 350 g. It is productive and resistant to diseases.
Goliath F1
A very tall hybrid reaches 2.5 meters in height. Medium early ripening with good immunity to mosaic. The fruits exceed a kilogram. They have a classic shape and appearance.
Pink flamingo
A mid-early variety with elongated purple fruits. It is distinguished by its productivity. Eggplants weighing from 250 to 450 g are quickly set and ripen. Which, in greenhouse conditions, allows you to quickly harvest the crop and clear the sown area. When gartered in a warm environment, it grows up to two meters.
Joker
Tall variety with extra early ripening. The ovaries of its small fruits are folded into clusters. A hundred eggplants can form and ripen on one bush. Purple-pink, thin-barked, weighing 100-130 g, they have excellent taste.
Swan
Mid-season variety with good keeping quality. Resistant to most diseases affecting nightshades. The pear-shaped fruits are white in color. The weight of an average eggplant is 250-300 g. High taste and delicate pulp.
Viola di Firenze
A mid-season, high-yielding variety bred by Italian breeders. Resistant to lodging and has good immunity. But it is very sensitive to temperature changes and is thermophilic. The fruits are oval, weighing up to 750 g.
Maxik F1
An early ripening hybrid, exceeding a meter in height. The fruits are classic, pear-shaped, of high taste. The bush grows compactly, which is a big plus for greenhouse cultivation. The fruits are small: 150-200 g, which is compensated by high yield.
The above hybrids and varieties will be successfully grown in greenhouse conditions. You definitely need to pay attention to them. New hybrid specimens appear every year.
When choosing seed plants, it is better to give preference to those that grew in open ground. They will have better immunity.
Video with useful tips from greenhouse growers
- Author: Konstantin
Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(19 votes, average: 2.9 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
5 secrets of a rich currant harvest: from watering to pollination
Technology for growing peppers in a greenhouse: all the wisdom in one place
Where to start growing eggplants in a greenhouse
Greenhouse work is, in fact, much simpler than gardening in the open ground:
- the greenhouse allows you to adjust the air and soil temperatures for eggplants;
- it is possible to organize the workplace so that everything is at hand;
- in cold weather it is much more comfortable to work in a shelter;
- the greenhouse creates an isolated environment, limiting the entry of pathogenic bacteria and insects into it.
When starting greenhouse planting, you need to focus on three important aspects as the key to a good harvest:
- greenhouse - correctly installed, processed and prepared and in the proper manner;
- planting material – varieties and varieties of eggplant selected taking into account the owner’s interest;
- neighboring plants - the confined space of a greenhouse requires special attention to the combination of different plants in one area.
Procuring your own seeds
Any vegetable grower knows that your own seeds always guarantee the exact variety that is planted. That is why they try to prepare them themselves. However, many disappointments will await the gardener who neglects the important points of this procedure.
The stages of preparation for obtaining your own planting material begin with the planting of the crop itself:
- You need to choose varietal crops;
- Given the ability of eggplants to self-pollinate, different varieties are planted at a distance;
- In northern latitudes, biologically mature material can only be obtained from seedling samples;
- To ensure that the fruit seeds are sufficiently ripe, a maximum of 3 fruits are left on a strong, healthy bush. All subsequent ovaries are removed;
- A fully ripened fruit has a yellowish-brown or greenish-gray color. After cutting, it is removed to ripen for 3-4 weeks in a cool place;
- After grinding, the ripened testes are rubbed through a sieve to separate the seeds;
- Eggplant seeds do not require pre-fermentation;
- The washed material is dried in the shade in the fresh air.
How to plant eggplants in a greenhouse
It’s good when it is possible to devote the entire greenhouse to planting plants of one type. But the vast majority of gardeners cannot afford this.
Neighboring plants should:
- share nutrients with each other so that they receive them in sufficient quantities;
- be exposed to different diseases - simultaneous treatment against one pest on different species does not give the same results;
- need to maintain a similar microclimate – temperature and humidity level;
- In order to be able to free the greenhouse from plantings and allow it to fallow, it is desirable that neighboring plants mature at approximately the same time.
Therefore, choosing companion crops is a true long-term strategy. It is undesirable for eggplants to have nightshades - potatoes, tomatoes, peppers - under the same roof.
The proximity to garlic, onions, and legumes has a very beneficial effect on the blue ones. And unexpectedly: with chrysanthemum, calendula, marigolds. These flower crops protect vegetables from mole crickets and other pests.
Low-growing eggplants can be combined with cucumbers, zucchini, and melon, placing the latter on a vertical support.
They work well alongside greens and herbs such as lettuce and basil.
If you still have to combine unwanted neighbors in one greenhouse, they should be planted, oriented in height to the cardinal points - from short to tall. Use green manure, onions, and garlic as a separating crop.
Disease and pest control
During growth, eggplants can contract a whole “bouquet” of various diseases. The most harmful diseases are: root rot, tracheomycosis, root rot, stolbur and leaf mosaic.
This crop is often infected with fungal and viral diseases, as well as bacterial rot. Disease control involves prevention and treatment of plants and soil with special preparations:
- Biochemical . They are not harmful to plants, animals and humans. They are also safe for beneficial insects such as bees.
- Chemical . They quickly cope with the cause of the disease, but they are harmful to humans and affect the quality of products. Chemical residues accumulate in the fruits.
We grow seedlings
Before planting in a greenhouse, eggplants must go through the seedling stage, which lasts depending on the ripening period of the variety.
Seed preparation
The preparation process consists of three stages:
- hardening by alternating temperatures;
- disinfection in potassium permanganate;
- stimulation - soaking in a weak solution of compost, 3% solution of potassium humate.
After which the seeds are germinated between two layers of damp cloth and planted in cups. Seedlings should germinate from the ground in a dark place at an air temperature of 26 to 28 C.
An infusion of willow branches is the best natural growth stimulator. To do this, you need to chop 2 kilograms of young willow branches and fill them with 10 liters of water for a week. You can soak the seeds in this infusion and water the seedlings diluted with it.
Preparing soil for seedlings
The following composition is well suited for sowing seedlings: peat, sand and forest soil in a ratio of 1/1/1.
Seedling soil can also be enriched with sunflower or buckwheat husks.
It is better to sow seeds in separate cups.
Peat pots for seedlings filled with soil are poured with boiling water so that the peat becomes soggy, allows water to pass through better and more actively releases microelements into the substrate. This procedure promotes disinfection. You can start planting only after it has completely cooled down.
Dates for sowing eggplants
The ripening time for different varieties of eggplant varies from 80 to 150 days. Seedlings develop from seed to adult plant in two to two and a half months. In peat pots, you can plant seedlings in a greenhouse without transferring them, a little earlier, after 1.5 to two months.
Its growth and development in natural conditions will depend on the length of the day and the natural change in temperature during the day. The peculiarity of greenhouse cultivation is the possibility of organizing artificial twelve-hour lighting and temperature conditions.
Transplantation into an unheated greenhouse can be planned for the end of April; accordingly, the seeding time for sowing falls in February.
We observe the temperature regime
For successful development, a temperature from 23 to 28 C is suitable. The interaction of lighting and temperature conditions is carried out in such a way that when daylight begins, the air warms by 2-3 C, and after the fluorescent lamps are turned off, the room becomes cooler. This will bring the seedlings closer to natural conditions and increase their endurance.
A mirror installed opposite the light source will illuminate the seedlings from all sides. If there is not enough light, the temperature is lowered a couple of degrees and the volume of fertilizing is increased.
How often to water seedlings
Eggplants are watered as needed, without allowing the soil to dry out. You can combine watering with loosening, but this must be done very carefully.
Watering is applied at the root with warm soft water. You can water with slightly diluted herbal or willow infusions, crystalline or other growth stimulants.
Feeding is required only if the appearance of the seedlings is alarming - the leaves turn yellow and wither.
Planting eggplants in closed ground
The hardening procedure before transferring it to the greenhouse may consist of ventilating the room and removing the seedlings to the greenhouse during the day. Even if in the future eggplants do not have to face the negative influence of the external environment, the stronger the seedlings are, the more harvest they will produce.
How to prepare the soil for planting eggplants
The composition of the soil should correspond to the needs of the blue ones - loose, slightly acidic, fertile. The earth has been preparing since autumn:
- the first stage is thorough cleaning and disinfection of the greenhouse;
- if time permits, after harvesting, the land is sown with green manure, which is later dug up;
- in the spring the digging procedure is repeated;
- apply mineral fertilizers;
- The timing of planting eggplant allows you to collect an early harvest of greens or radishes in this place - this will only benefit the blue ones.
The timing of planting depends on weather conditions, the type of greenhouse and the ripening time of a particular type of eggplant. Transshipment into the ground is indicated for seedling bushes that have the first peduncle.
How to plant seedlings in a greenhouse
Any manipulations with seedlings that injure the root system slow down its development and increase the risk of infection with fungal diseases. What’s good about growing in peat containers is that it allows you to lower the root into the hole without exposing it.
To do this, recesses are dug in the greenhouse bed, slightly larger in depth than the dimensions of the pot. The eggplant is placed in the hole without deepening it. If the pots look very strong, you can cut the bottom and walls in several places with a knife. This will make it easier for the root system to cope with the peat walls that limit it.
The soil in the hole is watered before and after planting, sprinkled with a layer of mulch on top and left without watering for three to four days.
After transplantation, the air temperature in the greenhouse must be maintained within 20-22 C.
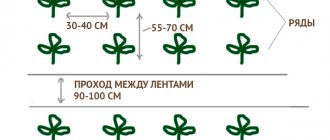
At what distance to plant eggplants in a greenhouse (planting patterns)
The landing method can be chosen linear - in one groove at equal intervals from each other. Or chess - in the holes.
The distance between the rows must be maintained at about 60 centimeters. And 30–35 centimeters in the row between plants. In heated greenhouses, planting density should be no more than 2 bushes per square meter. In unheated greenhouses, 3-4 bushes are the optimal number of plants per square meter.
The main rule of a greenhouse is that plants are planted according to their height. Tall two-meter eggplants can be placed in the center. Plants that are inferior to them in growth should be planted as their height decreases.
Preparing the soil for planting
The soil must be fertile and well dug so that the planted seedlings can grow better. The soil is cleaned of weeds and old tops, and then watered with clean water at least 2 times. Next, it is disinfected to destroy insect larvae and pathogens. It is best if the soil in the greenhouse is partially prepared in the autumn. It is loosened to a depth of about 12 cm. Heavy soil is dug up again in the spring.
Disinfection can be done by treating the soil with steam or pouring boiling water over it. Sometimes chemical methods are used - the soil is sprinkled with bleach at the rate of 100 g/m2 and sealed with a rake. Soil treatment with formaldehyde helps against blackleg. The treated beds are covered with film for a day. Copper sulfate also works well against pests, from which a solution is prepared (2 tablespoons/10 liters of water), which is poured onto the soil and then loosened.
Eggplants can be planted in black soil, fertilized sandy loam and loam, but this crop grows poorly on heavy clay or acidic soils. Dolomite flour at the rate of 2 tbsp will help reduce the acidity of the soil. l./m2.
Before planting, fertilizers are applied to the soil. Eggplants love organic fertilizers - rotted manure or compost. They are applied in an amount of 2-6 kg per 1 m2 in the arable layer. You can also use mullein solution, which is used to spill the beds at the rate of 4 l/m2. Sawdust will make the soil looser.
In order for eggplants to grow better, before planting, it is recommended to add a handful of ash to each hole prepared for them and mix it with the ground.
Caring for eggplants in a greenhouse
Activities for caring for eggplants in a greenhouse differ little from similar work in the open ground. They include:
- productive feeding - in greenhouse conditions it is more useful to underfeed than to overfeed, otherwise you will have to enjoy lush foliage instead of fruits;
- loosening and mulching the soil around the trunk;
- the formation of a bush, which for tall, tied plants differs from the usual;
- timely watering;
- humidity and temperature control;
- harvesting.
Feeding and watering
In a greenhouse, it is better to organize drip or ditch irrigation so that moisture does not fall on the leaves and does not evaporate in large quantities into the air.
In any case, this procedure is carried out in the evening to reduce the amount of evaporation. And only warm water.
Fertilizers are applied along with watering. This must be done more carefully, and dosages should be lower than for open ground.
If the soil is prepared in compliance with the technology, then it is more advisable to introduce organic matter in the form of weak solutions of herbal infusion, with mulching.
For greenhouse cultivation, it is more useful to foliar fertilize eggplants with slightly diluted compounds - a one percent solution of boric acid or weak potassium permanganate. This should be done in the evening.
Humidity in the greenhouse
Eggplants are big fans of abundant moisture to the roots and at the same time cannot tolerate high air humidity. The stuffy damp atmosphere is not for them. In addition, excessive humidity creates conditions for the development of fungal diseases.
You can reduce air humidity:
- ventilation;
- organization of drip irrigation;
- blocking evaporation from the ground with mulch.
Air temperature and ventilation
Eggplants feel good in the temperature range from 25 to 28 C. In summer, an increase in temperature is more dangerous for them than a decrease. If when the temperature drops to 14-10 degrees the plants slow down in growth, then an increase to 30 C or higher can kill the plants.
Organizing a cold draft is the wrong solution. If the microclimate of the greenhouse and the street air have a large temperature difference, ventilation should be carried out carefully, opening the transoms away from the eggplants.
In warm weather, you can keep the greenhouse completely open even at night. This will promote pollination and increase the immunity of the eggplant.
Bush formation and tying
When growing in greenhouses, it is important to pay special attention to the formation of the bush, so that in conditions of dense planting, the branches on which the crop ripens are evenly illuminated by the sun, and the fruits do not interfere with each other’s growth.
Tying is mandatory for bushes that have grown above half a meter. Otherwise they will bend under the weight of the fruit.
For low-growing varieties from 05 to 0.6 meters, one loop connecting them to a support, or a hammock tying to the greenhouse ceiling like a tomato garter, will be enough.
Specimens that reach a height of 2-2.5 meters will require a solid stake and several fabric loops along the trunk.
Large eggplant fruits, which weigh close to a kilogram, must be placed for ripening in mesh hammocks suspended from the ceiling of the greenhouse. Otherwise they may break branches.
Growing tall varieties
Tall varieties do not pinch at the growing point. Their advantage is that they transfer their productivity to the vertical plane, while taking up less space.
Stepchildren on tall trunks are pruned selectively, leaving the stems evenly over the entire height and tying each one separately.
An effective pinching technique for tall varieties: removing stems and leaves from the bottom to the first flower. In the future, the leaves around the new ovaries are also removed.
Growing undersized varieties and hybrids
Low-growing eggplant varieties are pinched at the growing point for better branching. Of the side shoots, the strongest ones are left in the amount of two to five stems. Others are deleted. Be sure to cut off stepsons without ovaries, deformed fruits and dried leaves.
In hybrids, the stepchildren are usually pinched, forming a cone-shaped silhouette for the plant so that each subsequent shoot is shorter than the previous one. The yield of hybrids is much higher; removing a large number of stepsons will reduce fruit formation.
Collection of greenhouse eggplants and their storage
Vegetables are considered ripe when the rind acquires a glossy shine and the fruit is rounded and takes on the shape characteristic of the variety. Eggplants are harvested frequently, without allowing them to become overripe. The sooner the ripened fruit is removed, the more new ones will form.
Eggplants are not designed for long-term storage. Their flesh darkens and accumulates bitterness. The easiest varieties can be stored without heat treatment for no more than a month.
If the fruits need to be kept for some time, they are stored in a cool, dry room, covered with paper or straw.
Harvest and storage
The harvest must be harvested on time, otherwise the fruits will overgrow. This will affect the taste and shelf life.
When to collect fruits?
If an eggplant is overripe, its skin will fade, lose its elasticity, and the flesh will become very hard and bitter. But you cannot pick unripe fruits from the bushes, since they will not be able to ripen on their own, like tomatoes, but will simply wither.
The fruits of this vegetable ripen very unevenly, so it is necessary to collect them selectively, checking them every couple of days. It is advisable to cut using pruners or a sharp knife.
Important! When cutting, be sure to leave a tail on the fruit 3-5 cm long . If you cut close to the fruit, it will quickly wither.
How to store eggplants
Before storing eggplants, wipe them with a dry cloth. After this, they are transferred to a dark place. The temperature should be from 0 to +2 degrees.
Important! If there is high humidity and a temperature of more than +5 degrees in the storage, then gray rot may appear on the fruits.
First, the fruits should be laid on the floor in 1 or 2 layers. After 2 weeks the harvest is checked. Only the most undamaged vegetables are selected, wrapped in paper and laid out on straw. The layer of straw should be 15-20 cm. Then the fruits should be covered with thick cloth.
At the right temperature in these conditions, eggplants can be stored for 3 months.
Late-ripening varieties lend themselves best to storage. Early ripening fruits are recommended to be consumed or processed immediately after collection.
These vegetables are not suitable for longer storage, so they need to be preserved for the winter.
If you don’t want to preserve, you can dry the vegetables and then keep them in a preheated oven for a while. Then they should be sent to the freezer . This product remains suitable for consumption throughout the year without loss of taste.