For all gardeners, working in the garden most often brings sheer pleasure. It’s so interesting to plant a tuber in the ground and see how nature allows something beautiful to develop. Centimeter by centimeter, the green sprout reaches higher and higher towards the sun, some time passes, and it is already a strong and powerful plant that produces lush flowers and gives a stunning floral aroma as a reward to the gardener for his efforts. At such moments, the summer resident agrees to work until his back and legs become tired, just to watch how the plant can bloom.
Mulch - fertilizer for garden flowers
A very good option is to mulch the soil. Many gardeners use organic materials for this purpose: rotted compost, decomposed peat, rotted leaves, and mown grass.
Mulch applied under flowers decomposes over time and enriches the soil with additional nutrients. At the same time, it can become an obstacle to the germination of weeds. They cannot break through it and die.
Mulching can be done twice per season: in spring and autumn. In the first case, it will additionally serve as protection against temperature fluctuations and retain moisture in the soil. Gradually decomposing in warm weather, the mulch contributes to a looser state of the soil surface. This means that flower roots can develop freely in it. In September, spring mulch is replaced by composting.
Mulching material added in the fall helps plants tolerate frosty, windy weather more easily. It protects the ground from deep freezing, which makes it easier for flowering plants to winter. In the spring it is simply embedded in the soil.
Important! If mowed grass is used as mulch, it must be watered with a solution of nitrogen fertilizers and loosened more often.
How to use mulch?
Many modern gardeners use the bark of various trees as mulching material. It takes a long time to decompose, up to 2-3 years. Typically, for perennial flowers, a layer of 3-5 cm is poured.
If there is a spruce forest near the site, you can collect coniferous litter. Rhododendrons love it very much. For them, adding a layer of 5-7 cm is enough. But you should know that needles increase the acidity of the soil. Therefore, they are not suitable for all garden plants.
The most popular are manure humus and compost. A layer of 5 cm is poured under perennial flowers. The main thing you should pay attention to is that there are no remains of weeds in them.
On a note! Roses and lilies love mulching with nut shells. If they grow in your garden, then when you crack nuts, do not forget to collect it for your pets. You can use anything from pine nuts, walnuts, peanuts, hazel.
Natural supplements. Recipes from grandmothers
If the need for fertilizer volumes is small, folk remedies are suitable at home.
Sugar. Pour a teaspoon of sugar into the pot and water. Recommended once a month. Glucose fills you with energy.
Yeast. They are useful for caring for plants due to phytohormones, fungi and B vitamins. To prepare a concentrate with your own hands, take 2 g of yeast and a spoonful of sugar for two liters of water. Leave for a couple of hours. Then dilute in a ratio of 1 to 5.
Leftover fruit. Bananas or citrus fruits are recommended; they nourish all flowering plants. Dry the peel, grind in a blender, mix with soil. Or put the peels in a three-liter jar, filling it a third full, pour boiling water over it, and leave for a day. Discard the pulp and add water. Use for spraying or watering.
Vegetable decoctions. The most common is a decoction of onion peels. A full set of microelements saturates plants and increases resistance to pests. How to prepare: boil 50 g of husk in a liter of water, simmer for 10 minutes over low heat. After cooling completely, strain, pour into a spray bottle, and spray the plants. Important: vegetable decoctions are prepared for one time use and cannot be stored.
There are other inexpensive methods; aquarium water, succinic acid, eggshells, water from washing cereals, tooth powder, coffee residues, tea leaves help to fertilize at home.
There are supporters and opponents of each remedy. Errors in selection will be immediately noticeable; it is important to independently monitor the response of each plant to a particular product.
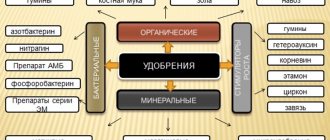
Mineral fertilizers for flowers in the country
How to feed flowers for lush flowering? Mineral fertilizers are the fastest and easiest method of feeding garden flowers. Only with their help can flowers develop in poor soils. They especially need mineral fertilizers on sandy and clay soils. Mineral fertilizers are nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus and complex.
Nitrogen fertilizers
Nitrogen fertilizers are applied in the spring, regardless of organic fertilizers, and then during the growing season as additional fertilizing. Nitrogen is very important for rapid plant growth. With its deficiency, the leaves become pale and small, and their density suffers.
Tips and tricks
When feeding plants, you should always pay attention to the composition of the soil in which they grow. If the soil is poor, the amount of fertilizer should be increased. If the soil is fertile, two feedings per season will be enough.
You should understand! At different periods of agricultural development, it requires different feeding. At the very beginning of sap flow, nitrogen fertilizers are applied, at the moment the buds appear - potassium and phosphorus, with the development of full-fledged flower stalks - superphosphates, in the fall - phosphorus and potassium.
Even a novice gardener can create a wonderful flower garden, thanks to fertilizers that will preserve the quality and decorativeness of the plants. It is recommended to create your first flower beds from unpretentious flowers, then gradually comprehend the science of floriculture in practice.
3 1 vote
Article rating
Fertilizers with phosphorus
Phosphorus is necessary for the development of the root system and the ripening of plant tissues. Thanks to him, they become more resistant to adverse weather conditions. Phosphorus is applied as a fertilizer for flowering perennials.
Phosphorus fertilizers are either water-soluble or sparingly soluble. The latter include phosphorus and bone meal, which are rarely used.
Superphosphate
Simple superphosphate comes in powder and granular forms. Both dissolve well in water, but leave sediment at the bottom. Granulated superphosphate contains up to 22% phosphorus and is better absorbed by flower roots. It is applied during spring and autumn tillage, when planting plants and as a top dressing. To plant perennial flowers in a hole, just add 1 tbsp. fertilizers
Important! Fertilizing with phosphorus fertilizers is combined with potassium fertilizers. This “commonwealth” promotes the best absorption of elements.
Double superphosphate contains up to 50% phosphorus. It is very convenient to store, as it does not cake, and consumption is halved. The drug dissolves well in water without sediment.
Feeding with superphosphate can be carried out either in dissolved or dry form. The latter is preferable in cold and wet weather. To apply superphosphate in liquid form, add water and leave for 2-3 days. Then drain the top and use the sediment for compost.
They are used for plants with a long growing season: clematis, lilies, roses. Annuals with a long flowering period also need phosphorus fertilizing.
Nutrient requirements of flower crops
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
The nutrients a plant needs depend on the growing season and plant characteristics. Flowers with a short growing season, such as spring bulbs or primroses, require fewer nutrients because their above-ground parts die off quickly. But the amount of nutrients they consume in a short period of time is very large, and even the soil, well fertilized before planting, often cannot satisfy this need, so additional nutrition is necessary for the normal formation of bulbs or preparing plants for the dormant period. Flowers with a long growing season need more nutrients, but their consumption is spread out.
In spring, flower crops, like most other plants, need nitrogen, which can be added in the form of organic or mineral fertilizer. However, an excess of this element can lead to a delay in flowering and the formation of a small number of buds.
The most important element that flowering plants actively use is potassium. It is actively removed from the soil in all periods, and the need for it increases sharply in cloudy weather and when the length of daylight hours decreases.
Potassium preparations
Potassium fertilizers increase the resistance of flowers to adverse weather conditions and improve the quality of seed material. This fertilizer must be applied to all flowering plants.
Potassium sulfate
This is the best potash fertilizer that does not contain chlorine. It contains up to 48% potassium. It is well retained in the top layer of soil and promotes intensive root growth. It is applied to the soil when preparing flower beds for planting flowers and as a liquid fertilizer. For 10 liters of water use 1 tbsp. powder.
Calimagnesia
On sandy and sandy loam soils it is better to use potassium magnesia, since plants on them suffer from a lack of magnesium. The fertilizer contains up to 28% potassium and 9% magnesium. Can be added dry at the rate of 1 tbsp. per 1 sq. m landings.
Deadlines
When feeding outdoor plants, adhere to the deadlines. Nitrogen preparations are applied in the spring, since in the fall it stimulates root growth. During the winter they may freeze and the plant will die. At the end of August or September, products with potassium and phosphorus are used. Nutrients are especially important for long-flowering garden inhabitants.
The easiest way to care for annual flowers is considered. The drug is applied 2 weeks after planting and in July. During this period, buds begin to form. Perennial plants are fed more often: in the spring, during budding, after flowering.
Autumn feeding is just as important as spring feeding. They lay the foundation for the formation of buds and saturate the soil with useful substances. Fertilizers for street and indoor flowers consist of similar components. The main difference is that it is better to fertilize indoor flowers with complex preparations, and garden flowers with products containing one substance.
Complex fertilizers are not used until the snow melts. The earth does not warm up and nutrients are not absorbed into the root system.
To ensure that the plants in the garden always delight with bright colors from spring to late autumn, fertilizers must be used.
Complex mineral fertilizers
More often they use complex fertilizers, which already contain basic chemicals.
Nitrophoska
Universal flower food contains nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in equal amounts (17% each). It does not cake easily and dissolves easily in water. Suitable for any type of soil. In dry form, add 1 tbsp after abundant moistening of the soil. per sq. m.
Organic fertilizers for flowering plants
Organic fertilizers improve soil structure. The effect of organics manifests itself gradually over a long period of time. Organic fertilizers, in addition to the main elements, often contain a large set of microelements necessary for the development of flower plants.
Humus
The most valuable organic fertilizer obtained as a result of the complete decomposition of manure, leaves, plant residues, and household waste. It is especially necessary on sandy and sandy loam soils.
To prepare manure humus, it is placed on material that does not allow moisture to pass through, the top is also covered to prevent the ingress of plant seeds, and it is left for several years. After complete decomposition, it is used the next year.
Apply as a mulching material or embed into the soil by loosening. For 1 sq. m add up to 1 bucket of humus.
For liquid feeding, it is dissolved in water in a ratio of 1:5. Leave for 3-5 days and water at the root.
Bird droppings
Chicken manure is effective for feeding garden flowers. It contains a large amount of concentrated substances, so it is used only in liquid form. Before use, it is dissolved in water at a rate of 1:10. Keep for 3 days. Before use, further dilute 1:1. Fertilizing with chicken droppings is done on moist soil, trying not to get on the plant itself. Afterwards the soil is watered again.
In autumn, dry droppings can be scattered over the surface of the flower bed at the rate of 1 bucket per 2 square meters. m flower garden.
Wood ash
Wood ash is easily absorbed by all flower plants. It contains a large set of microelements. Depending on the material from which the ash is obtained, its potassium content varies. The younger the burned plants, the more potassium. But the phosphorus contained in the ash is absorbed by plants much better than from superphosphate.
When planting perennial plants, it is enough to add 1-2 cups of ash into the hole. To feed in liquid form, ash is dissolved at the rate of 2-3 cups per 10 liters of water. Mix thoroughly and incubate for 3–5 days.
Dolomite flour
It contains 28% potassium and up to 20% magnesium. Used to alkalize soil. Apply regularly, every 2–4 years. The drug has a beneficial effect on plant development.
Thanks to him:
- the soil becomes healthier;
- the number of worms and beneficial microorganisms increases in it, and beetles, mites and flies die;
- Due to the formation of many young roots, the green mass increases, shoots and leaves grow faster.
Dolomite flour is added in dry form at the rate of 1 cup of powder per 1 square meter. m area. Then they are sealed using shallow loosening. Can be scattered on the snow to be absorbed into the soil with melt water.
Universal (organomineral)
"Ecofus" based on algae
A unique organomineral fertilizer that works due to the power of seaweed. Includes more than forty active nutrients, trace elements, amino acids, vitamins, enzymes, and natural antibiotics. Properties: immunostimulating, antiviral, antibacterial, fungicidal. Helps plants breathe, metabolize, and produce large, strong flowers. Improves soil structure and breathability. The manufacturer recommends a combination of spraying and watering.
Advantages:
- Super useful components;
- Increasing soil fertility;
- Flowering stimulator.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
Gumi-Omi Potassium Potassium Sulfate
The fertilizer produced by OZHZ Kuznetsov is a heterogeneous mixture consisting of powder, granules and agglomerates. As can be seen from the NPK indicators (0.5:1.25:30), it contains a lot of potassium. In addition, it contains humic acids, macro and micro elements, as well as 6% organic compounds. Potassium deficiency is visible in the appearance of the leaves; the edges turn yellow and become covered with “rusty” spots. Potash fertilizers are especially effective in peat and sandy areas. This is a popular group of fertilizers, not only for flowers. Customer reviews indicate that with the addition of Gumi-Omi, the plant comes to life, looks healthy, and delights with long-term flowering or a bountiful harvest.
Advantages:
- Universality, for all plants;
- Composition two in one: organics and minerals;
- Soil restoration;
- Visible effect.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
Miracle spray “Flower Paradise” Bui fertilizers
Liquid complex composition for the care of plants, decorative foliage and flowering plants. Suitable for indoor flowers and those growing in the garden or country house. NPK 0.23:0.23:0.34, as well as magnesium, iron, zinc and other trace elements. On the packaging there are tips on the amount of application: from March to September 1 time per week, from October to February 1 time per month. Customer reviews are the best: the effect is visible after a couple of days, it stimulates the compaction of leaves, the development of buds, and lush flowering.
Advantages:
- Ready-to-use solution;
- Independence from the season;
- Quick results;
- Economical consumption.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
IRIS OHYAMA INC Japanese Green Universal Fertilizer
The functionality of the Japanese-made product is striking in its diversity: it protects against excess moisture, aridity, and frost; increases resistance to pests and diseases; stimulates growth and root formation; guarantees abundant, long-lasting flowering. Designed for flowers, potted and decorative foliage crops. Formula of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, copper, iron, zinc and other elements. Manufacturer's recommendations for use: for intensive healing, insert the bottle into the pot at an angle of 45 degrees. Another way: dilute 8 drops per 5 liters of water for large areas and healthy plants. According to buyers, spraying is no less effective.
Advantages:
- Balanced composition;
- Variety of applications;
- Visible performance;
- Wide range of effects.
Flaws:
- Not detected.
What time and how many times should I feed flowers in the garden?
At each stage of development, garden flowers require different types of fertilizers. This is due to the fact that perennials develop wildly in the spring, then bloom, and retire in the fall. Spring small-bulbed flowers and tulips, on the contrary, are only planted in the fall so that they bloom in early spring. Therefore, it is very important to know the stage of flower development in order to help them develop correctly in time.
Important! It is necessary to follow the recommended dosage of fertilizer mixtures. Usually the package indicates the proportion of mineral fertilizers used for each type of plant.
The fertilizer application scheme for perennial garden flowers looks like this:
- spring fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers for growth (15–20 g/sq. m);
- during the formation of buds - water the roots with organic fertilizers (1:10) with the addition of 10 g of ammonium nitrate and 15 g of potassium sulfate per bucket of solution;
- in July, liquid fertilizing with ammonium nitrate, potassium sulfate and superphosphate (15 g: 15 g: 20 g per 10 liters of water);
- August - superphosphate and potassium for better ripening of shoots and seeds (15 g per 10 liters of water).
How to fertilize annual flowers? A combination of organic and mineral fertilizers.
- April - infusion of mullein or bird droppings (1:10);
- May - nitrophoska or Kemira (15 g per 10 liters of water);
- June - mullein infusion or complete mineral fertilizer (7-10 g per 10 liters of water).
Spring bulbous
- April - 15–20 g of ammonium nitrate per 1 sq. m;
- May—15–20 g of Kemira or nitrophoska per 10 liters of water.