Today, polycarbonate greenhouses are widely advertised and are becoming increasingly common among gardeners. They certainly have a lot of advantages. But there are also disadvantages.
In fact, polycarbonate has a number of significant advantages over traditional glass and plastic film. Unlike glass, it does not break and does not reduce the spectrum of penetrating light, and unlike film, it is more durable and does not tear from strong winds.
However, polycarbonate greenhouses have their own disadvantages that should be taken into account when using them. These shortcomings can be divided into two groups:
- constructive;
- quality;
- thermal insulation.
Advantages of a polycarbonate greenhouse
Regardless of what shape and size the greenhouse is made of cellular polycarbonate, in comparison with other structures and various coating materials, it has the following advantages:
- High level of strength and the ability to withstand significant loads in the form of precipitation;
- It is practically not exposed to direct sunlight, so grown plants are not particularly susceptible to ultraviolet irradiation;
- High level of thermal insulation, since polycarbonate consists of two layers;
- Excellent withstands temperature changes;
- Easy to process;
- A polycarbonate greenhouse diffuses sunlight, so the plants being grown will not burn at high temperatures;
- Reasonably priced;
- Durability in use;
- The material is quite light in weight.
pros
Cellular polycarbonate is usually used for cladding greenhouse structures. Its cellular structure determines the thermal insulation properties necessary for the development of greenhouse crops. Hollow honeycombs also determine the rigidity of the sheets, their resistance to weathering and, as a result, the durability of the entire structure.
The choice in favor of polycarbonate models is accompanied by other arguments:
- Variety of shapes. Polycarbonate is a flexible material. It is easy to give it any shape - greenhouse models are straight-walled, arched, arrow-shaped.
- Transmittance of light. Cellular polycarbonate is transparent, but not 100%. On the one hand, this is enough for natural light to penetrate into the interior space. On the other hand, the slight matte finish of the covering prevents the appearance of burns on the delicate leaves of growing plants.
- Long service life. Greenhouses with durable polycarbonate lining can be used for 10-20 years. However, resistance to snow and wind loads largely depends on the quality of the frame, so it is advisable to choose original models with a reliable frame.
- Aesthetics. Polycarbonate greenhouses are beautiful. They not only contribute to increased productivity, but also become an element of the landscape design of the garden plot.
Disadvantages of polycarbonate greenhouses
It is worth noting that cellular polycarbonate has some disadvantages, so when deciding to purchase or make a greenhouse from this material, the following aspects should be taken into account:
- With frequent exposure to direct sunlight, the material may fade slightly, which helps reduce service life;
- Cellular polycarbonate melts quite easily, so not all heating options are suitable for greenhouses made of this material.
It is also worth considering that quite often you can purchase low-quality material, so before purchasing you should carefully inspect the polycarbonate sheet and it is advisable to check the weight.
A high quality cellular polycarbonate sheet usually weighs at least 10 kg.
Types of polycarbonate panels
In order to choose polycarbonate greenhouse panels, you need to know several basic criteria, namely: how and how they differ from each other. By choosing the material wisely, we will protect ourselves and our harvest from unpleasant surprises.
Naturally, there are differences in both the quality and price of the material. The lower its price, the correspondingly lower the quality. Cheap polycarbonate has a lower degree of protection on its outer side, which means it will “deteriorate” from ultraviolet radiation and, of course, will become more susceptible to the risk of “sagging” under the weight of precipitation.
Let's consider two main types of these products: cellular and monolithic polycarbonates. And we’ll figure out which one is best suited for the construction of your greenhouse.
Polycarbonate greenhouse frame
For a polycarbonate greenhouse, you can make a frame from wood or metal. Each material has its pros and cons:
Wooden beam
Best suited for making a small polycarbonate greenhouse.
- Most often, bars of 5 by 5 cm are used, but in order for the greenhouse to be as stable and durable as possible, it is recommended to choose material with a size of 10 by 10 cm.
- It is also recommended that all wooden pieces be thoroughly treated with an antiseptic in order to extend their service life and so that the wood does not become a source of infection for grown plants.
As a rule, a wooden frame is created for single or double slope polycarbonate greenhouses.
Profile pipe
The most popular material for making greenhouse frames is made of polycarbonate of various types.
- Such material is, in principle, easy to process, but requires some skills in working with a welding machine.
- In most cases, to make a greenhouse frame, a rectangular pipe profile with dimensions of 2 by 4 cm is used, and the thickness of the metal itself is about 2-3 mm.
- The profile pipe frame can withstand loads quite well and is resistant to various weather conditions.
Galvanized profiles
Quite rarely used to create a greenhouse frame made of polycarbonate. Most of all, they are used for greenhouses that will be located in areas where there is no strong wind and low precipitation.
The main advantage of this material is that a welding machine is not required to form the frame.
Comparison table - properties of polycarbonate
| Structural PC | Monolithic PC | ||||||||
| SPK UV | LPK-P-SHIELD-3 | ||||||||
| Thickness, mm/Structure | 4 N/2 | 6 N/2 | 8 N/2 | 10 N/2 | 16 N/3 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Standard sheet width, mm | 2100 | 2050 | |||||||
| Standard sheet length, mm | 6000 and 12000 | 3050 | |||||||
| Distance between stiffeners, mm | 5,6 | 5,6 | 9,6 | 9,6 | 18,9 | _____ | |||
| Specific gravity, kg/m2 | 0,8 | 1,3 | 1,5 | 1,7 | 2,7 | 2,4 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 6 |
| Sound insulation indicator, dB | 16 | 18 | 18 | 19 | 21 | 26 | 27 | 27 | 28 |
| Thermal resistance to heat transfer, m2°C/W | 0,24 | 0,27 | 0,28 | 0,29 | 0,42 | 0,17 | 0,17 | 0,18 | 0,19 |
| Light transmission,% | 83 | 82 | 82 | 80 | 76 | 88 | 87 | 86,5 | 86 |
| (for transparent stamps) | |||||||||
| Minimum arch radius, m | 0,7 | 1,05 | 1,5 | 1,75 | 3 | 0,3 | 0,45 | 0,6 | 0,75 |
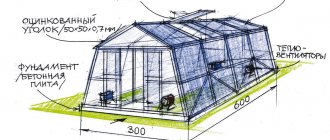
Polycarbonate greenhouse foundation
A polycarbonate greenhouse needs a good, solid foundation, and it can be done in several ways:
Belt type
One of the strongest and most durable types of foundation, while the construction is quite expensive in cost. This foundation is designed for polycarbonate greenhouses that will be used all year round.
It is recommended to start making a strip foundation at a depth just below freezing of the soil.
Concrete
Brick or concrete-beam are the most common options for constructing greenhouses made of polycarbonate of various types. In most cases, they make a concrete-brick type of foundation, since it is average in cost, not too complicated and does not require lengthy work.
It is worth noting that the depth of such a foundation directly depends on the type of soil:
- For heaving soil, the optimal depth is 50-60 cm, and for other types 25-30 cm.
- You should also spread a thick oilcloth on the bottom so that the solution does not get into the ground, and then pour in the solution.
As a rule, for such a foundation, add 3 parts of sand and 5 parts of small crushed stone to a part of M 400 cement; it is not recommended to add expanded clay, as it absorbs moisture.
Be sure to level the surface well; for this you can use wooden blocks. Then you need to tightly cover the foundation with film and leave it for a couple of weeks.
Bar type foundation
Can be used for a polycarbonate greenhouse, which is designed to last a couple of years. For this type of foundation, you should use bars with a cross-section of at least 10 by 10 cm, and be sure to pre-treat them with a special agent.
- When creating this foundation, you need to dig a trench deeper and wider than the bars by 8-10 cm.
- The bottom and sides should be covered with waterproofing material to increase the service life of the foundation.
- Then place the prepared wooden material and fasten it in the corners, fix it.
Wrap the waterproofing material around the wooden one, fill the cracks with soil or crushed stone. It is worth considering that such a foundation is only suitable for dry areas.
Pile - grillage
A fairly reliable and durable type of foundation, but it does not protect against frost at all. This foundation is best used for a summer greenhouse or in an area where there is no severe frost.
Monolithic polycarbonate
Monolithic or sheet polycarbonate is a solid transparent polymer plate with a thickness of 2 to 15 millimeters. This material is much less often used in the construction of greenhouses on personal plots due to its relatively high price. This polymer is very convenient for installation - it can be easily cut and drilled, and can also be bent without additional heating.
The thermal insulation of a monolithic PC is lower than that of a cellular PC, but it is more resistant to external factors - be it hail, snow or mechanical damage. Today it is considered the most durable of all transparent plastics. I will also note the fact that this material does not burn - in the event of a fire, the polycarbonate sheet smolders.
So, we weigh the pros and cons, select the appropriate material and begin installing our greenhouse. Of course, the foundation of our building plays an important role. The right location and additional heating system and properly organized watering will certainly give you the opportunity to grow plants throughout the year. And this will not only recoup the funds spent on the greenhouse, but will also delight you with a good harvest.
A polymer such as sheet or structural polycarbonate has very good resistance to chemicals. But it should be remembered that it is better to clean sheets of this polymer with isopropyl or methyl alcohol. It is necessary to exclude the possibility of contact of plastic with strong acids and acetone.
A mild soap solution is ideal for cleaning the greenhouse. The main thing is not to use any abrasive materials, such as a brush or cloth (sponge) with a metallized layer. So, build your own effective greenhouses and greenhouses and grow everything with pleasure. We hope that the material in this article with the main characteristics of polycarbonate was interesting and useful to you. We wish you good harvests!
DIY polycarbonate greenhouse
The plan for building a polycarbonate greenhouse consists of the following steps:
- Assembling the end parts of the frame.
- Fixation of frame arches.
- Assembly of arc connections and fixation.
- Installation of the frame on the foundation.
- Cutting polycarbonate.
- Removing film from cut out elements.
- Install polycarbonate elements so that UV protection is on the outside. It is worth noting that the installation of elements such as doors and windows is done last.
- Using a utility knife, cut off all protruding parts of the polycarbonate.
Types of greenhouse structures
Based on the shape of the structure, we can distinguish four main types of greenhouses: wall-mounted, gable, polygonal and arched.
With the wall option, the gardener can save building materials due to the fact that part of the house or other structure on the foundation will act as one of the walls of the structure. Often, when designing a house, the location of the greenhouse is included in the drawing.
The gable type is classic. It represents a structure with vertical walls and two slopes. Convenient and practical. Allows rational use of ceiling space, for example, for placing shelves.
Polygonal structures are aesthetically pleasing and characterized by high light transmittance.
The arched variety allows you to better retain heat and also withstand heavy loads during a snowy winter thanks to its smooth slopes.
Arched greenhouse on a concrete foundation
Photo of a polycarbonate greenhouse
Choosing a greenhouse location
When deciding where to install the greenhouse, pay attention to the landscape, soil composition and lighting.
When talking about the landscape, you should take into account the groundwater level, as well as the possibility of flooding in the spring. When water rises above 120 cm, you should consider creating a drainage system.
Do not place the greenhouse where there is shade
It is recommended that the soil be dry, so clay soil will not work. It is good if the soil contains a lot of sand. If necessary, sand or sandy gravel can be brought in.
Abundant insolation will save on heating and artificial lighting. In terms of lateral orientation, it is recommended to follow the directions from east to west or from north to south. The first option is considered more preferable. If the structure is square, the orientation can be any.
Diagram of the most favorable location of the greenhouse relative to the cardinal directions
It is important that no shadow from the house or trees growing nearby falls on the greenhouse.
Falling leaves covering the roof can also negatively affect the lighting.