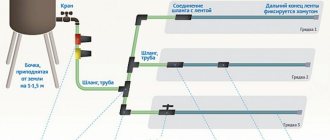
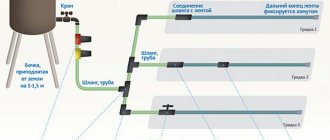
When choosing a source of food for plants, gardeners and gardeners usually give preference to those organic fertilizers that are available for purchase in their region. In areas where large amounts of wetlands occur, peat is often used as fertilizer.
This swamp inhabitant is used not only to create a highly nutritious environment for plants. It has many uses. Peat is burned for space heating, various solutions are filtered through it, and the walls of houses are wrapped in layers to ensure good thermal insulation. But most often this substrate is used as a fertilizer.
Peat intended for use in the garden is classified according to the degree of decomposition:
- Horse (has not been subjected to rotting, used as mulch for winter shelter);
- Transitional (the decomposition process has begun, but has not reached the end; it is used as fertilizer);
- Lowland (completely rotted, used as fertilizer).
This swamp organic matter contains components of not only plant but also animal origin. A significant amount of humus is formed under conditions of high humidity and low oxygen content, and sometimes reaches 60% of the total structural composition. The chemical composition of peat is as follows:
- Carbon 50-60%;
- Hydrogen – 5%;
- Oxygen – 1-3%;
- Nitrogen – 3%;
- Sulfur – 1%.
The presence of a large volume of carbon and hydrogen in the composition makes the physical structure of this organic fertilizer porous. With such a quantity of ballast (from the point of view of plant nutrition) substances, one should not be surprised at how much the volume of peat decreases during drying.
Nitrogen from peat is poorly absorbed by plants; they receive a maximum of 1.5 kg from a ton of substrate. This is not enough. One of the main rules when using this fertilizer is to combine it with other organic and mineral fertilizers. In this case, peat acts as an assistant that keeps agrochemicals in the soil. This property is especially important when used in protected ground.
Peat extraction technology
Extraction technology involves several methods. More details about this below.
Milling
The deposit is developed by open-pit mining, with the gradual removal of thin layers of deposits in short cycles. Characterized by the following operations:
- milling the surface layer: a strip no wider than twenty-five meters is cut and dried;
- to increase the intensity of liquid evaporation, the layers are turned;
- swathing - the formation of triangular cross-section rolls from the dried composition;
- removing compressed fertilizer from rollers;
- stacking - storing raw materials in stacks;
- isolation – protection from the effects of natural factors.
After harvesting and processing the layer, the sequence is repeated up to fifty cycles during the season. This method is used in the extraction of all types of this mineral, and is associated with numerous advantages, including low labor intensity, low resource consumption and high quality products.
Lump
Extraction is carried out in two ways:
- excavator - deepening with bucket equipment to the required depth with subsequent removal of raw materials;
- slot milling – recess no more than 0.4 meters.
The technology involves performing the following operations:
- extracting raw materials and forming them into briquettes;
- laying out briquettes for drying in an open place;
- storing dried products in stacks.
It is used for raw materials characterized by a low degree of decomposition and ash content.
Transitional peat
The transitional type of mineral is accompanied by groundwater, which makes extraction difficult. To develop such deposits, additional costs are required for draining the deposits, which is associated with a more labor-intensive process.
Peat acidity
This directly depends on how much calcium it contains. Due to the high degree of acidity, horse grass is practically not used for planting; it is suitable for mulching. Since its pH is 3-5. Summer residents prefer to use lowland peat, since its acidity level is 5-8. All particles in its composition are well decomposed and are suitable for feeding any crop.
Based on the degree of acidity, the following classification is determined:
- Strongly acidic, their ash content is 1.5-3%, lime content is 0.15-0.6%, pH 2.5-4.
- Medium acidic, ash content 3-6%, lime content 1%, pH 3.5-4.5.
- Slightly acidic, ash content 5-12%, lime more than 1%, pH 4.5-5.5.
- Neutral, high ash content, neutral pH above 7%.
It is worth remembering that when it comes to composition, it is impossible to say unambiguously about all types. Therefore, general characteristics are given.
Peat as a fertilizer: pros and cons
The use of peat as a fertilizer has the following advantages:
- increasing the looseness of clay or sandy soil;
- improved air exchange;
- enriching the soil with useful substances;
- soil disinfection - kills fungi and microbes, being a natural antioxidant;
- protects against the harmful effects of pesticides;
- normalizes soil acidity;
- promotes rapid warming of the soil;
- refers to complex fertilizers;
- good insulation for the winter;
- prevents the spread of pests and weeds.
However, along with the advantages, there are disadvantages when using only this type of fertilizer:
- if low-quality fertilizers are used simultaneously with peat, the development of crops slows down, even to the point of death;
- application in its pure form leads to an increase in soil acidity;
- worsens the properties of loose fertile chernozem;
- attracts mole crickets.
The use of this mineral on a non-alternative basis does not contribute to increasing productivity. It is recommended to use it to improve the structure of clay soils, along with other fertilizers.
High-moor peat: characteristics and methods of use in gardening
High-moor peat is characterized by porosity and a high ability to retain moisture. It is not biodegradable for a long time.
Thanks to the long fiber structure, it retains minerals in its composition for a long time. The soil, saturated with long-fiber high-moor peat, is light, has thermal insulating qualities and does not shrink when growing plants.
Unfortunately, high-moor peat is not rich in nutrients . High-moor peat deposits have an acidic pH of 2.5–3.1. and are often used to acidify soil.
Some plants require just such an environment to develop. For example, for potatoes, strawberries, hydrangea, sorrel, violets, heather. In this case, aerated peat is added in 1:1 proportions for loamy and sandy soils.
In order not to suppress plant crops with high acidity, high-moor peat is pre -composted in pits or heaps until organic residues are completely decomposed.
Based on the raw materials, substrates are prepared for growing seedlings of vegetables and flowers, and are also used in the greenhouse as the main material. Before this, the substance is mixed and ventilated , mineral fertilizer and dolomite flour are added.
Acidity must be measured, since the optimal pH level for plants is 5.5–6.5. The prepared base is kept for 1.5–2 weeks, stirring occasionally, after which the plants are planted.
To use useful raw materials in gardening, you should know some rules. Before use, peat fertilizer is “dissolved” and ventilated for about two weeks.
It is best to sift the material additionally through a special mesh. Ventilation is performed in order to reduce the degree of toxicity . Then the raw materials are piled up and kept for up to two or three months, periodically shoveling.
Peat fertilizer has proven itself well in growing flowers. Airy and porous soil promotes rapid restoration of flowers after transplanting. Peonies are especially favorable to peat substrate. Flowers develop quickly and delight with bright colors, while emitting richer odors.
Gardeners often use instead of manure . The only drawback of this method is the longer decomposition of peat in the soil than that of manure. In addition, high-moor peat has high acidity, which requires aging before use. But with proper preparation, peat compost is in no way inferior to manure.
Composting is carried out from early spring until late autumn . Various materials are added to peat in compost heaps, which serve as an excellent addition to beneficial microorganisms.
Most often, these are fallen leaves, plant waste, tops, weeds, food debris and sawdust. Compost takes about one to one and a half years to prepare. During this time, it is considered ready if the mixture has turned into a homogeneous mass.
Comparison
Next - in more detail about the qualities of peat fertilizer in comparison with other compounds, which is better to use in various cases.
With humus and manure
The main difference between peat and these fertilizers is its increased acidity, which contributes to the effectiveness of use in poor, non-acidic soils of sandy and clayey composition.
Humus and manure are a more universal remedy, rich in nutritional components. But many are deterred by the high content of pests and weed seeds and the need for additional soil preparation.
With black soil
Chernozem is characterized by high fertility and a granular, lumpy structure. The method of application is similar to peat; both compositions are mixed with sand and loam to improve the soil structure. However, chernozem is more acceptable for normal plant growth. It retains moisture better and contains a greater amount of nutritional components absorbed by plants, and has a more balanced acid-base balance. When choosing a product from these fertilizers, the feasibility is determined by the intended use.
Chernozem is used for crops over large areas, peat is used in greenhouses and greenhouses.
With chicken droppings
Chicken manure is the composition with the highest concentration of nutritional components of all organic fertilizers, so it is not applied in its pure form, but diluted as a top dressing. Compared to peat, its use requires more labor, and exceeding the concentration of the composition can damage plants.
See also
For which plants in the garden is soda used and how to use it against weeds
Read
Greenhouse use
Peat has a high absorption capacity, and it is this property that makes it indispensable for use in greenhouses, where high air humidity is constantly maintained. It absorbs its excess and retains it in its micropores, and when the need for liquid arises, the plant roots always have access to it. Using peat as a fertilizer in a greenhouse can reduce the content of pathogenic microorganisms in the soil. In closed spaces this property is especially important.
For abundant fruiting of crops in closed ground, it must be renewed annually. Fertilizing the land with peat in this case is the best option. Its content in the soil can reach 70% of the total composition, subject to the additional use of other fertilizers, both organic and mineral.
Recipe for peat-containing soil for a greenhouse:
- Garden soil – 40%;
- Lowland peat – 40%;
- Cow dung – 10%;
- Ash – 5%;
- Wood sawdust -5%.
What is peat used for?
The unique qualities of this mineral allow it to be used for various purposes:
- in the energy sector - as fuel in power plants and boiler houses. Lower energy intensity is compensated by greater environmental friendliness and high production costs;
- in agricultural activities - as an additive to other fertilizers, increasing their effectiveness and improving soil structure;
- in livestock farming - in the form of bedding for livestock and poultry. Retains heat and absorbs moisture. Used as water filters for animals and aquariums, purifying and normalizing the acid balance of liquids;
- in construction - as a moisture- and heat-insulating material;
- in the alcohol industry - in its pure form for making whiskey and drying malt;
- in medicine – for mud baths and the production of certain medications;
- for environmental purposes - in wastewater facilities, as filtering and sorbing elements, and to eliminate the consequences of environmental disasters.
The unique chemical composition of the substance ensures its versatility and indispensability in some areas of life.
Peat manure or black soil - which is better?
Peat substrate, due to its high absorbent properties, is often used as bedding for livestock. Together with the liquid, it absorbs a large amount of nutrients - ammonia, potassium, calcium, magnesium. Acidic peat contains substances with an antibiotic effect, which helps it simultaneously nourish and protect plants from pathogens.
Fertilizer from such litter surpasses even “rested” black soil in its nutritional properties . Peat manure soil contains the same amount of nutrients as highly fertile soil rich in humus, but surpasses it in terms of protection from harmful microorganisms and the quality of its structure.
You can distinguish between these two substrates manually - take a handful in your palm and squeeze tightly. The resulting lump must be left in the open air until completely dry. Chernozem will remain wet much longer, and peat will dry out very quickly and will crumble in your hand.
But when purchasing “clean” peat to create a fertile layer on the site, you need to be prepared for various troubles. It will have to be fertilized additionally to achieve optimal results. An ideal soil for a garden will be obtained if you add vermicultured compost, sand, and humus to peat.
Don't forget about safety precautions : It is better to carry out the mixing procedure immediately after shipping this substrate to the garden plot, using, first of all, wet sand. It is especially important to follow this rule in hot weather, as peat can spontaneously ignite.
The cost of peat and black soil is approximately equal. It starts from the position of 150 rubles. per m³, and depends on the composition of the substrate, as well as on the amount of fertilizer purchased.
Peat properties
The beneficial qualities, composition and properties of the fossil have been studied in detail during the long history of its use. This substance is an important component of the natural ecological balance, accumulating organic decay products and combining them with atmospheric carbon.
Peat composition
The substance is characterized by the content:
- biological residues;
- mineral components;
- humus.
The degree of ash content is determined by mineral components, and the color shade is determined by humus.
There are three types of state of this fossil - liquid, gaseous and solid.
Peat acidity
The acidity indicators of minerals range from:
- for lowland: 5.5-7.0 pH – slightly acidic or neutral environment;
- for transitional: 3.2-4.6 pH – slightly and moderately acidic environment;
- for riding: 2.6-3.2 pH – strongly acidic environment.
Note! If the acidity is less than five and a half, the use of the substance in its pure form is not recommended.
Decomposition rate
There are three degrees of decomposition of the specified natural fertilizer (in percentage):
- low - up to twenty; used as bedding for animals, thermal insulating material for greenhouses, as a raw material for hydrolysis;
- average - twenty-one to forty; purpose – fuel, production of complex fertilizer compositions;
- high - over forty-one; the widest scope of application in various industries.
The degree of decomposition determines the area of application of the composition.
What are the benefits of peat?
Peat is a porous substance that consists of plant remains with varying degrees of decomposition. Pores make up 93-98% of it. The material is capable of accumulating water, but even with complete saturation with liquid, about 15-20% of the pores remain free. Peat significantly changes the structure of the soil, making it light and loose. After watering, the soil retains water for a long time and does not dry out. Access of oxygen to plant roots improves.
Peat contains a lot of nitrogen (0.8-4%) and potassium (0.5-1.5%), slightly less phosphorus (up to 0.4%). Other microelements (calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, sulfur, manganese, iodine, bromine, fluorine) are contained in small quantities. All of them are necessary for plants to synthesize amino acids, vitamins, and enzymes. The amount of ash elements (minerals) in peat ranges from 5% to 50%.
The organic part of peat deserves special attention (from 50% to 95% of its mass). The composition largely depends on the type of peat. The upper and transitional zones are dominated by polymeric, sparingly soluble substances—cellulose, bitumen, and lignin. Lowland soil contains more humic acids, which are beneficial for plants. They convert microelements into accessible form and trigger biochemical processes in the soil.
Organic substances also include growth stimulants - amino acids, biogenic amines, cytokinins, ethylene, alkenes and a number of other compounds. They enhance the ability of plants to photosynthesize, improve metabolism and absorption of microelements from the soil, affect productivity and the development of roots and green mass.
When peat is added to the soil, beneficial microflora develops more intensively and the decomposition of organic matter increases. Biochemical processes are launched in the surface layers, as a result of which humus is formed. According to observations, the amount of this useful component increases by 4-5% with regular application of peat fertilizers. They prevent soil degradation, which inevitably occurs when using mineral fertilizers and intensive field exploitation.
But peat has several disadvantages. Most microelements in this material are in a form that is difficult for plants to reach. In its pure form, only lowland type with a high degree of decomposition can be used. The reaction of the material is acidic, which is not suitable for all plants. Therefore, peat is processed before use. We will tell you how this is done later, but for now we suggest finding out for what soils this fertilizer is suitable.
Types of peat
Depending on the conditions of formation of the biological mass that serves as the basis for the formation of the fossil, several varieties are distinguished.
Lowland peat
It is formed from mixed species of trees and shrubs growing in lowlands, river mouths, ravines, and hill valleys. Compared to other varieties, it has the highest content of nutritional components and a wide range of applications.
High peat
Includes remains of coniferous trees that grew in upland areas or along watersheds. The composition is characterized by a low degree of decomposition of the components.
Transitional peat
An intermediate stage between the above varieties. Contains from ten to ninety percent of slightly decomposed upland plants, the rest is lowland vegetation.
Neutralized peat
Obtained after mixing with lime, clay or dolomite of the upland and lowland varieties of the fossil to neutralize the acidic environment. Another way to neutralize is to mix the highland type with the lowland one.
Note! The use of highland and lowland varieties in their pure form is not practiced.
Peat for the garden: the benefits and harms of raw materials
Gardeners use peat raw materials to impart looseness to the earthen coma and create the correct structure of sod-podzolic soils, where sand and clay predominate. As you know, sand holds water poorly, while clay is airtight.
Therefore, there is no better option for such soil. How to choose peat for the garden? You can choose depending on the degree of decomposition of the substance. There are three categories:
- Lowland type. More than 40% decomposition rate. Due to its neutral composition, it is best suited for the garden.
- Transitional type. The degree of decomposition is from 25 to 40%. Used as composting material.
- Horse type. The minimum degree of decomposition, which is 20%. It is not recommended to apply it in its pure form to the soil due to its high acidity; it requires pre-treatment.
The main benefits and harms of peat on a garden plot. Let’s determine what the beneficial effects of the peat composition are:
- Allows you to increase productivity by improving the soil, with minimal costs.
- Increases the humus layer of the soil, thereby improving fertility.
- Increases porosity, air and water permeability of the substrate, improving the functioning of the root system of plants.
- Fights pathogenic microflora, fungi, bacteria, and is a good antiseptic.
- If the acidity of the substrate is low, this indicator can be normalized if you choose the right type of peat.
- It quickly warms the ground, is able to retain useful substances and stop their leaching.
- It is hygroscopic. Increases soil moisture capacity.
What disadvantages and harm can it bring:
- Peat is harmful only if it is used incorrectly or combined with low-quality fertilizers. Then the plants slow down their development, and in some cases even death is possible.
- The substance can increase soil acidity, which has an adverse effect on crop growth. To avoid acidification of the soil, lime the peat material - add 4–6 kg of lime per 100 kg.
- Peat will not bring any benefit if the soil is fertile and loose. The content of microelements in the substance is minimal and will only be absorbed by 5%. This should be taken into account.
Peat use
In the agricultural industry, the fossil has received a wide range of applications. It improves soil fertility and structure, which is especially effective for loam and sandy soils. Next - more details about the features of use.
For the garden
A thin layer of the substance, evenly distributed throughout the site, is dug to a depth of ten centimeters. The lowland variety of the fossil is used for mulching in the spring along with nitrogen fertilizers. After harvesting, the component is applied to the upper layers of the soil.
In addition to improving the structure of the soil and enriching it with nutritional components, this allows you to avoid the unpleasant odor from compost and manure and disinfect the area from pests.
Application rates are from twenty to thirty kilograms per square for the lowland variety of fossil.
For the greenhouse
In this case, the upland variety is used in the form of a substrate with mineral fertilizers. The duration of use of a one-time application is over three years. Maintaining the required level of acidity is ensured by liming.
For garden
For the garden, rotted composition is used. It is stored for several years, periodically loosening and turning to speed up ripening. Mixed with the addition of humus, it ripens faster. For application it is diluted with ash or lime.
For plants
In addition to fertilizing areas, the composition is poured into the near-trunk zone of trees and shrubs. The porous fibrous structure ensures the digestibility of nutritional components and moisture retention.
For flowers
Peat compost allows you to fertilize the soil and prevent putrefactive processes. This is an excellent way to insulate perennial flowers for the winter.
Application in winter
Used as an insulating agent to protect crops in winter. Plants are covered with a mulch composition with the addition of sawdust, manure, tree bark and leaves, which helps prevent damage in the most severe frosts.
The benefits of peat for plants
Getting into the ground even in small quantities, these beneficial substances stimulate the rapid growth of garden crops.
First of all, the spray does not affect the root system of plants, but the ground, the soil.
During use, peat is mixed with the soil and it is saturated with all the necessary components.
As a result, more oxygen appears in the soil, as if it begins to breathe, passing this opportunity on to the plants.
Experts note that what is most beneficial is not the natural, undiluted powder, but a substance mixed with other materials. Peat is especially necessary for soils with a high content of clay and sand, which block the proper supply of moisture and nutrients to the root systems.
It is important to ensure that the peat contains as little humus as possible from the results of the vital activity of living organisms, otherwise the soil will not begin to be fertilized, but will simply rot.
In general, peat composition is useful as an emergency remedy for drying crops that have lost color, moisture and strength for further growth. You can feed both the entire bed with the crop and especially the affected plants.
This substance can be created independently by adjusting the humus content, or it can be purchased at a specialized store by finding detailed information on the packaging about the humus content in a specific mass of peat.
What plants need peat?
For some plants, the use of peat is vital - without it they simply will not be able to develop adequately.
Examples of such needy plants are:
- blueberry;
- hydrangea;
- raspberries;
- heather;
- potato;
- strawberries;
- tomatoes;
- some varieties of cucumbers;
- roses.
Fertilization of individual crops
A little more detail about the use of this product for growing various crops.
Potato
It is used in conditions of loose, slightly acidic soils in combination with mineral fertilizers. It is introduced into holes when planting, and in the fall it is distributed with manure over the soil surface.
Strawberry
Improves crop fruiting. It is used in a mulching composition, mixed with sawdust or tree bark ten to one. When planting, it is introduced into the hole, and before the onset of winter - into the garden bed.
Note! It is not recommended to use the fossil in its pure form due to its high acidity.
Tomatoes
Apply no more than once every two weeks during the season, and place it in the holes before planting.
See also
Types and chemical formula of nitrate, composition and what the fertilizer is used for
Read
cucumbers
The raw materials undergo preliminary neutralization and are used in compost to fertilize the soil.
Cabbage
Use is allowed only with measures to reduce acidity. Apply directly to the hole before planting.
Peat composition
The composition includes plant residues that have not completely decomposed. Their decomposition products and mineral particles. Under natural conditions it contains 86-95% water. Botanical composition:
See also
Description of the Jelly potato variety, growing characteristics and yieldRead
- wood remains;
- tree bark and roots;
- various plant remains;
- hypnum and sphagnum moss.
The chemical composition varies depending on the type, botanical composition and degree of decomposition. That is, the percentage of micro- and macroelements in its composition depends on what type of peat is being studied and whose plant residues it is based on.
Fertilizing the soil with peat
Some information about the procedure for preparing and applying peat fertilizer.
Peat preparation
Peat with a high degree of acidity can adversely affect the quality of the soil, so it undergoes additional treatment before application. For the high variety, neutralization is carried out, while the low variety is ventilated and crushed.
When to deposit?
The composition is applied in the spring, when planting crops directly into the holes, during the season - in the inter-row spaces, in the autumn - the top variety mixed with the main fertilizer.
Dosage
Application rates are from twenty to thirty kilograms of neutralized or low-lying substance per square meter of area, when developing virgin soil - up to sixty kilograms.
Mulching with peat
Only lowland and transitional varieties of fossils with a low acidity level are suitable for mulching. The composition is applied in a layer with a thickness of one to seven centimeters, depending on the purpose. When sowing, the thickness is minimal. Pre-winter mulching is the most common and is used without taking into account standards for the purpose of thermal insulation. Additionally mixed with humus, sawdust, and black soil.
Soil feeding
Before using as a top dressing, it is necessary to take measures to neutralize the harmful effects of the substance:
- keeping in a well-ventilated cool place to reduce the concentration of toxins;
- ensuring the required level of humidity. An overdried composition does not absorb and retain moisture sufficiently.
Note! The use of peat fertilizer on fertile black soils is ineffective. Such compositions should be applied to improve the structure of clay and sandy soils.
How to improve soil structure with peat
Adding peat to too heavy or light soil improves its physical properties. Clay soil becomes more loose and breathable, while sandy soil retains moisture and nutrients better.
This effect continues until the peat decomposes, usually no more than three years. After this, it no longer affects the physical characteristics of the soil. To make its effect last longer, it is better to use slightly decomposed, i.e., high-moor peat for these purposes.
It is necessary to take into account the increased acidity of peat and add calcareous materials to the soil along with it. For 1 kg of acidic peat take 35–50 g of lime, chalk or dolomite. You can immediately purchase neutralized peat, whose acidity has already been brought to the desired value.
Organizing peat compost
For the preparation of peat compost, it is most preferable to use raw materials with a moisture content of about seventy percent. The ratio of components is determined by the time of application. In winter - in equal shares, in summer - one to four in relation to additives.
The composition additionally includes tops, weeds, sawdust, shavings, food waste, and manure.
Methods
There are several ways to make compost.
Local composting
Most often performed in winter. A half-meter layer of fossil is covered with a continuous or intermittent strip of manure up to 0.8 meters thick and covered with peat on each side. The work is carried out during the thaw.
Layer-by-layer
Carried out year-round, as needed. A half-meter layer of fossil is applied in a five-meter strip and alternates with manure until a two-meter stack is formed, ending with a peat covering.
Methods
There are 2 ways to organize compost, which of them is preferred by the summer resident himself.
Local composting
A layer of peat of 50-60 cm is laid out at the selected location. Then manure of 70-80 cm is laid out in a continuous layer or in heaps. Moreover, the width is made 1-1.5 m less than peat, then the top is covered with a layer of peat, 50-60 cm. Covering the manure from all sides. This method is preferable in winter.
Layer-by-layer
Peat is distributed over a width of 4-5 m, the length of the area is possible, the layer thickness is 50 cm, then a layer of manure is laid, then peat again, and so on several times, the height of the finished compost heap is 2 m. The last layer is necessarily peat.
Peat based fertilizer
Fertilizer manufacturers create fertilizers for plants. They make it for those who cannot make a compost heap on their own. Made in the form of granules, which are added directly to the wells. And liquid fertilizer, which is absorbed much better. It is watered on plants and used as a growth stimulator for seeds.
Peat oxidate
Economical plant nutrition, which is much cheaper than imported analogues. Helps plants accumulate nutrients, improves soil structure, and prevents toxins from entering the plant.
It contains amino acids, monosaccharides, proteins, humic acids, minerals and sulfic acids. When using, be sure to dilute with water.
Peat extract
For manufacturing, a low-lying type is used; using electro-hydraulic processing, a hood is obtained. The fertilizer is very convenient to use. Contains many useful substances. Recommended for areas where there is no need to fertilize the soil.
Peat-based fertilizers
In agricultural production, to enrich soils with nutrients, fertilizers prepared on the basis of this fossil are used.
Peat oxidate
Environmentally friendly products that accelerate crop growth. Effective for tomato seedlings and other plants during the development period.
Peat extract
The manufacturing method involves electro-hydraulic processing, enriching the nitrogen content. It is used not only to improve soils, but also to enrich it with nutritional components.
Application of peat as fertilizer
In any case, it will not be possible to spoil the beds by applying peat fertilizers: it can be applied in any quantities. The average norm is 4-5 buckets per 1 square meter of land.
Peat has high humidity. When storing, it is important that it does not dry out (it is very difficult to soak it). When mulching with a substrate, it quickly dries out on the surface, losing its beneficial properties and not retaining moisture.
Therefore, it is better to embed it in the soil:
- Lay it out on a fresh bed and dig it up with half a shovel (depth 20-25 cm);
- Place between the plants and gently loosen, mixing with the top layer of soil;
- Water regularly.
This way the beneficial substance will remain moist, gradually going deeper into the soil and improving its structure.
Photo pixabay/AndreasGoellner: When fertilizing the beds, peat is incorporated into the soil.
Alternative to peat fertilizers
Along with this mineral, many other nutritional compounds are used in crop production. Next - more details about the alternative to peat-based fertilizers.
Manure
The main and most popular organic fertilizer. Used for any crops, it enriches the soil with nutritional components, but attracts pests and promotes intensive weed growth.
Humus
The main organic component of soil, added to improve the structure and properties when growing crops. Ninety percent consists of organic matter and significantly affects soil fertility.
Humus
This is rotted manure, ready to be used as fertilizer. It is applied in the winter, in the spring, before planting crops, or during the season.
Bird droppings
One of the most concentrated varieties of organic fertilizers. Use in its pure form is not allowed. It is diluted in water and is most often used as plant nutrition during the growing season.
IL
Lake silt is the most effective means in agriculture, increasing soil fertility, stimulating crop growth and acting as a natural antiseptic. Used in agriculture since ancient times.
Feces
Methods of application include industrial scale, calcination, disinfection and fermentation. They are not used for growing food crops due to the high salt content of heavy metals. Available as formulations for lawn grass and ornamental plants.
Sawdust, tree bark
Allows you to improve soil structure. Used for mulching or making compost.
Green manure
Specially grown herbs that, after grinding, serve as fertilizer. An environmentally friendly form of soil enrichment with nutritional components has been widely used in agricultural production.
Decomposition rate
The presence of humus in it depends on how much the peat has decomposed. That is, the greater the degree of decomposition, the higher the percentage of structureless particles. This characteristic is the main one when describing qualities and useful properties.
This indicator is determined as a percentage, “by eye” or under a microscope. In the first case, only fresh peat is taken, which has its own natural moisture. Signs by which the degree of decomposition is determined:
- plastic;
- quantity and preservation of plant fragments;
- quantity and color of squeezed water.
The decomposition is divided into 3 groups:
- 30% - highly decomposed. It is pressed through the fingers, leaving individual, large fragments of plant residues in the hands. After squeezing out the water, which is either very little or not at all, it remains plastic. The water is dark brown.
- 20% - moderately decomposed. It is difficult to press through your fingers; there is a lot of plant residue left in your hands. The water that is squeezed out is light brown or brown in color. Pressed peat springs weakly.
- Less than 20% - slightly decomposed. It's impossible to push through your fingers. Plant remains are easily distinguishable. The water is easily squeezed out, its color is yellowish or colorless. Pressed peat is springy and rough on the surface.
More detailed information is provided by the macroscopic method; it was proposed by P.D. Varlygin.
In field conditions, when it is not possible to conduct laboratory tests, the smear method is used. The disadvantage of the method for determining the degree of decomposition is that traces of slightly decomposed soil are difficult to discern. A plus is the quick determination of results.
Production
Peat, which lies on the surface, is not easy to obtain. To do this, use one of two methods: milling or lump (excavator).
Milling
This method is based on layer-by-layer peat extraction in short cycles. In other words, the top layer with a depth of 0.6-2 cm is milled using milling drums. As a result of this work, peat crumbs with fractions of 1.5-2.5 cm are formed.
Attention!
After milling, the layer must be constantly turned over to dry.
When it dries, they begin to roll and stack it. After this, the procedure is repeated from 10 to 50 times.
This extraction method has been used since 1930. The advantages of this method are that it is completely mechanized, that is, the cost of the resulting material is low. Milled peat is used in production and nuclear power plants. And in agriculture 15-25% of extracted minerals. The milling method is intensive drying and requires good weather conditions. In addition, it is more in demand, since the cost of human resources is minimal, and production is carried out in large quantities.
Lump
Excavators are needed for mining. Development is carried out to a depth of 4-8 m. First, peat is extracted using bucket equipment, then bricks are formed from it. They are laid out on fields to dry. Then they are stacked and taken away.
Taking into account the location of extraction and other development costs, the cost of the mineral is determined. The weight of one piece varies and can be 0.5-1 kg. This extraction method is no more than 90 years old.
mama-knowet.com
If you plan to plant rhododendron, hydrangea, azalea, heather, Erica, blueberry, cranberry, lingonberry, blueberry, as well as conifers, you will need acidic peat, since these plants require acidic or slightly acidic soil for normal development. Peat, which has an acidic reaction (pH), is added to the planting hole for them, and then periodically mulched with it. Many manufacturers, under the guise of acidic peat with a stated acidity of about 2.5-4, sell neutral peat, which is absolutely unsuitable for the above plants. Find out what kind of peat you need to buy and how to check its acidity in this topic.
What kind of peat should be purchased so that it provides the plants with the necessary growing conditions? Let's figure it out, because not everyone knows how different types of peat differ. What kind of peat is there?
Peat is the rotted, more or less compressed remains of plants and animals. Plants and organisms that live in swamps, in overgrown reservoirs, and lakes with low-flow water die over time, forming biomass, which is increasingly layered on top of each other and compressed every year. In conditions of high humidity and lack of air, they turn into peat. Peat acidity ranges from 2 to 6 units and depends on the degree of biomass decomposition. Depending on the degree of decomposition, peat is:
- riding - almost not decomposed;
- lowland - completely decomposed;
- transitional - an intermediate state between highland and lowland.
High-moor peat is well structured, has high porosity and moisture capacity. As a rule, it has a brown or red color. High peat gives an acidic reaction, its pH is in the range of 2.5-4 (according to another classification 2.8-3.6). Lowland peat is darker in color than highland peat, as it contains a larger amount of humus (40-60%) and has a denser structure. By these signs it can be visually distinguished from a riding one. It has a decomposition rate of more than 15%. The acidity of lowland peat is close to neutral - pH 5-6 (according to another classification 5.5-7). Since the formation of high-moor peat is closely related to the vital activity of the sphagnum moss growing on it, high-moor peat is often called “high-moor sphagnum peat” on sale. The acidic environment of high-moor peat is associated with the ability of sphagnum mosses to release hydrogen ions into the environment (due to which acidity decreases). The lower the degree of decomposition of sphagnum, the greater the acidity of the peat. As a soil, types of peat are used as follows: 1. Lowland peat is used for growing most garden, ornamental and fruit crops that require acidity within the pH range of 5.5-6.5, and is also used as greenhouse soils, where it is optimal pH 6-6.8. 2. For the same purposes, deoxidized (neutralized) high-moor peat is used. It is preferred to grassroots because, thanks to its structural properties, it provides the roots with comfortable conditions for growth. The pH of such peat is close to neutral due to the addition of slaked lime, dolomite flour and other deoxidizing agents. 3. For plants that need acidic soil, high acidic peat with a pH of 2.5-4 is needed to prepare the soil.
Why do you need to know the acidity of peat?
To grow some plants, only acidic soil is required. Such soil is prepared, as a rule, using high-moor peat as an oxidizing agent. Soil classification according to pH level is as follows:
| Soil type | pH level |
| Strongly sour | pH 3 – 4 |
| Sour | pH 4 – 5 |
| Subacid | pH 5 – 6 |
| Neutral | pH 6 – 7 |
| Alkaline | pH 7 – 8 |
| Highly alkaline | pH 8 – 9 |
Blueberries need acidic soils with an acidity in the range of pH 4.3 - 4.8. Optimal - pH 4.5. According to other sources, it is even more acidic - pH 3.5-4.5, and optimal pH 4.0. It’s difficult to say which numbers are correct, but one thing is clear - blueberries need fairly acidic soil. Rhododendron grows in soil with slightly less acidity - pH 4.5-5.5 Hydrangeas “love” slightly acidic soil - pH 5-5.5 Coniferous plants grow well in slightly acidic soil with an acidity in the range of pH 5-6. However, each individual species has its own range. For example, fir, spruce, and cedar will grow well in soil with pH = 5 (and even 4-4.5). More decorative and southern yew and cypress will require pH = 5.5. Pine and larch need almost neutral soil pH = 6-7.5. To prepare the soil for such plants, you need to use the most suitable peat with the desired pH range. The more acidic the initial peat is, the less often acid-loving plants will have to adjust the soil pH by watering with acidic solutions. After all, a peak decrease in pH when watering with an acidifier is stressful for the plant and it is not advisable to carry out such a procedure often.
There are points that you need to pay attention to when buying peat for acid-loving plants - the name of the peat must include the prefix “sour”.
After all, high-moor peat is often sold deoxidized (neutralized), its pH is in the neutral region. Such peat is not suitable for acid-loving plants. Also pay attention to the pH indicated on packages of peat! And that's not all: before you buy a lot of peat, it is better to first buy a small amount (one package) and measure its acidity. Unfortunately, manufacturers do not always indicate the actual pH value. If the acidity is in the desired range, say “Hurray!” and buy the required quantity. Determining the acidity of peat at home
Very often the pH of peat does not correspond to the values indicated on the packaging. Peat is “sour”, it turns out to be slightly acidic or even neutral. Unfortunately, not all sellers are responsible. In order not to ruin the plants purchased for planting, you need to know exactly what acidity the peat has. To do this, you just need to take a couple of simple measurements. The method is not expensive, you will only have to buy indicator strips for measuring pH.
The method for determining the acidity of peat was taken from the workshop on agrochemistry by V.G. Mineeva:
We will perform the analysis according to the instructions given below.
So that this analysis can be carried out at home, we will slightly change the methodology: not everyone has a pH meter at home; instead, we will measure acidity using universal indicator strips. The accuracy of the determination will decrease, but for our task it will be sufficient. If you have a pH meter, use it.
Depending on the acidity of the solution, the indicator paper will change color.
Instead of a solution of potassium chloride, we will use a solution of sodium chloride (verified salt). Given our accuracy, such a replacement is quite possible. It is advisable to use distilled water; it is sold in many stores in the hardware departments.
But if there is no water filter, then you can take water purified using a reverse osmosis system or other household filter. Sometimes purification filters change the pH of the water, so it is necessary to measure the pH of the water used before starting experiments. If it is not close to the neutral value, then correct it, for example, using acetic acid or soda. My water (reverse osmosis purification) has a pH of about 6.
A solution with a concentration of 1.0 M (the approximate concentration of food grade vinegar) has a pH of 2.4. If our peat turns out to be sufficiently acidic, then the indicator paper will look about the same.
Prepare a sodium chloride solution. To do this, weigh 58.42 g of the verified salt and dissolve it in 1 liter of water - we get 1N. (single normal) NaCl solution.
I have a 0.5 liter volumetric flask, I will prepare a more concentrated solution (2 N) and then dilute it by half as I use it. Don't let my photo confuse you.
For analysis you need 4+4 = 8 g of dry peat. Taking into account that the humidity of the peat is about 60% and after drying its weight will decrease by about half, we make weighed portions of about 20 g. We dry the peat until it reaches a constant weight (6-8 hours, or even a day). This can be done in air at room temperature or on a battery, the main thing is that the temperature does not exceed 110°C.
After drying, the peat will significantly decrease in volume. There really is a lot of water in it. Grind the peat and sift through a strainer.
We take 4 g samples and place them in any container in which it will be convenient to mix the suspension. I have regular glasses.
Add 100 ml of clean water to the peat in one glass, and 100 ml of table salt solution in the other.
According to the method, we wait 3-6 hours until the equilibrium concentration is established, stirring occasionally.
I measured after 6 hours, and then again, a day later, to check if the pH was changing and then - no, it didn’t change. Dip the indicator strip into the solution, shake off excess liquid and compare it with the scale. Based on the color change, we find the pH value.
Below are the results of measuring the acidity of peat from various manufacturers.
As I purchase peat, I will add to the list. Results of measurements of peat acidity from various manufacturers
No. 1. Peter Peat sour peat 50 l (A-01-50) AGRO https://tvoydom.ru/catalog/1001438867/ 289 RUR
The manufacturer indicates only the acidity pH (KCl) - no less than 2.5. There is no data on pH in an aqueous solution.
Peat is dark brown. Loose, fine fraction, without large inclusions.
pH peat + water = 5-6
pH peat + NaCl solution = 4-5
The photograph does not accurately convey the color that the eye sees. In reality, the changes are more clearly visible. In the photo you can only notice that the bottom strip is more orange, its pH is lower.
pH did not change after 24 hours
Thus, this brand of peat is not acidic, as the manufacturer claims.
The pH is in the region of 5-6, and pH (salt) = 4-5 No.2. Eco peat Peter Peat for country toilets 20 l https://tvoydom.ru/catalog/1002192948/ 199 RUR I have a 50 kg bag.
I couldn’t find such a package on the store’s website. This peat, as the manufacturer indicates, is not really intended for planting, but if its pH is suitable, then why not)
The pH of this peat is not specified. Only the composition mentions that it is high-moor peat.
Peat is red in color, finely ground, homogeneous, loose, without large inclusions.
If you compare it in color with No. 1, then it is significantly lighter.
pH peat + water = 5
pH peat + NaCl solution = 4
Two stripes in comparison.
Peat pH after 24 hours is the same.
Thus, peat has pH = 5, pH NaCl = 4. For blueberries this is not enough, you need at least pHwater = 4, but that’s better.
Despite the fact that peat is not designated as acidic and is declared as a toilet filler, it is suitable for the garden as a slightly acidic peat. No. 3. Horse peat “Botanist's Dream” 50 l https://leroymerlin.ru/product/torf-verhovoy-mechta-botanika-50-l-18468146/ 226 rubles
According to the manufacturer, peat acidity pH = 2.8-3.3.
The peat is brown in color (not red). Quite crumbly, fine-grained.
pH water+peat=5
pH water+peat+NaCl = 3.5
If the indicator strip is well moistened, then the photo shows better that it has turned orange.
It's hard to see how different the stripes are in color.
And from this perspective, the difference is really noticeable: pH 6; pH 5; pH between 3 and 4 (3.5).
This brand of peat is more acidic than No. 1 and No. 2, but the acidity declared by the manufacturer is not achieved.
Water pH = 5, pHNaCl = 3.4 No. 4. High sphagnum peat Pelgorskoe-M acidic 150 l https://www.obi.ru/universalnyi-grunt/torf-verkhovoi-sfagnovyi-pelgorskoe-m-kislyi-150-l/p/2807014 Article No. 2807014 559 RUR pH 3, 0-4.0
I will add real photos of the packaging later. The peat is in the trunk and weighs 50 kg) I don’t really want to drag it into the apartment, it will immediately go to the dacha) The peat is quite dark in color. Contains many impurities in the form of large undecomposed plant remains - sticks and threads, they are clearly visible in dried peat.
pH peat + water = 6
pH peat+water+NaCl=5
This photo shows the correspondence to the scale better:
Compared to pure water:
This type of peat does not have the acidity pH 3-4 declared by the manufacturer. In reality, the indicators are as follows: pHwater = 6, pHNaCl = 5.
Peat from the Darvin store https://darvin-market.ru/catalog/products/torf-verkhovoy-fasko-pressovannyy-100l-4600757945089/
Fasko pressed riding peat 100l 469 RUR
The acidity declared by the manufacturer is pH(H2O) 3.0-4.1; pH(KCl) 2.5-3.5
Dark colored peat. Quite homogeneous (impurities are crushed).
pH peat + water = 5.5-6
pH peat + water + NaCl = 4-5, closer to 5.
Compared to pure water:
This type of peat does not have the acidity declared by the manufacturer (pHwater 3.0-4.1; pHKCl 2.5-3.5).
In reality, the indicators are as follows: pHwater = 5.5-6, pHNaCl = 4-5. Peat from the Darvin store https://darvin-market.ru/catalog/products/torf-verkhovoy-buyskie-udobreniya-kislyy-40l-4607019657841/ Buyskie fertilizers sour riding peat 40l 249 RUR
Manufacturer declared acidity pH 2.5-3.5
The peat has a reddish tint, but is quite dark. Contains inclusions.
pH peat + water = 5.5-6, more like 6.
pH peat + water + NaCl = 5.
Compared to pure water:
This type of peat does not have the acidity declared by the manufacturer (pH 2.5-3.5). In reality, the indicators are as follows: pHwater = 6, pHNaCl = 5.
Peat purchased at Globus.
https://www.globus.ru/products/233958_ST/?sphrase_id=5632768 Good helper. High-moor sphagnum peat (acidic), 50 l 269 99 rub.
The acidity declared by the manufacturer is no less than 2.5. Peat is brown in color, light and crumbly.
pH peat + water = 5
pH peat + water + NaCl = 3
Compared to pure water:
Peat does not have the acidity declared by the manufacturer (at least pH 2.5), but it is quite acidic and suitable for preparing soil for acid-loving plants. In reality, the indicators are as follows: pHwater = 5, pHNaCl = 3.
The result of the experiment can be presented in a table for clarity.
| Brand of sour peat | pH specified by the manufacturer | pH measured | |
| pH (water) | pH (NaCl) | ||
| Peat Peter Peat sour AGRO | pH (KCl) not less than 2.5 | 5-6 | 4-5 |
| Eco peat Peter Peat for country toilets | — | 5 | 4 |
| Peat "Botanist's Dream" | pH 2.8-3.3. | 5 | 3,5 |
| High-moor sphagnum peat Pelgorskoye-M sour | pH 3.0-4.0 | 6 | 5 |
| Fasco pressed high-moor peat | pH(H2O) 3.0-4.1; pH(KCl) 2.5-3.5 | 5,5-6 | 4-5 |
| High-moor peat Buyskie fertilizers, sour | pH 2.5-3.5 | 6 | 5 |
| Good helper. High-moor sphagnum peat (acidic) | pH (KCl) not less than 2.5. | 5 | 3 |
From the experiment, it becomes clear that acidic peat does not have the acidity of 2.5 declared by many manufacturers. I think that such peat is not on sale at all. The maximum that can be found is a pH of about 3.5-4. It is not a fact that the commercially available acidic peat is not high-moor, but transitional, as indicated by the fairly high degree of decomposition indicated on the packaging by the manufacturers.
Perhaps I’ll also look for acidic peat from small stores or private companies and add measurement data on its pH.
Based on the results obtained, I will choose the most suitable peat for blueberries (peat pH 3-4 is needed), which I plan to plant in my summer cottage in the spring. I’m preparing for planting in advance and want to do everything according to the rules. I hope my conclusions will be useful to you too.
Types of peat
According to the study, there are 38 types of peat fertilizer. But all these types are combined into 3 types, which are divided taking into account the properties of peat and the nature of the waters that feed the swamps.
- Lowland.
- Horse.
- Transition.
Lowland peat
Fed by groundwater. Its acidity is neutral or slightly acidic. In total, it contains 70% organic residues, as well as a large amount of minerals.
Lowland peat is often used to improve the soil composition of soil that has been used for a long time without applying any fertilizers. It is formed in the depths of swamps without air access, when interacting with groundwater.
The quality of decomposition is weak, medium and strong.
Attention!
As soon as the peat is removed outside, it begins to quickly lose its beneficial qualities due to reaction with air. Therefore, when adding it to the soil in the garden or fields, the soil is immediately dug up so that the peat does not remain on top.
This type is suitable for all types of soil. When mixed, peat improves the soil and its characteristics.
Differences between lowland peat:
- increased acidity;
- short shelf life;
- slow decomposition;
- contains 70% organic substances.
Pressed peat does not allow air to pass through and does not oxidize.
High peat
Of all types, it is the most infertile, therefore suitable only for mulching or plants that require high soil acidity for growth and development.
It contains sphagnum moss, pine, cotton grass and a certain amount of moisture. There are also no parasites or weed seeds. These qualities are especially valuable for those summer residents who have greenhouses.
High peat is formed in the process of interaction and decay of spruce and sphagnum moss with sediments. This top layer is loose, decomposes slowly and contains most of the air.
It is mined in the upper layers of swamps. Often interacts with open air. Mostly composed of sphagnum moss.
Used for the manufacture of filter elements and cleaning systems. Also used as fuel and insulating material.
Attention!
This peat does not contain weeds and parasites, which is why it is well suited for filling in greenhouses. It is also used as bedding for livestock.
Pros:
- easy to transport;
- used for reclamation of alkaline soils;
- convenient to store;
- used in the production of mixtures for planting seedlings and house plants.
Transitional peat
It is located under the high and above the low layer of peat. The properties are more similar to lowland. It can be weak or medium in acidity. Rich in useful microelements. Organics in such peat do not decompose quickly. Suitable for composts and livestock bedding.
With a high organic content, it is poor in potassium. Transitional peat consists of 90% high-moor organic matter, the remainder being a low-lying mixture.
It is slightly acidic with an acidity of 4.5-5.5. Can improve the quality of turf soil and increase yield.
Neutralized peat
Subspecies of the riding species. It is called so because of its neutrality and weak oxidation. The acidity of such peat is 5.5-7.
It is used for the preparation of substrates; for this, raw materials with a low degree of decomposition are taken. In this case, limestone flour is used to neutralize acidity. It is used to make greenhouse soil, or soil for plants grown in pots. For open ground, used when planting trees and shrubs.
Good for deoxidizing the soil. It contains no more than 3% nitrogen and 1% phosphorus, so it is the most useful peat of all other types.
What plants need peat?
The substance will not harm garden crops when used correctly. Peat is considered as an alternative to chemical fertilizers, which, with prolonged use, lead to complete leaching of humus from the soil. The only limitation is that you should add peat under moisture-loving plants; drought-resistant ones can rot.
When using peat in a garden plot, soil fertility increases and, accordingly, beneficial microorganisms, earthworms, etc. receive better living conditions. This has a positive effect on the growth of vegetable and fruit crops, they receive all the necessary compounds, retain their taste and nutritional value.
By adding peat, the moisture capacity of the soil increases. The roots of the plant develop better and consume more nutritional compounds, because the latter dissolve in the liquid and become available.
Attention!
The composition of the lowland layer of the substance contains all the necessary components for normal growth, but even they cannot satisfy all the needs of plants. For effective growth and development, nutrition must be complete, so it is worth using a combination of several feedings.