Cucumber originates from India. It was cultivated in Ancient Greece and Rome. In Europe, the cucumber became popular in the 16th century, when agriculture began to develop. This vegetable is of great importance. It is eaten en masse in raw and processed forms - salted, pickled and pickled. It is difficult to meet a person who does not like fresh or pickled cucumbers. Most gardeners always plant several beds.
In this article we will tell you everything about growing cucumbers in open ground, care, watering and fertilizing, and we will tell you some secrets of experienced gardeners.
Seedling method: pros and cons
There are two ways to plant cucumbers: by sowing the seeds directly into the garden bed or by first growing them as seedlings.
The second method is more labor-intensive, but is considered preferable by most gardeners. Especially in central Russia and northern regions, where spring comes much later.
By growing seedlings in a heated greenhouse or on a windowsill, the owner provides himself with early cucumbers.
Advantages of this method:
- seedlings fall into open ground after the end of frost, there is no need to fear that they will be damaged by the cold;
- in the process of growing indoors, it is easier to monitor young cucumbers, assess their condition, and feed them;
- The seedling growing method allows you to get the first cucumbers in the open ground at the end of May. But such cucumbers fade very quickly and by the month of July the vines usually dry out.
If the size of the estate allows, then it would be nice to find a place on it for sowing cucumbers. They appear later, but bear fruit safely until the end of the season. During the summer, you can always sow new plants to replace the drying canes.
Sowing and planting
Preparing for landing
After harvesting, the garden needs to be dug up and harrowed. Before the onset of winter frosts, deep plowing or digging is carried out. If harvesting is carried out late, only pre-sowing digging is used.
Spring preparatory work includes:
- digging,
- harrowing,
- enveloping
A set of these treatments is used to improve soil water-air conditions by loosening the soil. Thanks to these measures, weeds are destroyed. Spring plowing is used only on heavy soils during a cold, wet spring to improve the rate of soil heating. After this, the area needs to be covered.
Sowing
The most common form of planting cucumbers is sowing in open ground. This method of planting can be done if the soil and conditions are suitable - if the temperature is too wet and the temperature is too low, the seeds will not germinate and will most likely rot. High temperatures and moderately moist soil will work great.
When to sow cucumbers?
The sowing time depends on the region of the country and is associated with air temperature and soil heating. The soil temperature should be at least 15 degrees Celsius at a depth of 5 centimeters. As for the optimal temperature for germination, it is 15-18 degrees.
In practice, this date falls in May. Usually sowing is carried out from May 10 to 15. In regions where temperatures are lower, cucumber seeds are sown on May 20.
You need to choose seeds with proven germination power and good quality. Before sowing, it is recommended to protect the seeds by treating them with a solution that protects against pathogens of fungal diseases (for example, a solution of potassium permanganate).
Sowing pattern and sowing
The number of seeds for sowing depends on the variety:
- Strongly growing ones sow 5-6 pieces per 1 m²;
- weakly growing - up to 10 pieces per 1 m².
Ordinary planting scheme:
- the optimal distance between plants in a row is 8-10 cm;
- the optimal distance between rows is 0.8-1.2 m.
Scheme of planting by nesting method of sowing in single rows:
- 2-3 seeds per nest;
- distance – 25-30 cm;
- sowing depth 2-3 cm.
You can also grow cucumbers from sprouted seeds. It is necessary to soak the seeds for 24 hours in warm water, then place them in sand or peat. This method is recommended mainly for small areas due to the high requirements for maintaining sufficient soil moisture before emergence. In the absence of sufficient moisture, the sprouts die.
Rotted manure is poured into the bottom of each hole and covered with soil. Sow cucumber seeds in this prepared soil. Then they are sprinkled with sifted soil and watered abundantly from a watering can with a strainer.
Planting and caring for seedlings
It is recommended to grow cucumber seedlings in small areas or in case of accelerating harvesting. Cucumbers do not like transplanting or picking.
- Sowing. Seeds are sown in the second half of April, 2 seeds per pot with a diameter of 6-8 cm. It is necessary to fill the containers up to ¾ with special soil or peat substrate.
- Germination. The daytime room temperature during seed germination should not be higher than 26 °C and lower than 24 °C. At night, cucumbers should be kept at 14-16 °C. After the emergence of seedlings, cucumbers are selected and weak plants are removed. Then the pots are filled with soil to the full capacity. This leads to better rooting of the plant.
- Hardening cucumbers. This method involves slowly, gradually lowering the temperature and reducing watering to increase the plant's tolerance to low temperatures and low humidity. A good cucumber seedling should have, in addition to cotyledons, 3-6 true leaves and a height of 15-25 cm.
- Transplanting. It is recommended to plant cucumber seedlings on cloudy days, after rain, and in warm weather. It is better to choose daytime hours. The distance between rows is the same as for sowing. Plants are planted in a row every 20 cm, sometimes every 10-15 cm. After planting, the seedlings are watered.
- Mulching. To accelerate the growth and development of cucumbers, you can use mulching. This treatment leads to faster harvesting. For mulching the following are used: perforated polyethylene films, polypropylene non-woven materials, organic mulches (straw). The black film absorbs light rays and prevents their penetration into the soil, which increases the soil temperature by 3-4 °C. A microclimate is created under the film cover. When choosing this growing method, the seeds are sown earlier - in early May.
Preparing the soil for cucumber seedlings
It is better to prepare the soil for growing any seedlings on your own and store it in the fall. Purchased substrates can bring unpleasant surprises in the form of fungal diseases.
Cucumbers require light, loose soil that is neutral or slightly acidic.
For cucumber seedlings, you need high quality soil mixed in equal proportions with humus. You can take well-rotted mullein or horse manure. Add a glass of wood ash to a bucket of this mixture.
To make the soil loose, mix sawdust or peat into it. Approximately one third of the total volume.
It is better to apply the mulching element before sowing seedlings. Coniferous sawdust is not suitable; it increases the acidity of the soil. It is important to let the sawdust rot before use. If this is not done, additional nitrogen fertilizers must be applied. The sphagnum peat substrate requires increased attention, as it dries out very quickly.
Types of greenhouses and their features
Various materials are used as the basis for constructing protected soil, so the cost of greenhouses, their heat-saving characteristics, and service life vary significantly. The frame of greenhouses can be wooden or metal, differ in height and ability to withstand the weight of the covering:
- Made from polycarbonate.
Modern, durable, fairly lightweight material allows you to set up greenhouses for early spring use. They retain heat well when heated. Such greenhouses are not warm enough for winter use.
- From glass.
This covering material is quite heavy, so the frame must be strong. Glass greenhouses, with proper design and heating, can be used all year round.
- From film.
They build both high greenhouses and low temporary protective structures. Lightweight material allows the use of a simple frame made of wood, polyethylene, plastic pipes and thick wire. Such greenhouses are intended for spring use after the ground has thawed, growing seedlings for open ground and obtaining earlier products.
Preparing seeds for sowing
The choice of seeds begins in the garden. The best representatives of the variety are allowed to over-ripen on the vines; they are removed only when the skin acquires an orange tint and cracks. Seeds are selected only from the front part of the fruit to prevent bitterness. They are ground and fermented for several days in a small amount of water, like tomatoes.
This is necessary in order to free them from liquid without injuring the seeds. All seeds that float should be thrown away.
Upon completion of fermentation, the seeds must be dried and sorted. If there is no shortage of planting material, then it is better to leave only large and symmetrical ones.
These seeds are soaked for 12 hours in a pink solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection, dried and placed in paper bags. Cucumber seeds are stored at room temperature in a dark place. They do not lose germination until 5-6 years.
An interesting property: the germination capacity of cucumber seeds increases during storage. Therefore, before sowing, it is better to age the seeds for two to three years.
Basic requirements for temperature, light, humidity
Cucumbers are delicate, vulnerable creatures. To the extent that climatic indicators are observed correctly - temperature, light and humidity - they grow together.
Temperature
Cucumber culture loves warmth. When it gets colder to +16-18 degrees, it slows down its growth. At a temperature of +10-12 degrees, it experiences stress, closes the flowers, and refuses to develop. Temperatures from 0 to +5 degrees and above +40 kill it. Optimal for culture – +23-30 degrees.
Lighting
A cucumber needs 12 hours of light a day. Longer lighting speeds up its life cycle. The fruiting period is shortened. Lack of light causes the seedlings to stretch out excessively. This weakens crops, provokes diseases, and reduces yields. The ovaries of adult plants, not receiving enough sunlight, turn yellow and fall off.
Humidity
Cucumber needs a lot of moisture, because it consists of 96% water. Most of its root system is located in the top fertile layer of soil, which easily dries out when exposed to the sun. Without enough water, the plant is deprived of adequate mineral nutrition. The fruits cannot gain the required volume and become lethargic and lifeless. They are bitter.
The bitter substances in cucumber are good for the intestines - they stimulate its work.
Excess moisture is also not good. Too damp soil does not “breathe” well and does not saturate the plant’s roots with oxygen. They suffocate and rot. Regular loosening of the soil helps to correct the situation.
- Optimal soil moisture is 80%.
- The recommended air humidity is 95%.
Pre-landing activities
It is necessary to sow cucumbers for seedlings a month before planting the plants in the ground. Typically this work begins in March.
Immediately before planting, the seeds are checked again for germination with salt water. They are dipped in a glass of water with a dissolved teaspoon of salt, shaken and left for 10-15 minutes. Everything that comes up is thrown away.
The remaining seeds are stimulated and hardened. First, they are warmed up near the battery for two days.
Then it is kept in a thermos with very hot water for two hours (the temperature should be such that it can barely be tolerated by a finger). And then, wrapped in cloth, they are sent to the bottom shelf of the refrigerator for twelve hours.
If the germination of seeds is in doubt, they can be treated with a growth stimulant. Careful owners treat them with potassium permanganate a second time.
After all procedures, the seeds are left to germinate between two layers of damp cloth in a cool place.
When the seed hatches and the root reaches half its length, you can begin sowing.
Deciding on the method of cultivation: seedlings or non-seedlings
When all the preliminary preparations are completed, you can start planting - all that remains is to decide: grow cucumbers through seedlings or simply plant seeds in the garden. In the middle zone, and even more so in the south, both options are possible. In the northern regions, it is better to prefer the seedling method.
From experience, it is quite possible to combine both methods: sow some of the seeds at home and grow them in pots on the window, and sow the other part directly in the garden bed. Then you will get two waves of cucumbers - those grown from seedlings will produce a harvest approximately 2 weeks earlier. In any case, we will consider both options - first with seedlings, and then without them.
How and where to plant cucumber seeds for seedlings
Sow the seeds in pots with soil at the rate of approximately 0.3-0.5 liters per seedling root. The capacity can be any:
- cardboard or plastic boxes - you must make several holes in them for the outflow of liquid;
- special peat cups, in which cucumbers are then planted directly into the ground, have only one drawback - they lose moisture very quickly;
- cellophane rolls fixed with a stapler or paper clip - to get to the root when planting, they are simply unrolled.
The pots are placed close to each other on a common tray for ease of care. Fill with prepared soil and sow two seeds in each so that the weaker shoot can be removed later. The sowing depth is no more than 3 centimeters.
If the seeds are planted in a common container, then the distance between them is kept two centimeters and three centimeters between the rows. With such a planting, you will have to pick up the seedlings later. Not everyone finds this procedure useful.
The container with seedlings is watered, covered with a damp cloth and put in a dark place until germination. Approximately 5-7 days. The optimal temperature for seedlings should be from 18 to 25 C. Overheating is no less dangerous than cold.
Mulch cucumber beds
It doesn’t matter whether you grow cucumbers spread out or on supports, the soil under them must be cleared of weeds. After all, the thicker the grass, the greater the chance that the cultivated plant will be left without food or become a victim of insect pests.
Therefore, cucumber plantings need to be regularly weeded and loosened so that the ground does not become crusty. And if you are at the dacha only on weekends, and you don’t have time for such careful care, make it simpler - mulch the ridges. For cucumbers, mulch made from peat, humus, grass clippings (without seeds), and straw is suitable. Geotextiles will also be a reliable and long-term solution.
- Geotextiles - what is it and where is it used?
Geotextiles have become a real salvation for summer residents. Thanks to this material, weeds disappear and productivity increases.
Crop care
It’s good if it is possible to allocate a separate temperature-controlled room for seedlings (ideally, a heated greenhouse).
Without such conditions, resourceful gardeners organize mini-greenhouses directly on the windowsills, separating boxes with seedlings from the room and window with cellophane screens. This allows you to create an increased level of humidity.
For the first 4-5 days, young seedlings should be kept at a temperature of about 20 C. Then it rises to 25 C. Drafts should be avoided throughout the entire growing period.
When the sprouts rise enough to be assessed, the weaker ones are carefully removed at the root with nail scissors.
“Alternative” ways of cultivating crops
Traditionally, cucumbers were grown horizontally outdoors. At the same time, only the growth of the main stem was limited, allowing the side vines to “spread” freely, since the most abundant fruiting in most bee-pollinated varieties is observed on shoots of the 3rd-5th orders. This method is still practiced in the mass commercial production of soil products, but for summer residents it is often unacceptable: in small plots it is simply not possible to allocate a significant area to one crop. Therefore, gardeners use various methods of “vertical” cultivation of cucumbers :
- Growing on a long trellis. Plant vines are launched along pre-arranged supports. The best option is a plastic mesh stretched along the bed in its center and secured to stakes, but you can simply string inclined cords for each plant. With this method, shoots and buds growing from the axils of the first 4-5 leaves are plucked out from strongly climbing varieties to allow the bush to gain green mass and accelerate the development of subsequent stems. Varieties with weak climbing are formed without pinching.
- Cultivation on a support in the form of a cone. The method is similar to the previous one, but sowing or planting seedlings is carried out in a ring groove located around a driven stake, to the top of which inclined cords or a mesh are attached.
- Growing in a barrel. A container with a volume of about 200 liters with holes in the bottom, prepared in the fall or early spring, is used. Drainage material (expanded clay, crushed stone or broken brick) is placed at the bottom. The barrel is filled to half the volume with compost, then a 30-centimeter layer of dense soil (preferably clay) and a 20-centimeter layer of humus are laid. The upper part of the container is filled with a mixture of compost and garden soil. A plastic bottle with the bottom cut off is dug in the center, neck down (a convenient device for watering and applying liquid fertilizers). Seeds or seedlings are placed around the bottle at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other. The growing cucumber vines are allowed to hang down freely, or cords are pulled, tying them to pegs located around the barrel.
- Instead of a barrel, sometimes they take a thick polypropylene bag, but do not fill it completely with soil, but add soil as the stems grow. In this case, the whips are often launched upward along cords tied to the top of a stake driven into the center of the bag.
The use of various types of supports allows you to obtain decent yields in small areas
“Vertical” cultivation of cucumbers has undeniable advantages. In all options, plants are better ventilated and heated more evenly by the sun, which reduces the likelihood of developing various bacterial and fungal diseases. It is easier to inspect the bushes, remove dried leaves and harvest without allowing the green plants to overgrow. The efforts of the gardener to apply root and foliar fertilizers and spraying with preparations that protect against diseases and pests are noticeably reduced. It is clear that for “vertical” plantings it is more difficult to organize shelter from the first autumn cold in cases where the summer resident really wants to prolong the fruiting of the bushes as much as possible, but the advantages of such methods (especially in the sense of easier care) still prevail over the disadvantages.
Watering and fertilizing
Watering should be done frequently - once every two days. Warm melt or settled water. This should be done in the morning, at the beginning of daylight. Cold and hard water is detrimental to seedlings.
Cucumber foliage loves bathing; moisture can be sprayed from above from a spray bottle.
A little trick: to prevent water from stagnating in the pots, they can be placed in a plastic mesh box, which in turn can be raised on a stand so that air circulates under the container with seedlings.
Fertilizing is carried out when the first pair of leaves appears.
Mineral fertilizers for cucumbers
- specialized ready-made mixtures for cucumbers;
- urea 20 g, potassium sulfate 20 g, superphosphate 50 g, diluted in ten liters of water.
Organic fertilizers:
- chicken droppings or mullein, diluted with warm water in a ratio of 1:10;
- a three-day infusion of onion peels, banana peels or eggshells, prepared from three parts water and one part crushed biological material;
- wood ash diluted in hot water in a ratio of 1:10;
- aged solution of 1 g of bread yeast in a liter of water.
Choosing a landing site
In order for the plant to take root well, you need to choose the right place for planting and prepare the soil.
When choosing a place on the site, preference should be given to well-lit places, protected from wind and draft . Cucumbers love loose soil, for which they dig up the soil in the fall, and in the spring they dig and loosen it again, apply fertilizers (per 1 m2 a bucket of humus, 15 g of ammonium nitrate, 40 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium sulfate).
Neighbors and predecessors
For cucumbers, the best neighbors in the garden will be:
- beans;
- carrot;
- beet;
- potato;
- celery and dill;
- spinach;
- mint and rosemary.
You should not plant cucumbers next to pumpkins or zucchini, as their vigorous greenery will take away the strength of neighboring plants.
Do not plant cucumbers after pumpkins and tomatoes, but peppers, garlic and onions are good predecessors.
Preparing the beds
The correct choice of beds depends on the composition of the soil, the presence of nearby groundwater and the desire to put a lot of effort into creating the beds.
Simple beds
For simple beds, the prepared soil is divided into strips about 1 meter with 50 cm between the beds. If the soil is heavy, add additional sand and humus, dig it up and loosen it.
For highly creeping varieties, the width of the bed can be reduced to 50 cm , and the passages made wider - this reduces the risk of damage to the vines.
Raised beds
On clay soils and in the presence of nearby groundwater, the beds are filled with a ridge about 30 cm and about half a meter wide. Such beds are easy to process, and they also protect plant roots from rotting.
Warm beds
To better warm the soil, warm beds are used, which come in two types:
- Deep - they dig a trench, lay down drainage and fill it with organic matter. Organic matter will warm the plants and nourish them.
- Tall - a box made of boards or other available materials is filled with organic matter. Such a bed will protect from groundwater.
Light mode
Cucumber is a short-day plant. For intensive development, seedlings need individual lighting:
- for them you need to choose the brightest place, but not in direct sunlight;
- daylight hours for cucumber seedlings should last ten hours;
- if there is not enough natural light, fluorescent lamps are installed above the drawers.
Light requirements when growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
The yield of vegetable crops, including cucumber, depends on the intensity of photosynthesis, especially in a greenhouse. The main influence on photosynthesis is the illumination of plants. To make the most optimal use of plant lighting, it is necessary to properly place the plants in it. To tie a cucumber, a trellis, that is, a wire, is pulled across the greenhouse. Distance. between two trellises - 100 cm. This trellis can be used not only for cucumbers, but also for tomatoes, peppers and eggplants.
Features of picking cucumber seedlings
Cucumbers have a very delicate root system. Unlike tomatoes, transplants do not benefit them. Broken hair roots are not restored, new ones take time to grow and the plant slows down in growth without receiving any benefits.
Supporters of the picking procedure begin this activity when the cotyledon pair of leaves of the cucumbers has fully opened and at least one true leaf appears.
Picking cucumber seedlings follows the general rules. The main thing is to soak the soil in the box well in advance and replant the roots, carefully prying them up with a spatula.
After transplanting, it is better to give the plants rest, leaving them for a day in a dark place and lowering the temperature to 18-20 degrees for three to four days. Then you can carry out a second feeding of the cucumbers. If the seedlings do not pick, then the second feeding is carried out two weeks after the first.
Climatic and soil requirements
Cucumbers are heat-loving plants. For proper growth and development, they need certain conditions; you need to know what temperature is optimal and dangerous for cucumbers, what soil is needed - watering, fertility and other parameters.
Optimal temperatures for growing cucumbers
Table. What should be the growing temperature in open and closed ground for a cucumber.
| Development phase | Air temperature °C | |
| nominal | optimal | |
| Seed germination | 15-18 | 20 |
| Plant growth | 20 | 25 |
| Flowers Blooming | 15 | 18 |
| Anthers begin to produce pollen | 17 | 19 |
Temperatures dangerous for cucumbers:
- at temperatures below 10 °C, the growth of young cucumbers slows down;
- prolonged temperatures of 4-6 °C can destroy plants;
- at 0 °C cucumbers freeze and die.
Proper watering of cucumbers, soil and air humidity
For proper development, a cucumber needs a lot of heat and high humidity. To understand how much to water cucumbers, you need to check the soil moisture.
Optimal humidity levels:
- soils – 65-85% of the lowest moisture capacity (MC);
- relative air humidity – 85-100%.
It is necessary to maintain sufficient moisture in the top layer of soil for seed germination and development of cotyledons and leaves. Otherwise, the sprouts may die. At the beginning of flowering, water requirements are relatively low. During flowering and before fruiting, the need for water increases again. During this period, plants make the highest demands on watering.
Cucumbers grow well in a quiet place protected from the wind, but not in the shade. The wind reduces the temperature and relative humidity of the air and can break or fray the shoots. It is worth using natural cover - a bed of corn.
Soil requirements
To grow cucumbers and get a good harvest, you need appropriate soils with the following properties:
- permeable,
- humus,
- quickly warmed up.
The plant grows well in the following soils:
- loess,
- black earth,
- sandy loam.
It is not recommended to cultivate cucumbers on the following soils:
- heavy,
- poorly heated,
- with high groundwater levels.
The best soil pH is 6.5-7. Interestingly, cucumbers grown in low light and cold air temperatures often produce more female flowers.
Predecessors
To get healthy plants and a good harvest, you need to know how to grow cucumbers in crop rotation. This is an important stage of agricultural technology, allowing you to avoid a number of problems. It is recommended not to grow cucumber and other pumpkin crops in one place more often than every 3-4 years; this can lead to so-called soil fatigue due to the accumulation of toxic compounds for this type of vegetable in the soil, pests, and pathogens.
The best predecessors for cucumbers:
- plants of the legume family (peas, beans, beans) - thanks to papillary bacteria, they help bind nitrogen to the soil in a form accessible to plants;
- plants of the cabbage family;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- potato
- cereals.
Cucumbers themselves are good precursors for growing other plants thanks to the measures taken to care for them during the growing season.
The best neighbors in the garden are dill, parsley, celery, corn, peas, beans, and sunflowers.
Power Requirements
Cucumbers have a moderate need for nutrients, but organic fertilizers are not enough; the nutritional deficiency is compensated for with mineral fertilizers.
One liter of soil should contain the following microelements:
| N (NO3 + NH4) | P | K | Mg | Ca |
| mg | ||||
| 55-80 | 60-80 | 175-250 | 60-80 | 1000-1500 |
The importance of individual nutrients in growing cucumbers
| Battery | Importance for growing cucumber | Consequences of shortage | Consequences of excess |
| Nitrogen (N) | affects the vegetative growth of cucumber |
|
|
| Phosphorus (P) | Affects the quality of fruits, is absorbed in the initial period of growth in small quantities due to the lower temperature. It is applied in full at the beginning of cultivation, before digging. |
| Inhibition of the development of bushes when soil is phosphated |
| Potassium (K) | It has a positive effect on the development and growth of roots, shoots, the formation of fruit buds, and their shape. The greatest demand occurs during the flowering period of the plant. |
| No negative effect found |
| Calcium (Ca) | Cucumber has little need for this element. It is enough to supply it with phosphorus fertilizers. Calcium is used when growing cucumbers to improve soil quality and reduce acidity. | – | – |
| Magnesium (Mg) | Positively affects the growth and development of plants. |
| – |
| Micronutrients – iron, manganese, boron, molybdenum | They are part of many enzymes and participate in plant biochemical reactions. |
| – |
Organic and mineral fertilizers
It is optimal to grow cucumbers in the first year after manure. The main organic fertilizer is the use of manure in the fall at a dose of 300-400 kg/area or well-distributed compost at a dose of 400-600 kg/area.
Doses of mineral fertilizers should be taken into account based on soil analysis, depending on:
- soil fertility;
- growing method.
Suitable doses of mineral fertilizers are on average:
| Fertilizer | Dose, g/are |
| N | 1000-1500 |
| P(P2O5) | 800-1000 |
| K (K20) | 1000 |
It is important that potash fertilizers contain sulfur (K2SO4) and not chlorine (KCl); cucumber is very sensitive to this element.
Nitrogen is added twice:
- half the dose is applied in the form of calcium nitrate 10-14 days before sowing or planting;
- the second half is applied in 1-2 doses.
Fertilizers should be mixed with a 20-centimeter layer of soil to protect it from excessive salinity, to which cucumbers are especially sensitive.
If the pH is too low, liming of the soil is carried out. A single dose should not exceed 15 kg/area in terms of CaO, on light soils - 10 kg/area. Liming is carried out before fruiting - the plant is sensitive to this operation. The application of manure should not be combined with the application of calcium.
Preparing seedlings for planting in open ground
In order for the plants to quickly adapt to outdoor conditions, they begin to harden off about ten days before planting. Then the last fertilizing is applied.
The container is taken out into the air. You can install it for a day under film in special, recessed greenhouses. The water temperature cannot be lowered throughout the growing season - these plants do not tolerate watering with cold water.
Seedlings are planted in open ground after they have formed four true leaves and stable warm weather has established.
Solving issues with the garden bed
In the middle zone, cucumbers grow better not just in level ground, but in beds. Their width is 90-100 cm, height 20-30 cm. An excellent solution is a warm bed, where under a layer of soil there is the decaying organic matter that these plants love so much; in such conditions they will be warm and comfortable.
There are also other placement options: cucumbers are grown on compost heaps, in barrels filled with branch cuttings, chopped straw, sawdust and other organic residues at the bottom, and with fertile soil at the top. They even cultivate it in large, durable plastic bags - well, this is more of an exotic thing, although such a place for cucumbers is very easy to set up: you don’t need to dig up the ground, the entire “structure” is on the surface.
Planting seedlings in the ground
It is reasonable to plan the placement of crops on the estate three to five years in advance so that the soil does not deplete and the vegetables do not get sick or degenerate.
The bed for cucumbers must be prepared in advance by adding rotted manure to the previous plantings.
The place for cucumber beds must be chosen in a well-lit area, sheltered from the wind. In warm climates, these may be furrows deepened to the point of a shovel. To grow cucumbers in the north of the country, you can organize warm beds in a wooden building.
Such beds are prepared in advance. First, a wooden box is knocked down and installed according to the size of the future bed. All season long, you need to put organic matter in the box: leftover food (except meat and fatty foods), grape trimmings, chopped branches of fruit trees, fallen leaves. Over the winter and summer, all this rots; in the fall, you need to cover the top with a layer of compost soil with a layer of 10 centimeters. In early spring, cover the bed with old film. Organic matter generates heat, and the bed warms up well. This makes it possible to plant cucumbers at an earlier date.
Regular planting begins when the ground temperature warms up by 12-14 degrees. Fertilizers (humus and mineral complex mixtures) are applied to the soil. After that, the pots with seedlings are well filled with water, and the plant is removed from them. The less the root system is damaged during replanting, the better.
The cucumber is buried at the cotyledon base and watered with warm water under the trunk. The watering area is sprinkled with a layer of loose compost on top. At first, it is advisable to shade the bed with transplanted seedlings with black non-woven material.
Two bushes are planted per square meter - these plants need a lot of space for weaving.
The best predecessors for cucumbers
In order for cucumbers to grow well and not get sick, you need to choose a place for them taking into account the rules of crop rotation:
- preceding plants should enrich the soil with elements desirable for them, and not make it too acidic;
- it is good if the root system of the preceding plants lies at a different depth than the cucumber one;
- Cucumbers and previous plants should not have common pests and diseases.
Tomatoes and white cabbage fit this description perfectly. Cucumbers will grow well in the garden after onions, garlic, legumes, carrots and beets.
Neighbors are also very important - ideally, these are corn or sunflowers, as a screen from cold winds. Also suitable: lettuce, beets, beans and savory.
Method of planting directly in open ground
Cucumbers begin to be sown directly into the ground in late May or early June. As the vines dry out, new seeds can be planted to harvest until the end of summer. For these purposes, it is better to make a bed in partial shade, even under trees, outside the crown.
Preparing the soil for sowing seeds is similar to cultivating beds for planting seedlings.
Proper planting of seeds
When planting seeds directly into the ground, it is not recommended to pre-germinate them. They are sown in wells that are heavily flooded with water to a depth of 1.5-2 centimeters, maintaining a distance between seeds of 20 centimeters and between rows of 60 centimeters.
After planting, the bed is covered with cellophane film to retain moisture and increased temperature. If it is 25 C or higher outside, then this is not necessary to do during the day.
Before the seeds germinate, make sure that the soil in the garden bed is not covered with a crust; it is regularly moistened and loosened. Loosening is carried out until 4-5 true leaves appear, until the plant enters the horizontal growth phase. Fertilizers for seeded cucumbers are applied by analogy with cucumber seedlings.
Finding a place to grow in the garden
Now you need to understand where on your site there is a suitable place for ground cucumbers.
Good neighbors for cucumbers are beans, peas and corn, and bad neighbors are cilantro, oregano, hyssop and basil. The best predecessors: legumes, cabbage, potatoes, onions, tomatoes.
A cucumber bed cannot be used for two years in a row, since many pathogens accumulate in the soil over the course of a year. So next year we will have to look for a new place.
When choosing a location, do not forget that cucumbers love warmth and protection from the winds. And although the requirements for the amount of light differ for different varieties, the bed must still be sufficiently illuminated.
Before planting seedlings or seeds, the area must be prepared. The soil should be light, well fertilized, non-acidic with a pH of 6.4-6.8. In the fall, the earth is dug up to the depth of a spade bayonet, without breaking the clods. Heavy clay soils are diluted with peat with the addition of lime (1 cup per bucket), old sawdust, and coarse sand. Then compost or manure is added (1-2 buckets/sq. m.). Acidic soils are deoxidized by adding lime, chalk, and ash. In the spring, while moisture remains in the soil, the soil is dug up again and the clods are broken up.
Cucumber care
Proper care allows you to extend the fruiting phase of cucumbers. First of all, productivity is lost due to lack of heat and moisture. If the summer is cool, then continue to cover the cucumbers with cellophane at night.
Sometimes you have to set up a tent made of non-woven material for the day to protect from the wind or too hot sun.
Watering and fertilizing
Watering cucumbers is done only with warm, settled water, preferably no later than 16-00 hours, so that the moisture on the leaves has time to dry before nightfall. This should be done at least once every two days. Frequent watering erodes the fertile layer, so periodically you need to add rotted manure or compost near the roots.
From the beginning of fruiting, liquid organomineral fertilizers can be added to the water.
Root feeding of cucumbers
With this type of feeding, nutrient mixtures are applied to the soil, at the root of the plant. They can be done once a week or ten days. The composition of the mixture is selected based on external signs of a lack of a particular substance:
- if the fruits have pointed, underdeveloped tips, then the plant needs nitrogen - 1 tablespoon of urea per 10 liters of water;
- expanding, short fruits indicate a lack of potassium - 2 cups of wood ash per bucket of water;
- You can prevent the leaves from drying out by feeding 4 tablespoons of superphosphate per 10 liters of water;
- to stimulate growth, feed with fermented infusion of nettles and other weeds - fill a large container with chopped grass, fill with water and leave under the lid for a week;
- Fertilizing with whey (1 liter per bucket of water) serves the same purpose.
Cucumbers are fed on damp ground early in the morning.
Foliar feeding
You can also feed cucumbers by spraying nutrients from a spray bottle onto the leaves. Foliar feeding is often used for preventive purposes. Along the way, such procedures help solve the problem of many pests and diseases.
It is better to spray early in the morning, choosing cloudy days so that the moisture has time to evaporate before bright sunlight hits the leaves. On such a day, you can stretch non-woven material over the treated bed.
- To increase the yield before flowering, cucumbers are sprayed with a solution of boric acid at the rate of 10 g per 10 liters;
- spraying a solution of 1 g of calcium nitrate in a liter of water strengthens the immunity of cucumbers;
- spraying with a weak solution of potassium permanganate saves you from pests such as spider mites and aphids;
- against late blight, it is useful to water the leaves from above with a daily infusion of wood ash (0.5 liters per 13 liters of hot water);
- Powdery mildew and root rot are prevented by spraying 30 drops of iodine and a liter of whey per 10 liters of water;
- for the same purposes, you can use bread (one loaf per 10 liters of water) or yeast (10 g per 10 liters of water) infusion with 10 drops of iodine;
- spraying with a urea solution at the rate of 15 grams per 10 liters of water enriches the plant with nitrogen and helps fight weevils and aphids.
The procedure is carried out in the same way as root feeding - once a week or a little less often. If there is a fear of burning the leaves, then initially you can take half the dosage of the nutrient mixture and increase it gradually.
Harvesting
Ideally, cucumbers should be removed at least 2, or even 3 times a week, without allowing them to overgrow. Infrequent harvesting inhibits the formation of new ovaries, reduces the yield, and harms the quality of the fruits themselves: they lose their taste, voids appear inside, and the skin becomes coarser. This is especially true for gherkin-type cucumbers; some of them are recommended to be collected daily or every other day.
When harvesting, the fruits are carefully broken off or cut off without tugging or turning over the vines, especially those lying on the ground.
Bush formation
Cucumbers are creeping or climbing plants. Removing excess vines, tying them, creating favorable conditions for fixing cucumber tendrils on vertical surfaces - all this also helps to increase fruiting time.
The method of forming a bush depends on the variety, method of cultivation and type of garter.
Under no circumstances should pinching or removing stepchildren be done by hand. For these purposes, it is necessary to use scissors or pruning shears, periodically dipping the blades into a solution of potassium permanganate.
Topping
Horizontal cultivation is the most common method of cultivating cucumbers in open ground. The correct strategy in this case would be to pinch out the central shoot, which has reached a length of one meter (some owners do this above the tenth leaf). The central lash stops developing. And the stepsons are actively growing, braiding the soil around the root. It is on them that the bulk of the ovaries are formed.
Someone recommends pinching the stepson lashes, leaving two or three leaves on them.
Pinching horizontally growing plants in this way is a classic technique, developed over decades of growing bee-pollinated varietal cucumbers in open ground.
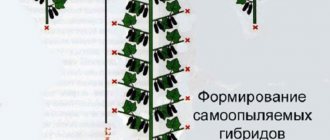
When starting to form a bush, you need to understand that hybrids develop differently than bee-pollinated varieties. You cannot pinch them using the same method.
For modern hybrids with a predominantly female type of flowering, the vertical method of growing while maintaining a long main shoot is more suitable.
Stepsoning
When growing vertically, the method of forming in one or two lashes is usually used.
When growing a cucumber bush in one vine, all the stepsons are removed as they grow, and the central vine is allowed to grow up the trellis, carefully twisting it onto the support counterclockwise. When it reaches the top of the support, it is allowed to parallel the ground or lowered to grow down another meter. Then they pinch.
Formation into two lashes occurs in a similar way, but in addition to the central shoot, another stepson closest to the root is left. The lashes grow in parallel.
Botanical description of cucumbers
Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) is an annual plant belonging to the Cucurbitaceae family.
| Botanical characteristics | Description | Photo |
| Root system | The shallow root system consists of a main root and lateral roots growing to a depth of 20-25 cm. | |
| Stem and shoots | The stem reaches a height of 2 meters, forms the main shoot, from which lateral shoots of the first order extend, and shorter shoots of the second row and subsequent rows grow from them. The stems are covered with numerous hairs. | |
| Sheet | Heart-shaped, green, five-lobed. | |
| Flowers | Flowers grow in the axils of the leaves. The plant is monoecious - there are male and female flowers on one bush. There are cucumber varieties that require and do not require insect pollination. | |
| Fetus | The fruit is a multi-seeded vegetable. The shape of the fruit is barrel-shaped, cylindrical or elongated. The skin color is usually dark green with a whitish or yellowish tint. First, the fruits are covered with numerous large or small, depending on the variety, pimples. On the tubercles there are hard spines - hairs, which then wear off and fall off. | |
| Seeds | The seeds are flat, smooth, ovoid, elongated, light cream color. 1 g contains 30-60 seeds. Germination lasts up to 10 years. |
It's worth knowing how cucumbers grow. The plant grows vertically until 4-6 leaves appear, then the plant climbs the supports with the help of tendrils growing from the leaf axils. It should be remembered: cucumber is a fragile, delicate plant.
The male flowers appear first, individually or collected in clusters of 5-7 pieces. Flowers grow on the main and side shoots. Then female flowers appear exclusively on the side shoots, usually solitary, less often 2-3 each. The female flowers are easy to recognize; a small cucumber can be seen at the base of the flower.
Cucumber is a plant pollinated by insects, primarily bees. There are parthenocarpic cucumber varieties that do not require pollination. In cases of bee-pollinated varieties, care should be taken to eliminate competition for the cucumber in the form of flowering weeds that distract the bees. Cucumber flowers bloom from early June until the end of fruiting. It is important to ensure that bees fly around the plant during the growing season. In greenhouses, for example, small evidence is placed for this purpose.
How to tie cucumbers
When gartering cucumbers, the main thing is not to damage them. You need to use wide nylon or cotton ribbons, do not overtighten the stem. If possible, only create conditions for natural weaving and support the plant.
The two main methods of growing bushes have already been described above and it has been noted that for open ground it is more convenient to form horizontal vines. This is due to the fact that plants lying on the ground are less affected by wind and bright sunlight. However, if you install an arc over a horizontal bush and send several shoots along it, this will allow the cucumber to branch over a larger area.
You can also install four supports above the furrow with cucumbers weaving along the ground and stretch several lines of wire or twine parallel to each other on them. The low-growing bush will climb along these supports.
Vertical cultivation is suitable for tall varieties or hybrids planted in an area sheltered from the wind. It should be noted that this method is more labor-intensive, and the plant grown in this way needs more attention.
Tying methods:
- the most successful one is weaving on a mesh - a support is installed near the bed, on which a nylon or plastic net is fixed, the central shoot of the plant is fixed vertically on it;
- weaving on a thin vertical support - a twine stretched vertically or a rod stuck into the ground is used as a support for the whip;
- weaving on a V-shaped support is suitable for growing a bush formed from two lashes;
- weaving on a pyramid - several bushes are planted from different sides on a pyramid from twine or wire stretched to a common rigid support.
Some varieties of cucumbers can be used to braid arbors and decorative hedges.
Growing and care
Proper agricultural technology is a necessary condition for obtaining stable, high yields.
Weeding
Weeds growing near a cucumber can lead to a decrease in its yield. They compete for water, light, and shade the plant. It is important to remove weeds from the field as early as possible. Proper spacing between plants will help with hand weeding. Weeding must be done extremely carefully, paying attention to the very fine root system of the cucumber. When removing weeds after they bloom, care should be taken to prevent weed seeds from spilling into the ground.
Fertilizer during the growing season
Usually 2-3 feedings are used.
Some of the most popular nitrogen fertilizers are:
- calcium nitrate,
- ammonium nitrate.
The first dose of fertilizer is applied before sowing. The second is when the first fruit buds begin to appear.
Foliar fertilizers are also used. To apply them, you need to choose the right weather, when the air temperature rises above 12 °C. The best time to apply is in the morning or evening. Recommended multicomponent fertilizers:
- Florovit,
- Bioflor,
- Calcinitis,
- Crystal.
Fertilizers should be used carefully according to the information provided by the manufacturer on the label.
Watering
Cucumbers need to be watered frequently, with small doses of water. Watering should be carried out every 4-5 days at 15-20 l/m² in the morning. Irrigation in the evening contributes to the attack of plants by various diseases.
Important! Cucumbers should be watered with warm water (never cold), preferably in the morning.
Pinching
Often, to increase yield, gardeners pinch cucumbers - the main shoot is cut off above 4-5 leaves. Then more side shoots with female flowers grow.
Garter
Cucumbers can be grown both ways - vertically or horizontally.
It is recommended to tie up cucumbers, as vines lying on the ground can rot and become painful. There are different methods and technologies for growing: on a trellis, on a grid, on supports, on trellises. Plants tied vertically take up less space and are healthier and easier to harvest. Plants love to climb onto the trellis. Most varieties of cucumbers reach several meters in length and can easily climb onto a support - they cling with their tendrils. Sometimes it’s worth helping them - tying them up. Cucumber stands must be strong enough to support the weight of the fruit.
Growing cucumbers on different types of supports has several advantages:
- Plants take up less space, which is especially important in greenhouses, on balconies, and in small areas.
- Easier to assemble. Cucumbers climbing along the ground form a tangled bunch of shoots. To collect the fruits, you need to bend down and be careful not to trample the shoots, flowers and fruits. When cucumbers grow on stands, harvesting is easier.
- Better illuminated by the sun. Cucumbers love sunny positions - then they bear the best harvest.
- The shoots do not touch wet soil, which makes them grow healthier.
- Less and easier watering. Cucumbers growing vertically can be watered at the roots without watering the leaves. Water consumption is lower.
- Less illness. Frequent watering promotes the occurrence of fungal diseases. If cucumbers are grown on supports or trellises, this is easier to avoid. Wet leaves dry out faster after rain.
- Decorative screens. On balconies and terraces, cucumbers can be considered as ornamental plants. They bloom with yellow flowers, have green, white and yellow fruits (depending on the variety), and make up decorative green walls on the balcony.
It's worth knowing! Some varieties of cucumbers are not vines; they are called bush cucumbers. They grow like bushes, for example, the Dar bush cucumber.
Collection and storage
The cucumber harvest usually lasts from the second decade of July until the end of August - beginning of September. Cucumber fruits are harvested as they ripen. Cucumbers intended for canning should be collected daily. Harvesting should be done in the morning, after dew has appeared, or in the evening. Harvest carefully, trying not to damage the vegetables. Damaged vegetables should be eaten quickly; they cannot be stored; they can be a source of pathogens. After harvesting for sale and storage, the cucumbers are sorted and placed in boxes. Rotten, moldy, wilted fruits are thrown away.
Storage is carried out under appropriate conditions:
- the optimal storage temperature for cucumbers is 1-2 °C;
- relative air humidity – 80-90%.
In such conditions, cucumbers can be stored for 10-20 days. Once removed from the refrigerator, cucumbers should be consumed within 48 hours.
Cucumbers can be stored in cellars and dugouts for about 7 days.
Techniques for increasing cucumber yield
With timely watering and fertilization, proper garter, the following methods can also increase the number of fruits:
- when cucumbers begin to grow, the first four ovaries must be removed so that the plant gains strength before it begins to spend it on ripening the crop;
- when a large number of “male” flowers form, cucumbers need to be stressed - reduce feeding, lower the temperature or skip watering;
- spraying a weak honey solution (1 teaspoon per liter of water) on the foliage will attract insects for better pollination and enrich the plants with microelements;
- when growing hybrids, it is worth planting several bushes of a bee-pollinated variety next to them;
- Ripe cucumbers must be collected daily, carefully cutting them with disinfected scissors.
Questions and answers
Even experienced gardeners periodically have problems growing cucumbers, and they cannot get a decent harvest.
There are a lot of barren flowers on the bushes
Barren flowers are male flowers; they do not produce an ovary, but contain pollen. If there are too many of them, then this indicates:
- low seed quality;
- violation of agricultural technology and conditions for pollination;
- dense plantings;
- excess nitrogen.
Bitter cucumbers
Cucurbitacin is a compound that, when its content increases, makes cucumbers bitter. Its amount increases when the plant is stressed . Problems arise when:
- watering with cold water;
- sudden change in temperature;
- sun deficiency;
- whip damage;
- using horse manure, which saturates the soil with ammonia.
Cucumbers are empty inside
Fruits with a void inside appear deformed, slightly concave and wrinkled. The core is yellowed, dried out or is not there at all. Causes:
- temperature changes;
- uneven watering;
- excess nitrogen;
- varietal characteristics;
- consequences of diseases.
Cucumbers grow with crochet
Hooked fruits appear as a result of a lack of potassium, insufficient lighting of the ovaries and a temperature drop below +20°C . Use potassium fertilizers and do not rush to plant vegetables in the ground if there is a danger of a sharp cold snap.
Leaves wither and turn yellow
Healthy leaves wither during prolonged drought; in this case, the bushes are watered abundantly. If this does not help, then the reasons are different:
- lack of light, thick lashes;
- leaves are burned from direct sun;
- damage to roots during loosening;
- little food;
- plant infection by disease.
Diseases and pests of cucumbers
Cucumbers are quite vulnerable to common garden pests and diseases such as powdery mildew, late blight, and root rot.
Diseases can be prevented by following the rules of garden hygiene:
- timely and high-quality harvesting of crops and plant residues;
- following the rules of crop rotation;
- disinfection of seeds and tools;
- purchasing only high-quality seed material.
Prevention of diseases and pest attacks is also achieved by applying appropriate foliar fertilizers (as described in detail above).
Several recipes for chemically harmless pest repellents that you can use at the first sign of aphids or mites:
- a glass of tobacco, a glass of wood ash, a tablespoon of laundry soap shavings, pour 10 liters of boiling water;
- pour half a bucket of chopped onion peels, one glass of wood ash with boiling water, add a tablespoon of laundry soap shavings, then proceed in a similar way;
- 10 g of dry red pepper, 100 g of tobacco, 2 tablespoons of soap shavings per 10 liters of boiling water;
The above products are infused for a day, filtered, and then the leaves are sprayed from bottom to top. Then they must loosen the ground to destroy fallen pests.
Compared to ready-made insecticides, these drugs are less effective, but do not cause harm. It is worth resorting to them several times a season, as preventive measures, so that you do not have to use the “heavy artillery” of industrial chemistry later.
Varieties and hybrids of cucumbers
When choosing varieties for planting, you need to focus primarily on local varieties, or those bred in similar climatic conditions.
Giving preference to a hybrid or choosing varietal cucumbers is the individual choice of the gardener. With the available variety (more than 500 varieties and hybrids), you can try the best of the proposed options on your site.
Hybrids
They are usually devoid of bitterness. They have higher immunity. Every year more and more hybrid options appear for different purposes.
The only drawback of hybrid cucumbers is that you cannot collect seeds from them. To resume growing cucumbers with remarkable characteristics next year, planting material will need to be purchased again.
Some of the most popular modern hybrids:
Herman F1 is a parthenocarpic, high-yielding, early-ripening hybrid, resistant to diseases, fruits up to 10 centimeters long, pimpled without bitterness.
Miranda F1 is a universal ultra-early hybrid with high immunity, fruits up to 11 centimeters long, without bitterness.
Chinese cucumber is a tall hybrid, vertical cultivation is recommended, the fruits reach 60-70 centimeters in length, have exceptional taste, and are devoid of bitterness.
Masha F1 is a parthenocarpic hybrid, early ripening, small-pimpled, fruits up to 11 centimeters, have a sweetish taste, lack bitterness, good for canning and fresh consumption.
Friendly family F1 is a parthenocarpic hybrid, characterized by high yield; short fruits with longitudinal stripes are well suited for preservation, without bitterness.
Briefly about reproduction
Cucumbers are an annual crop and therefore reproduce by seeds. They can be collected from varietal plants, but it is useless to do this from hybrids - maternal qualities may not be passed on to subsequent generations.
Collect seeds from the testes. These are large fruits, 40-50 days old, with a smooth surface, sometimes it can be covered with a network of tiny cracks. In unfavorable weather and climatic conditions, the testes are harvested at the age of 30-35 days, they ripen indoors.
It is better to take seeds from the middle part of the cucumber: here they are stronger, larger, and therefore the plants will be strong.