To grow cucumbers, many owners of suburban areas install protected ground structures: greenhouses and greenhouses. The result of cultivating vegetable crops in such structures is almost always high yields of healthy fruits. However, to achieve results it is necessary to follow a number of agrotechnical rules. Planting cucumbers in a greenhouse should also be carried out using a certain technology.
Necessary equipment
One of the important issues for a gardener is the choice of greenhouse and its location. The greenhouse is chosen so that it is spacious in size and provides vegetables for the whole family. The optimal ratio of volume to area is 2:1. The height in the greenhouse should be on average 2 meters (more towards the center, less at the sides). The average height of the ridge is 2.5 meters.
A lower height is undesirable, since cucumber vines grow to 3-3.5 meters during the season. And it is not advisable to do it higher, since the air will warm up more slowly. The greenhouse must have a ventilation system. Ideally, it would be automatic.
The greenhouse is placed on a flat surface or with a slight slope to the south. The direction of the greenhouse is the same: from north to south, for better lighting of the plants. A container is placed in the greenhouse to water the cucumbers only with warm water.
When to sow cucumber seeds for greenhouse seedlings
When determining the timing, it should be taken into account that seedlings are transferred into closed ground approximately 3-4 weeks after sowing the seeds (when 4-5 true leaves grow). By this time, the greenhouse should have suitable conditions for young plants.
The climate is different in different regions. Therefore, if we are talking about structures without additional heating, you should focus on approximately the following dates for planting seeds in the spring:
- southern Russia: early March;
- northern Russian Federation, Siberia: mid-April;
- center of Russia: early April.
Choosing a variety for indoor soil
Self-pollinating or parthenocapic cucumber varieties are suitable for indoor soil. Both do not need bees. Plants set fruit in closed ground conditions without external intervention. But the process of ovary formation itself occurs in different ways.
Self-pollinating cucumbers are those in which pollination occurs as a result of pollen being transferred from the stamens to the pistil within one flower. In this case, the plant does not have female and male flowers, and accordingly, there are no barren flowers.
Parthenocapic is translated as “virgin”, that is, the cucumber sets without pollination. In adulthood, parthenocapic fruits are always distinguished by their appearance. They have virtually no seeds. And if they exist, they are very tiny, in their infancy.
Among self-pollinating varieties there are varieties and hybrids. The variety differs from a hybrid in that it is a fairly stable form that transmits its basic qualities through the seeds. If you buy a variety of cucumber once, you can plant it year after year, collecting the seeds yourself. Its varietal characteristics will be preserved.
Currently, hybrids are more common; they are designated in their names as F1. Such cucumbers do not transmit their qualities through seeds, so gardeners have to buy them every year. If this is not done, then splitting occurs in the second generation, and it is not known exactly what characteristics will appear as a result.
Let's consider several popular varieties and hybrids for greenhouses and greenhouses:
- Adam F1. Dutch self-pollinating high-yielding hybrid. Valued for setting fruit very early. In just a month and a half you can start harvesting. The second undoubted advantage is the extended fruiting period. Cucumbers are arranged 5-7 together. With insufficient care, 2-4 fruits are tied in the knot. Cucumbers grow not only beautiful in appearance: dark, small, with small thorns. They are delicious both prepared and fresh.
- Zyatek F1. A very popular parthenocapic hybrid. It is loved for its early ripening, the first fruits appear already on the 40th day. The bouquet arrangement of the ovaries is also appreciated. The cucumbers of this hybrid are gherkin-type, cylindrical in shape. They do not grow large; growth stops at 14-16 cm. The fruits of this variety are tasty and productive.
- F1 is the envy of everyone. Despite the fact that this hybrid appeared relatively recently, it has already become popular among gardeners due to its super-yielding and bunched arrangement of fruits. The variety's lashes are powerful. They develop right up to frost and produce an excellent harvest on the side shoots. The thin skin makes it possible to use these fruits both fresh and pickled.
- Well-fed dad F1. One of the salad varieties for indoor soil. Long, smooth, cylindrical fruits are suitable for salad and fresh consumption. This variety is not suitable for whole-fruit canning, but it is just right for preparing lecho and other preparations where chopped fruits are needed. Just like the previous ones, this variety has bunched ovaries, is early ripening and disease resistant.
- Ecole F1. One of the new, very successful parthenocapic hybrids. This cucumber is suitable for those who can preserve pickles (greens 3-6 cm). That is why it can be picked within 35-38 days after the first shoots appear. Ecole's greens are smooth, cylindrical, and grow in bunches. They are collected every day so that they do not overgrow.
- Chinese cold-resistant F1. From the popular series of long and sweet cucumbers. It is suitable for growing in greenhouses, where it is easier to tie it up. Its lashes are powerful and grow quickly. The fruits themselves reach half a meter in length. Smooth and tasty cucumbers can be used in salads or prepared into slices for the winter.
The labels on the bags of cucumbers “Parthenocapic (self-pollinating)” are incorrect. A variety or hybrid can be one or the other. Most often we are talking about parthenocapics.
How to properly plant cucumbers in a greenhouse with seeds
Planting cucumbers in a greenhouse with seeds is not much different from planting cucumber seeds in polycarbonate greenhouses. In this case, the plants will grow under film covers, but all care for them will be the same as for cucumbers growing in greenhouse conditions.
Important! You cannot grow cucumbers in the same place every year. Since pests and diseases remain in the beds and the harvest falls.
Maintain crop rotation in your garden. In addition, experienced gardeners recommend that beginners carefully select seed material at garden markets or specialty stores. The choice of seeds has been huge lately. However, not all varieties and hybrids are suitable for a certain area. In the northern regions, it is desirable to grow early ripening varieties of cucumbers. They can produce a harvest already on the 40th day after germination.
On average, cucumbers begin to bear fruit on the 50-55th day after full germination. Add to this number of days another week for germination and as a result we get the approximate date when the plants will delight with their first crispy and tasty fruits.
3.7 3 votes
Article rating
Soil preparation
The preparatory planting process begins with the soil. If you grow cucumbers through seedlings, then first you need to prepare or buy a special mixture in which you will plant the seeds.
Cucumbers love loose and fertile soil, which means that they need the same soil for sowing seeds. The soil should not only be light, but also moisture-retaining, which is very important for cucumbers who like to “drink.” That is why it is better to exclude peat from the composition or use it in small quantities. Store-bought soil, which most often contains a lot of peat, begins to dry out quickly at home.
Watch the acidity, it is peat that has an acidic reaction. In order for cucumbers to develop normally, the pH level should be approximately 6.5-7.
Composition of the substrate for cucumber seedlings:
- turf soil - 3 parts;
- humus or fully matured compost - 2 parts;
- sand - 1 part.
This mixture must be sifted so that there are no large parts. The mixture can be heated in the oven for 10-20 minutes or frozen. It is best to prepare the mixture in advance, in the fall, and put it in a bag. Place the bag on the balcony to kill pathogens. Before sowing, add a liter of vermiculite to the mixture bucket for looseness, a glass of ash and 2 tablespoons of superphosphate.
How to distinguish seedlings of cucumbers from zucchini?
There are several ways to find out which vegetable is planted in the garden - zucchini or cucumber:
- if the plant has produced only cotyledon leaves, then the zucchini leaves are large, and the cucumber leaves are smaller
- The true leaves of zucchini are rounded, while those of cucumbers have a sharp tip.
- rub the leaf of the plant: cucumber leaves are odorless, but zucchini leaves have a specific aroma that is difficult to confuse with anything else
Cucumber seedlings
Properly preparing seeds for sowing
Previously, before germination, gardeners performed a procedure such as heating the seeds. This is long-term heating of dry seeds near heating devices at a temperature of 30-35 degrees.
Such events have a positive effect on increasing the formation of female flowers in all pumpkin plants.
When preparing self-pollinating and parthenocapic hybrids for sowing, the seeds do not need to be heated, since they do not have the problem of forming barren flowers.
Nowadays, seeds that have already been treated with thiram are often sold. Information is contained on the packaging. The seeds are colored poisonous green as a warning about the toxicity of the applied substance. Thiram is a fungicide that is used against a complex of diseases. Such seeds are not soaked or germinated.
If you have ordinary seeds, then they need to be treated with some kind of fungicide or a saturated solution of potassium permanganate. When there are many varieties, you need to put them in gauze bags and place them in the prepared solution for 15-20 minutes.
After this, you need to wash the seeds and start germination. Germination does not affect the yield, but avoids planting empty seeds.
Before germination, the seeds should be placed in a small amount of water for several hours or overnight to swell. The water should cover the seeds a little so that they do not “suffocate”. There is no need to harden cucumbers because they do not have the cold tolerance gene.
Advantages of the seedling method:
- allows you to get results earlier than when sowing seeds;
- the plant will grow and become stronger in comfortable conditions;
- sorting is possible: you can see which plants develop better and which worse;
- some seeds do not germinate immediately or freeze during seedling growth.
Plants of the same height will be easier to care for. The rest can be planted in a corner so that plants of the same type grow in one place. Such measures will allow you to get an early and healthy harvest.
Seed processing and sowing
Some seeds require treatment before planting. This applies to those grains that you bought secondhand or prepared yourself from any fruit. Before planting, it is necessary to complete several stages of processing, namely:
- calibration;
- disinfection;
- hardening;
- warming up;
- bubbling (if the seeds are more than six years old);
- germination (if necessary).
For “homemade” seeds, these are necessary procedures. This way you can get rid of empty and diseased seeds. You will carry out the disinfection process, which in the future will save you from a number of problems with fungal or infectious diseases of the bushes, and you will also be able to increase the quality and quantity of the harvest.
If you purchased seeds in a store, read the instructions. As a rule, the manufacturer carries out all the necessary manipulations before the grains are sent for sale. Therefore, you will not be required to waste time on processing.
Preparing seeds for sowing is a responsible task. The quality of your future harvest will depend on how correctly you plant the seeds. Every step and every detail must be followed. One small grain that has become infected can destroy all the cucumbers growing nearby and leave you without juicy and ripe vegetables.
Growing seedlings
In order for growing seedlings to become an advantage, you need to try to do it correctly. Cucumbers ready for planting should not be overgrown, strong, and without signs of disease. The ideal option is 3-4 sheets.
For sowing, take separate cups at once so that the root system is formed correctly. If this is not possible, then seeds are planted in trays at a distance of 5-10 cm from each other. Seeds must be properly prepared and germinated. The sprouts are small, so-called “beaks”, so as not to break them.
Before planting, the hole in which the seed is placed is spilled with hot water and a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Sprinkle the cucumber seed on top with loose soil in a 2 cm layer.
If possible, cover the container with cucumbers with a damp rag or plastic bag for 1-3 days until seedlings appear.
Planting seeds
Planting seeds is not much different from the method of planting with seedlings. The only difference is that germination is lower than that of an already germinated seedling. For the correct and high percentage of germination, buy branded seeds that have been tested by you.
Choice
On the shelves you can find about 80 different varieties that are suitable for planting in open ground and about 60 for greenhouse cultivation. Hybrids (marked with the name F1) have proven themselves best for greenhouses.
Storage
To store seeds you need to choose a warm and dry place . Then the seeds will dry thoroughly and grow well. Seeds 2-3 years old perform better.
Preparation
Before sowing, seeds must be selected and only the best can be planted in the ground.
First of all, we remove the peeling, puny and unsuitable in appearance.
Next, we check in a salt solution (3 g of salt per 100 g of plain water). Throw the seeds into the solution, leave for 5-10 minutes, stirring gently. Those seeds that float to the surface are not suitable and we remove them. We wash the rest in plain water.
Hardening
Let's consider the process of seed hardening.
What does this give?
Hardening off seeds results in faster growth at lower temperatures.
How does this happen?
First way
- Soak the seeds in warm water.
- Place in the refrigerator for 10-12 hours at a temperature of 0 minus 2 degrees.
- We move the seeds into a warm place for 10 hours at a temperature of +20 degrees.
- We perform the process twice to enhance the effect.
Second way
We germinate the seeds as usual.
Place the sprouted seeds in the refrigerator on the middle shelf (24 hours).
We plant the seeds in the ground cold, only from the refrigerator.
Preparing soil in a greenhouse
Cucumbers love loose and fertile soil. This is what fertile loams are. Clay is too heavy for them and lacks breathability. The sand is loose, but it does not hold water, and without it, cucumbers will not grow. As a last resort, sandy loam is suitable, to which you can add a little heavy clay soil to balance the composition.
In a greenhouse, you need to prepare the soil in advance. You can plant green manure immediately after harvesting vegetables, and dig up with them before frost. The best option would be mustard greens. It will disinfect the soil and enrich it with valuable microelements.
With the onset of winter, you need to throw snow into the greenhouse so that in the spring moisture saturates the soil. After all the snow has melted, the soil in the greenhouse is dug up. The holes must be prepared in advance before planting seedlings. The ideal option is warm ridges, because cucumber is a very heat-loving crop.
They can be made both in autumn and spring. If this is not possible, then humus or compost mixed with ash and double superphosphate is placed in the prepared furrows or holes: half a glass of superphosphate and a liter of ash per bucket. Then sprinkle with 10-20 cm of loose soil.
If you change the soil in the greenhouse in the fall or spring, then you should take into account that you need to take the soil from those areas where the day before you grew vegetables that do not have common diseases with cucumbers: cabbage, onions, carrots, peppers or potatoes.
What temperature can cucumber seedlings withstand?
- Cucumber seed germinates at a temperature of 10-12ͦ C. For normal growth and development of leaves, it is necessary to maintain a temperature of 15-16 degrees.
- Cucumber seedlings require a special temperature regime. During the day, the normal temperature for sprouts is from 25 to 30 ͦ C, at night the temperature is slightly lower and normally it should be from 15 to 18 ͦ C.
- If the temperature drops (for example, beyond +10 degrees during germination), then the seedlings stop growing and begin to turn yellow and rot.
| Temperature, °C | ||||
| air | soil | Additional illumination, hour | ||
| Growth phase | daytime (period when supplementary lighting is turned on) | night (additional illumination is turned off) | ||
| Sowing - shoots | 27 | 27 | 24-25 | — |
| The first 3 days after germination | 24 | 24 | 23-24 | 24 |
| Next 2 days | 23 | 22 | 23 | 20 |
| Subsequent period until the 3rd leaf phase* | 21-22 | 20-21 | 22 | 18* |
| The day before planting in the greenhouse | 19-20 | 17-18 | 22 | -* |
| The first 2 days after disembarkation | 21 | 21 | 21 | — |
| Subsequent period | 21 | 19 | 20-21 | — |
Transplanting
Seedlings are planted in the ground when the soil temperature reaches 15°C. This is a very important point. The air temperature in the greenhouse is important, but of secondary importance. Although any shelter for growing cucumbers should be equipped with a thermometer.
Cucumbers love warmth, and soil temperature is especially important to them. For objectivity, you need to take measurements in the morning. Experienced gardeners cover the place where the temperature will be measured with a board or plywood so that the place is not heated by the sun.
A thermometer is placed under the shelter to a depth of approximately 20 cm and left for 15-30 minutes. This way you get a fairly objective result. In order for the soil to heat up faster, it can be covered with plastic film, and also a warm ridge can be made.
But it starts to work only at a certain temperature, so you first need to spill it with hot water and then cover it with film. To activate biofuel on cold days, you will have to do this several times before the start of the season.
We plant seedlings like this. First, we make a hole in the hole already filled with fertilizers the size of the cucumber’s root system. We leave the distance between future plants about 40-60 cm. Then you need to pour warm water with the addition of a weak solution of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
The seedlings must be buried to the cotyledon leaves or the first true one. The soil around is compacted a little, and the surrounding area can be sprinkled with dry soil.
You can additionally mulch the beds with cucumbers to retain heat in the soil.
Problems and diseases
When growing cucumbers, gardeners often encounter various unpleasant phenomena. Among them are such as falling leaves, yellowing of the ovary, cessation of growth.
These and other phenomena are caused by several reasons.
- The bushes wither during the daytime, the reason for this is insufficient air humidity. Watering or installing any open container of water is necessary.
- Cucumbers have a curved shape - the soil is dry, the reason for this is elevated temperature, poor moisture and lack of nutrition.
- Young seedlings have whitened leaves - this is a consequence of low soil temperature or disease of the sprouts. The soil must be watered with a solution of potassium permanganate and the temperature increased. In another case, the diseased seedling is urgently removed so that the disease is not transmitted to neighboring healthy bushes.
- The absence of an ovary can be observed for many reasons, for example, the absence of male flowers, few pollinated flowers, poor soil nutrition. To get rid of this problem, the soil must be saturated with vitamins and fed with urea or mullein. If there are ripe cucumbers on the bushes, they must be collected daily. The plant is in no hurry to set new fruits; it gives nutrients to already prepared vegetables.
- To speed up the growth of cucumbers, it is recommended to create a “poultice”, pour water on the polycarbonate in sunny weather and close all the windows of the greenhouse. Water the plant and soil thoroughly and leave everything for one hour. Then ventilate the room.
- If the cucumber is bitter, then the growing conditions have been violated or the fruits on the bush have been overexposed.
- The appearance of aphids is observed in places where there is a large growth of weeds. To combat this parasite, make a solution of hot pepper and treat the plant.
- The formation of powdery mildew is indicated by the appearance of oily spots on the foliage. To cure cucumbers from this disease, common mullein and urea are used. The entire plant is sprayed.
A careful approach to each plant is required daily. Only in this case can the problem be detected in time. Treatment should begin at the first signs of damage, so as not to lose the vegetable harvest.
Optimal conditions for the growth of cucumbers
There is a reason why cucumbers and tomatoes are planted separately. Although some manage to get good results by growing them together. Cucumbers need special conditions to grow and have a good harvest: light, heat, humidity, watering and others. The growing conditions for cucumbers are almost the same as for all pumpkins.
Watering
Cucumber is a very responsive crop to watering. It must be regular, without this the harvest will not be good. In dry years, it may not exist at all, since the water is instantly absorbed by the soil. Watering in a greenhouse or hotbed should be done frequently; the leaves should not be allowed to wilt.
This feature is associated with the structure of the cucumber root system. It is located close to the soil surface, so the plant does not have the opportunity to take water from the depths, as, for example, tomatoes do. The health of the plant depends on how often you water it. In hot weather, when fruits are forming, this should be done every day.
Cucumbers are recommended to be irrigated using the sprinkling method. With this method, water is poured out in small drops, partially evaporating. This increases the air humidity in the greenhouse, which is very important for cucumbers. The soil is gradually saturated with water, which allows the roots to better absorb moisture.
Water consumption per 1 m2 is approximately 15-25 liters per day or every other day, depending on the weather. When fruits form, water consumption increases and amounts to 20-30 liters.
Do not water cucumbers with cold water. They used to say that this makes the fruits bitter. Now the fruits are genetically sweet, but cold water is not advisable for watering because it increases the likelihood of plant disease.
Feeding
We must not forget about fertilizing. Cucumbers grow rapidly, and modern hybrids produce very high yields. In order for the plant to be able to “feed” them, it is necessary to apply fertilizer 1-2 times a month, literally from the first days.
Fertilizers are organic and mineral. Organic are natural fertilizers. These include manure, green fertilizer from grass, ash, and chicken droppings. When growing seedlings, only ash is used from the listed fertilizers when preparing the substrate for sowing seeds.
Before planting in the ground, seedlings are fed 1-2 times with mineral fertilizers. Preference is given to nitrogen or complex ones with a predominance of nitrogen, because first the plant must increase its green mass and become stronger.
After planting in the ground, cucumbers are not fed for 2 weeks until the plant has completely taken root. In addition, there is usually enough nutrition in the holes. After this, you need to start “feeding” green fertilizer, a solution of mullein, chicken droppings and ash. From the beginning of flowering, potassium fertilizers are added.
Light mode
The time of fruiting, as well as the yield of cucumbers, depends on the intensity of light and the length of daylight hours. The second has a greater effect on plant growth. Cucumbers are short-day plants, so they need a 10-12 hour day to fully develop. During the period of growing seedlings, this is no less important. If there is not enough light, then conditions of 10-hour daylight hours are created using artificial lighting.
Temperature
Cucumber is a very heat-loving crop. If it's cold outside, you can't expect good harvests. In addition, the plants will be weakened, which will affect the increase in morbidity. The average temperature in the greenhouse should be maintained at 17°C. But for the first time after sowing, the temperature should be 25-28 degrees.
That's why it's better to grow cucumbers at home first. Severe cold spells have a negative impact on growth. But too high temperatures are also harmful to cucumbers.
If on hot days the temperature in the greenhouse is above 30C, then you need to ventilate and spray the plant to reduce the temperature.
Humidity
Cucumber has an increased need for air humidity. For cucumbers, this norm is 85-95%. If you compare it with peppers, the difference is very big. Peppers need a moisture content of 60-65%. At low humidity, the process of pollination and fruit set is significantly reduced.
Of the greenhouse crops, cucumber is perhaps the most moisture-demanding crop.
Ventilation
At first, when the cucumber seedlings are still small, you need to ventilate the rooms where they grow very carefully. Cucumbers do not tolerate drafts at all. And in the greenhouse it is necessary to ventilate, especially when the thermometer rises above 30C.
The windows are opened only on one side to avoid drafts.
Bush formation
In order for cucumbers to produce a bountiful harvest and bear fruit for a long time, the plant must be shaped correctly. There are a lot of opinions on this matter, but the overwhelming majority believes that formation is necessary.
Topping
Pinch the cucumber vines as follows:
- the first 40-50 cm - the shoots “blind” completely;
- pinch the next 40-50 cm above the first leaf;
- the next 40-50 cm above the second;
- then 40-50 cm above the third;
- and so on.
Some gardeners cut off the plants' tendrils to save energy. For the same purpose, not all ovaries are left; some are removed. If it is noticed that when fruits are formed in bunches, some do not have enough nutrition and they begin to dry out, then one fruit at a time is left in the axils. In this case, watering and fertilizing are increased.
It turns out like a “herringbone” in reverse. At the end of growth, under the roof, the plants set fruits freely. Some people pinch the whip under the roof so that it does not waste energy on growth. All potential is spent on the formation of fruits.
It has been noticed that without pinching, the yield is significantly reduced.
Stepsoning
Stepsons on cucumbers are only appropriate when the stepsons are removed at the beginning of growth, half a meter above the soil surface. There is no need to do this higher, since many large ovaries are located on the side shoots. The meaning of pinching is that the plant’s forces are released for further growth and development.
For this procedure, carefully bend the leaf and remove the shoot with a cloth or knives. Subsequently, the leaves at the bottom of the vine dry out and the main stem becomes bare. There are many root primordia on it. If you lay the stem in a ring, roots will begin to grow very quickly in this place and the cucumber will have additional nutrition.
Tying up
Cucumbers are tied up in a greenhouse for the following reasons:
- plants in this position are better illuminated by the sun;
- the lashes are ventilated and the cucumbers get sick less;
- they are easier to care for;
- plants do not intertwine with each other;
- Almost 100% of flowers and ovaries are preserved;
- watering and loosening are simplified;
- good visibility when picking fruit.
You need to start tying up the plant at one month of age, when its height reaches 30-40 cm. There are several types of materials from which ropes for cucumbers are made. Everyone chooses the best option for themselves. For some it is rags, for others it is nylon. Some people opt for synthetic twines, which are sold in hardware stores.
The length of one twine is 2-2.5 meters. One end is attached to the ceiling, and the other should freely go down. The lower end is carefully attached between the lower leaves. As the lash grows, it wraps clockwise around the twine.
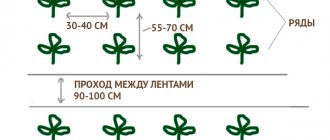
Schemes for planting greenhouse cucumbers in narrow beds
Cucumbers are demanding when it comes to lighting and nutrition. Therefore, although all greenhouse owners want to plant as many plants as possible, plantings should not be too thick. In addition, if the bushes grow too closely, they are more susceptible to diseases and pests. And it becomes difficult to care for vegetables. But even in narrow beds you can place enough plants to get a good harvest.
Planting density depends on the crop variety. Weakly branched bushes require less space for growth and development. You should also take into account the saturation of the soil with nutrients. Plants are planted less often on poor soil than on soil rich in microelements. Usually per 1 sq.m. The beds contain 3-4 plants.
Most often, long narrow beds with a passage between them are arranged in greenhouses. The plants on them are easy to care for. They are convenient to control, which helps to detect signs of disease or beetle infestation in time.
Horizontal method of planting seedlings
When growing cucumbers in this way, there is no need to install supporting structures. The stems grow along the ground and grow in different directions. In this case, they receive a sufficient amount of sunlight, but caring for the plants is difficult. Weeding the plantings, treating them from diseases and pests, and picking cucumbers is very inconvenient. The distance between seedlings in this case should not be less than 40...60 cm. As a rule, this method is rarely used in greenhouses.
Vertical method of planting seedlings
Installing various kinds of supporting structures that help the plant cling to them and stretch upward allows you to plant cucumbers more compactly. You can leave only 30...40 cm between the bushes. Tied cucumbers develop well, they are sufficiently blown with air. Cutting crops, watering, feeding, forming bushes is easy. Supports can be: trellises, ropes lowered from above, mesh or several rows of wire.
Harvesting
Oddly enough, the regularity of harvesting affects the harvest itself. If cucumbers are not picked on time, they grow and develop further. The plant spends nutrients on them. Especially a lot of microelements go into the formation of seeds.
Therefore, the greens are collected when they reach a size of 10-15 cm. They are picked carefully, holding the whip with one hand so as not to damage them.
During the period when plants begin to bear fruit en masse, cucumbers are harvested once every 1-2 days, depending on the area of the greenhouse.
All diseased, dry and crooked fruits are removed without waiting for them to grow, as they deplete the plant.
Then plant cucumbers in the beds
To prevent plants from being affected by diseases, it is necessary to observe crop rotation and not plant them in the same bed every year. In addition, cucumbers should not be planted after crops such as zucchini , pumpkins , melons and watermelons . But if tomatoes grew in the greenhouse last year, then cucumbers can be planted in their place.
It’s a good idea to sow and grow green manure in a greenhouse a month before planting, which will enrich the soil with nutrients. These herbs are then simply dug in with the soil.
Warm beds for early harvest
A warm bed is a great way to get early cucumbers in May, especially if the spring has been cool. In addition, such a bed also provides additional feeding.
Two types of warm beds are used: buried and raised. Such beds resemble a multi-layer sandwich, where the ingredients are organic fertilizers. It's good to make raised beds. In such beds, excess water can drain away during rains.
The advantage of a layered bed is the following: when organic matter decomposes, a double effect is obtained - warmth and nutrition.
It is preferable to make such a bed in the fall so that its components rot over the winter, then the bed will be ready for planting seedlings in the spring.
Here are a few rules for making a warm bed:
- you need to choose a spacious, sunny place;
- before filling the next layer, fill the bottom one with water so that the layers are wet all the time;
- to fill the bed, take parts of only healthy plants, without fungal infections or damage by insect pests; the width of the bed is chosen arbitrarily, but not more than 1 meter, and the depth is the size of two shovels with a small margin, which is about 50 cm;
- the bottom layer of the bed filling consists of large coarse waste, which takes more time to rot; these can be thin branches of deciduous trees, thick stems, small wood waste;
- the next layer consists of coarse herbaceous plants, vegetable peelings (pre-boil potato peelings to avoid sprouting), soft stems;
- leaves and freshly cut grass without seeds are laid on top in a thick layer; the grass layer must be well compacted to avoid the formation of unevenness; add complex fertilizer: nitroammofoska - 1 tbsp. a spoon per square meter - and a glass of wood ash, you can fill it with a solution of manure with or without straw;
- cover this filling with fertile soil 15 - 20 cm thick;
- cover the finished bed with dark film.
Read more about creating warm beds in the article Proper beds - less work, more harvest.
You can make a warm bed in the spring, but in this case the bed is filled only with soft green mass, which is quickly processed in the ground, and plant food waste. It is especially good to use nettles without roots, clover, dandelion, and onion peels. Mix with compost or vermicompost. Pour boiling water over, cover with dark film. Seedlings are planted after a few days.
Growing cucumbers in warm beds significantly speeds up their fruiting. © ekotec