Gardeners often plant cucumbers in a greenhouse to get an earlier harvest. Under these conditions, in terms of speed of ripening, they are probably second only to radishes. Such plants require special care. Under shelter they are protected from cold and wind, but at the same time they are completely dependent on human care. It is necessary to know exactly the intricacies of feeding these vegetables, the timing of application and types of fertilizers.
The need to feed greenhouse cucumbers
Cucumbers are successfully grown both in street beds and in greenhouses and greenhouses (including polycarbonate ones). In closed ground, the crop is provided with optimal climatic conditions for vegetation, but the owner of the garden is solely responsible for the supply of nutrients. Plants require various micro- and macroelements at different phases of vegetative development (rooting, growth, growth of green mass, flowering, fruiting).
The root system, located close to the surface, cannot independently obtain the necessary nutrition from the depths. Feeding cucumbers in a greenhouse allows you to provide the crop with everything it needs, as well as increase its immunity to diseases. This operation must be performed at all stages of growing cucumbers: from planting seeds to the stage of harvesting fruits.
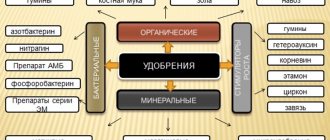
Two methods are used to apply fertilizers:
- Under the root. Nutrient compositions are applied to the soil in dry form, but most often solutions based on organic and mineral components are pre-prepared; a watering can is required to fertilize the plantings. Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to moisten the soil around the bushes, which ensures better absorption of the applied substances.
- Foliar (additional). The foliage of plants is sprayed with nutrient solutions. For these purposes, you can use any type of sprayer. You need to feed cucumbers early in the morning or in the evening. Example of fertilizer compositions: 10 g wood ash/1 liter of water, 1 tsp. boric acid + 10 crystals of potassium permanganate / 1 liter of water.
Foliar feeding, despite its effectiveness and speed, cannot replace the application of fertilizers to the soil.
Popular questions and answers
agronomist-breeder Svetlana Mikhailova about how to feed cucumbers in a greenhouse
Are traditional feedings of cucumbers effective?
They have no proven effectiveness - no one has ever conducted scientific experiments feeding cucumbers with yeast or anything else. Gardeners often write about increased yields after using such fertilizers, but this may be a subjective feeling, misconception, or even deception. But such fertilizers can cause harm.
Is it necessary to give cucumbers foliar feeding?
Not necessarily - soil nutrition is quite enough for them. But foliar feeding can increase the yield and quality of fruits.
How long before you can feed cucumbers after planting seedlings in a greenhouse?
After 2 weeks - this is exactly the time it takes for young plants to take root in a new place.
And this rule applies not only to the greenhouse, but also to open ground. And not just cucumbers - all plants. Sources
- Romanov V.V., Ganichkina O.A., Akimov A.A., Uvarov E.V. In the garden and vegetable garden // Yaroslavl, Verkhne-Volzhskoe book publishing house, 1989 – 288 p.
- Group of authors ed. Polyanskoy A.M. and Chulkova E.I. Advice for gardeners // Minsk, Urozhay, 1970 – 208 p.
- Shuvaev Yu.N. Soil nutrition of vegetable plants // M.: Eksmo, 2008 – 224 p.
Types of fertilizers used when growing cucumbers in a greenhouse
The types of fertilizers required for vegetable crops vary depending on the stage of vegetative development, the type of soil and the requirements of the variety being grown.
If cucumbers do not grow well in a greenhouse: how to feed the plants:
Mineral supplements
The main elements that cucumbers require when growing them are nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus.
What are these fertilizers for?
- Without nitrogen, any plants cannot develop normally. The element is necessary for the growing season in any period; it is needed for metabolism and the formation of green mass.
- Potassium is important for stimulating photosynthesis, increasing the rate of protein-carbohydrate metabolism and countering external adverse factors.
- Phosphorus is required for metabolism, stimulating the development of the root system, accelerating the process of fruit formation and increasing their number.
These substances can be applied separately or be part of complex fertilizers.
Also required for the development of culture are: calcium, copper, boron, iron and other elements.
The most common types of chemicals used to fertilize cucumbers:
- Potassium: potassium chloride and sulfate, potassium salt, potassium nitrate.
- Nitrogen: urea, ammonium nitrate.
- Phosphoric: superphosphate, orthophosphate.
Today, manufacturers offer phosphorus-potassium, nitrogen-phosphorus, nitrogen-potassium, as well as complexes containing all the most important components for cucumbers. They are available in both powder and liquid form. For example, nitroammophoska contains nitrogen and phosphorus, as well as some other elements. The main components of potassium phosphate are K and P.
The most popular compositions for fertilizing cucumbers:
- 10 g of ammonium nitrate, potassium salt and superphosphate per bucket of water;
- 20 g of superphosphate, urea, potassium sulfate per 10 liters of water.
Organic fertilizers
Such fertilizing is perfectly absorbed by cucumbers and helps to obtain a decent harvest.
How can you feed cucumbers grown in a greenhouse:
- Compost.
This substrate is obtained after the decomposition of various types of organic matter: plant residues, mowed grass, household waste, etc. The nutrient mixture is formed as a result of natural decay (with the participation of microorganisms) and the influence of worms and insects. The speed of composting depends on the temperature and humidity of the environment, as well as the access of air to the rotting raw materials. Without the use of process accelerators, fertilizer (soil mixture) enriched with nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus can be obtained approximately two years after planting.
What is good about compost:
- it is environmentally friendly;
- contains a large number of micro- and macroelements;
- can be applied in any quantity to the soil.
- To obtain fertilizer, no financial investment is required, which can also be considered its advantage. Compost is placed in the holes before planting the plant or applied under it during the process of growth and development.
- Manure
.
Of the fertilizers that are excrement of farm animals, the most popular are mullein and bird droppings.
Using manure as a top dressing allows you to:
- saturate the soil with the necessary elements;
- improve the physical and mechanical characteristics of the earth;
- activate microflora;
- increase the absorption of mineral fertilizers by plants;
- saturate the soil with carbon dioxide.
Fresh manure is not recommended for fertilizing plants, as it can harm them due to its high toxicity. It can be used if there is no direct contact with the crop, for example, to warm the soil or to add it to the ground during the autumn digging of beds. Rotted manure is more suitable as a top dressing, as it perfectly restores soil fertility.
To apply under cucumbers, prepare solutions: chicken manure is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:15, cow manure - 1:6. It is recommended to infuse the compositions for a week. Before applying under the bush, you should dilute them with water (for 1 liter of solution you need 2 liters of water).
- Peat.
Despite the rather low content of nutritional components, this fertilizer improves the soil structure well. The most nutritious is lowland peat. To increase the fertility of the land, you need to add 5...10 kg of peat per 1 m2. In a greenhouse, peat retains its characteristics for about 2-3 years.
You can also use other types of organic matter as fertilizers: wood ash, sawdust, silt, etc.
Necessary nutrients, appearance of cucumber bushes if they are deficient
During the growing season, cucumbers need different nutrients.
This is due to the time intervals: growth, flowering and fruiting. At the initial stage, nitrogen is important for the growth of green mass. It is used throughout the growing season to stimulate the growth of cucumber bushes. Phosphorus is needed during flowering and ovary formation. And at the peak of active fruiting, potassium is required. The lack of nutrients is clearly visible in the appearance of the bush:
- with a lack of nitrogen, the leaves lose their emerald green color, becoming faded; growth slows down, the stem becomes thinner, the leaves droop;
- with phosphorus deficiency, the leaves become dark, gradually turn black and dry out; the lashes grow more slowly;
- the absence of potassium is noticeable by the yellow edge on the leaf and by the shape of the fruit, which becomes pear-shaped.
Each nutrient affects the growth and development of cucumbers in its own way. This must be taken into account when creating fertilizers and mixing various components. The plant must fully receive all the necessary substances.
Fertilizing cucumbers during flowering and fruiting
When mass flowering of plantings begins (at the end of May), vegetables require more nutrients.
The following combination of fertilizers can be used as top dressing:
- diluted cow manure (500 ml);
- nitrophoska (1 tbsp);
- wood ash (1 tbsp.);
- boric acid (0.5 g);
- manganese sulfate (0.3 g).
These components are diluted in a bucket of water and mixed thoroughly. For 1 sq.m. beds require about 3 liters of composition.
At the fruiting stage, cucumbers also need additional feeding. To do this, you can use: ash diluted in water in a ratio (1:5), potassium nitrate (25 g/10 l of water), a solution of cow manure (in a ratio of 1:5).
What to do if you add excess fertilizer
It is better to slightly underfeed cucumbers in the garden than to overfeed them. Because in the second case, undesirable phenomena may occur, such as changes in leaf color, slower growth, growth of shoots or burns on leaf blades. What will overfed cucumbers look like with one fertilizer or another:
- If plants are overfed with nitrogen, then the formation of ovaries on cucumbers slows down. The lashes become too thick, and the leaves become denser and acquire an intense green color.
- With an excess of phosphorus fertilizers, the leaf blades become yellowed, and necrotic spots may appear on them, increasing in size. If appropriate measures are not taken, the leaves begin to fall.
- If too much calcium is added to the soil, this can also be judged by the leaves. They develop interveinal chlorosis.
- Cucumber plants overfed with potassium immediately begin to slow down their growth.
If a mistake does occur and you exceed the dose of fertilizer, this will certainly affect the condition of the plants. The situation can be normalized by abundant watering of plants at the rate of 15 liters per square meter. m. Thanks to this technique, excess amounts of fertilizer are washed out from the upper layers of the soil into deeper layers inaccessible to cucumber roots. Leaching the soil when there is an excess of fertilizer in the soil always gives a positive result.
Feeding for yellowing leaves and ovaries
A deficiency of macroelements immediately affects cucumbers: their appearance deteriorates, they develop worse, fewer ovaries appear, fruits are deformed, yield decreases, etc. Most often, gardeners are faced with yellowing of foliage and cucumbers.
Table. Signs of nutritional deficiencies and recommendations for correcting the situation.
| Type of problem | Signs | Troubleshooting methods |
| K deficiency | Yellow stripes appear along the edges of the leaves. After some time, the leaves curl. The fruits are deformed (closer to the stalk their diameter decreases), their taste characteristics deteriorate. | To compensate for the lack of potassium, use an aqueous solution of potassium sulfate or wood ash. |
| N deficiency | The leaves growing in the lower part of the vine acquire a light green color and gradually turn yellow. The stem becomes thinner, the ovaries fall off, the cucumbers lighten and become hook-like. | Solutions of urea or ammonium sulfate are used as fertilizing. |
| Ca deficiency | The ovaries begin to crumble, the fruits turn yellow and become bitter. | The situation can be corrected by adding powdered eggshells or, preferably, calcium nitrate. |
| Lack of P | Brown-yellow spots may appear on the leaf blades in a chaotic manner. Leaves become wrinkled. | You need to add superphosphate. |
| Mg deficiency | The first sign is the fragility of the sheet plates. Yellowish spots appear on the leaves growing in the lower part of the bush. | It is recommended to feed cucumbers with magnesium sulfate. |
How to understand what a plant lacks?
If the plant begins to lag behind in development, does not set fruit well and changes the color of its leaves, this is how it “signals” to you that it needs additional nutrition. And such signals will help you understand what else to feed your cucumbers in the greenhouse and at the same time not overfeed.
The soil itself that you used in the greenhouse will tell you what your cucumbers may be missing:
- On soddy-podzolic soils, a lack of nitrogen and phosphorus is common.
- On light sandy and sandy loam soils - potassium, boron and copper.
- On peaty, alkaline and carbonate soils there is a deficiency of manganese.
- Highland and lowland peatlands are usually deficient in copper.
But the lack of watering gives the following picture: the fruit is underdeveloped at the base and swollen at the end. The fetus appears to have a “waist” - you will notice it.
Potassium deficiency
If the fruit is narrowed near the stalk, this is a lack of potassium. The deficiency of this element negatively affects the process of regulating the water regime in the plant. All this affects cell turgor, the ability of stomata to close and open. In the overall picture, fruits lacking this element are prone to wilting.
Potassium deficiency also causes burns of old leaves - they quickly turn yellow from the borders of the leaves to the center between the veins. It is on the leaves that the “diagnosis” is made: if there are still green areas of the leaf around the main veins, then the deficiency is not yet pronounced. Further, brown burns appear on the yellow areas, which lead to the death of the entire leaf. And so - throughout the plant, which is facilitated by hot weather. Note that potassium is quite mobile and quickly moves to young leaves, even if its supply is seriously limited. This is why the cucumber's growth may remain the same, but the harvest will suffer.
To replenish potassium reserves, feed the plants root and foliar with an aqueous solution of potassium sulfate. If you don’t have this on hand, just dilute wood ash in water (a wonderful remedy that has been proven for centuries).
You will be interested to know that with a lack of potassium, nitrogen metabolism is also disrupted, which leads to yellowing of the tissues along the edges of the leaves. After this, the leaves curl downwards and wrinkle. The internodes of the cucumber become shorter, and the veins on the leaves seem to be pressed in. Where is the connection? The fact is that if there is a lack of moisture, beneficial microorganisms cannot actively supply nitrogen to the roots, and therefore do not rush to immediately increase the dose of fertilizing - start with watering. Have you seen changes for the better? So, that was all there was to it.
Nitrogen deficiency
If you get hooked fruits, the plant always lacks nitrogen. And its deficiency in the soil affects plant growth. The first sign is the light green color of the leaves and light, pointed fruits. Then the leaves turn yellow, the roots turn brown and die, and the entire bush slows down its growth.
A lack of nitrogen can also be determined by thin, hard vines that quickly become woody. The leaves are small and directed upwards. There are few side shoots. The ovaries crumble and some of the flowers die. If during this period you do not save the cucumbers by feeding, then even the fruits will begin to acquire a pale yellow color, become shortened in size and acquire a pointed tip.
If you have identified a clear lack of nitrogen precisely during the fruiting period of the cucumber, do not rush to water it with chemicals - all this will now go into fruit. It’s better to prepare the so-called “green stuff”: collect various weeds from around the garden, chop them finely and fill them with water. For 10 liters you should get up to 2 kg of green mass. Leave this herb for a week until it ferments, then feed it to hungry plants in the greenhouse.
Magnesium deficiency
If you have acidic soil in the greenhouse, also make sure that the cucumber does not lack magnesium. The first sign is light green spots on the leaves, which then turn yellow (this is partial chlorosis), become brittle and even fall off. And here the plant stops its growth. Magnesium deficiency can also occur from an excess of potassium. From a lack of this substance, the leaves become variegated: between the veins the color can be yellow, red and purple.
Calcium deficiency
Acidic soils may also lack calcium. This will be noticeable by light yellow spots on young leaves, slow growth of the bush and rapid aging of the root system. This problem can be easily solved by ordinary liming, which will add an additional element of boron. With calcium deficiency, the apical buds and roots gradually die off. The leaves not only become smaller, but also bend and become fringed at the edges. The color of the leaf also changes: dark green above, with pale edges, and purple below. The fruits are small, rough and completely tasteless.
Boron deficiency
Boron deficiency leads to the fact that the roots and growth points die, the stems are noticeably shortened, and the fruits are deformed.
A lack of boron also causes the leaves to take a spoon-shaped shape and become brittle. The flowers are no longer capable of fertilization and fall off - all due to the suppression of photosynthesis and the outflow of carbohydrates. The fruits no longer develop, and their shape is distorted.
Phosphorus deficiency
With a lack of phosphorus, the leaves become dark green, even bluish, and then purple shades appear on them. When these leaves dry out, they become dark, almost black. The shape of the leaves is small, dense, curled down, with purple-red veins. During acute starvation of this element, the leaves become covered with watery spots, even young ones.
To solve the problem with phosphorus, use solutions of ammophos and diammophos. Alternative: 1 tablespoon of superphosphate per 10 liters of water.
Molybdenum deficiency
But if the plant lacks such a valuable substance as molybdenum, this will quickly become noticeable by chlorosis and curved edges like tubes. The veins on the leaves will turn pale and the flowers will grow small. And an excess of ammonia nitrogen and heavy metals leads to a lack of molybdenum.
Iron deficiency
A lack of iron in cucumbers manifests itself as follows: the plant stunts its growth, the leaves become light green, even almost white, and the growth points do not develop. It is the lack of iron that is the main reason why the process of chlorophyll formation does not occur in the leaves. And, as you remember, it gives the characteristic green color.
With progressive deficiency, the leaves become lemon-colored and then yellow-white. Moreover, there may actually be enough iron in the roots, it’s just that it is almost not absorbed - due to a lack of potassium, or an excess of phosphorus, calcium, copper or zinc.
Traditional methods of feeding greenhouse cucumbers
Using weeds growing in the garden, as well as products or means available on any farm, you can prepare compositions that can provide the necessary nutrition to plants in closed beds.
Feeding cucumbers in a greenhouse:
- A solution of iodine and milk. A simple top dressing can be prepared from 1 liter of milk and 25 drops of iodine, which should be dissolved in a bucket of water. The liquid is used to spray bushes and soil once every 10 days.
- Ash fertilizer. This fertilizer can be applied to cucumbers in its pure form, but a solution of wood ash is no less effective (2 cups dissolved in a bucket of water). This amount is enough to fertilize 10 bushes.
- Onion broth. Bring water (10 l) with onion peels (200 g) to a boil. The pan must be closed with a lid and removed to infuse for 10 hours. After the liquid has cooled and infused, you can water the cucumbers with it (1 liter per 1 plant).
- Yeast feeding. A package of fresh yeast is dissolved in a bucket of warm water. After daily fermentation, the composition is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:5 and can be used as fertilizer (1 liter per 1 bush).
- Bread infusion. Rye bread crusts are filled with water and infused for 7 days. After this, the composition needs to be filtered and you can use it for watering cucumbers (preferably during flowering).
- Nettle fertilizer. The weeds are placed in a bucket, water is poured into it, after which the container is left for several days. The finished fertilizer must be diluted with water (1:7). To process one bush, about 500 ml of liquid is required.
Also, according to folk recipes, you can use boric acid, ammonia, soda and other products as a top dressing.
What to feed so as not to turn yellow
Sometimes, even when fertilizing, gardeners are faced with the phenomenon that cucumber leaves turn yellow. This can occur under normal microclimate in the greenhouse and in the absence of pests and diseases, the activity of which can also cause yellowing of the leaves.
If you notice in your plantation that the cucumber plants are starting to turn yellow, try using the following foliar feeding:
- place a loaf of bread in a ten-liter bucket overnight;
- In the morning, knead the bread and add a bottle of iodine to the bucket;
- dilute 1 liter of the resulting master composition in 10 liters of water.
After straining, apply the solution to spray on the leaves.
In addition, gardeners make a nutrient solution for foliar feeding from nettles according to the following recipe:
- prepare young nettles free from seeds;
- put it in a bucket and fill it with water;
- the composition must be infused for 22 hours.
To prepare the working solution, dilute 1 liter of mother solution in 10 liters of water and start spraying.
Excess fertilizer: signs and solutions to the problem
Excess of certain macronutrients can also negatively affect plants, especially those grown indoors. It is especially dangerous to get carried away with applying chemical fertilizers; it is better to use organic matter.
What to do if too much fertilizer is applied to the bushes? The first step is to water the problem plants with water (in large quantities). If the bush has not had time to develop, it can be carefully dug up and planted in another place.
Signs of excess minerals
How does excess macronutrients added to the soil affect cucumbers:
- With an increased content of K in the soil, burns of the root system and the appearance of necrosis of the edges of leaf blades (brown-yellow stripes) are observed.
- Too much P causes the vines to turn yellow and leaves to fall off.
- Excess N causes leaf deformation. Yellowish spots appear between their veins, gradually merging with each other. The fruits become smaller. In the worst case, the cucumber may simply die, since with an excess of nitrogen, the deficiency of other substances is more difficult for the plant to tolerate.
Gardeners who grow vegetables indoors, as a rule, do not have the opportunity to completely replace the soil, which is not very rich in nutrients, with fertile soil every year. Therefore, it is necessary to apply fertilizers. In this case, you can achieve excellent results in terms of yield and taste of cucumbers.
Types of fertilizing
You can feed plants in two ways - by watering at the root and spraying the leaves. In the first case, nutrients are absorbed more slowly. In the second, they immediately reach the leaves, but the content of nutrients in a not too concentrated solution is less. The root system of cucumbers is superficial, but distributed throughout the entire garden bed, so watering the base of the bush is not enough. Fertilizer is applied to the entire planting area.
Root
Root feeding is the main method of delivering nutrition to cucumber plants. Roots absorb solutions of mineral salts from the soil and deliver them to stems, leaves and fruits. When carrying out root feeding, you must strictly follow the instructions that are on the package with the fertilizer mixture, otherwise, instead of benefit, you may end up with harm - burnt roots, slower development, and reduced yield. Don't forget about pre-watering.
Foliar
This is an ambulance for plants in case of poor development or obvious lack of some element. Solutions for them are made less concentrated, and the fertilizer should dissolve in water without residue. Foliar feeding is carried out when it is cloudy to avoid foliage burns.
Signs of nutrient deficiency or excess.
Signs of nutrient deficiency or excess.
When growing cucumbers in a greenhouse, you must pay attention to these signs in order to take prompt action in time. Signs of nutrient deficiency in cucumbers are quite specific.
It should be remembered that not only a lack of nutrients, but also an excess of nutrients has a negative impact on the harvest.
Let's start with the signs of nitrogen deficiency. If there is a lack of nitrogen in cucumbers, the leaves turn yellow, become lethargic and fall off. The tips of the fruits narrow and the stalks become thick. The scourges are thinning.
Potassium deficiency is characterized by yellowing of the leaves on the sides in the form of a border. The fruits become in the form of “hooks” or “light bulbs”. In this case, it is necessary to feed the cucumbers with potash fertilizer, such as ash.
A thin stem in cucumbers is the main sign of phosphorus deficiency. Especially if this symptom comes in combination with the leaves acquiring a purple tint. With a lack of phosphorus, new ovaries are very poorly formed. There is no excess phosphorus in cucumbers.
Dying of the lower tips of leaves is a sign of calcium deficiency.
If you correctly determine the reason for the improper development of the plant, it can be very easily corrected by feeding it with the necessary fertilizer.
How to prepare the soil for sowing seeds for seedlings?
Containers or boxes need to be filled with fertilized soil, and also add a little wood ash. After this, you need to pour the manganese solution well, it should be hot. Why do you use wood ash? It is an excellent source of potassium. Potassium permanganate, in turn, gives your plants not only potassium, but also manganese. These elements have a strong influence on the further growth and development of your plants.
After your seedlings have “migrated” to the greenhouse soil, you need to feed the plants so that they, so to speak, “eat up” the stress of replanting. For the first greenhouse fertilizing, mullein, superphosphate and ammonium nitrate are used.
Remember that with any feeding you need to be careful and follow all dosages. The fact is that if you overdo it with certain fertilizers, the plant will not process the excess amount of nutrients. And your excessively added nutrients will go into the fruits themselves and turn into nitrates.
In garden stores you can buy fertilizers that do not contain nitrate nitrogen. These include: potassium sulfate, Crystallin A, humatized fertilizers.
Feed cucumbers after planting in the ground: why do cucumbers need fertilizer?
Many gardeners who are just starting their journey in this field often do not understand why additional feeding of cucumbers after planting in the ground or greenhouse is necessary, if at the very beginning they prepared and fertilized the soil in the fall. The reason for this is the fact that the roots of cucumbers are in the surface layer of the earth and plants simply cannot obtain the elements necessary for life from the deeper layers of the soil. Therefore, when the supply of nutrients put into the soil during planting runs out, the cucumbers will begin to lack nutrition. And this threatens the deterioration of plant immunity, poor resistance to various diseases and pests, as well as an overly sensitive reaction to temperature changes.
Cucumbers are a crop that does well in conditions of fairly high humidity, as well as with a small amount of fertilizer. You need to water and fertilize your plants when the sun's rays are not bright, for example, early in the morning or late evening. If you carry out these procedures during the day, there is a risk that your plants will “catch” anthracnose or powdery mildew.
A prerequisite for watering is warm water. Feeding cucumbers is carried out after you have planted them in the greenhouse. However, this measure will not be so effective if your plants, while still seedlings, felt a lack of nutrition.