Features of growing in greenhouse conditions
Growing cucumbers indoors has its own characteristics:
- the possibility of cultivating long salad cucumbers that are not suitable for open ground;
- carefully monitor the quality of the soil, since in a limited area the amount of nutrients is quickly consumed by plants;
- annual soil replacement or planting catch crops after cucumbers to prevent the development of diseases;
- obtaining a harvest at any time of the year, regardless of the climate;
- with the vertical growing method, the color of the fruit is uniform;
- absence of the likelihood of mechanical damage and the influence of weather conditions on the growing season of cucumbers.
Optimal distance between greenhouse cucumbers
In protected ground, several plant placement schemes are used. The frequency of planting seedlings also depends on the method chosen.
- Two-line method.
In this case, the seedlings are planted in 2 rows. Cucumbers are located opposite each other. A distance of about half a meter should be maintained between rows, and 40 cm between sprouts. A row located near the wall of the greenhouse should be no closer than 25 cm from it. For crops that do not have large green mass, this method is preferable. In order for the bushes to be illuminated by the sun and ensure their aeration, it is important to promptly remove lateral shoots and excess foliage.
- Chess order.
If you move the holes of the second row by half the step that is maintained between plants, the cucumbers block each other from sunlight less. This planting method is used when growing crops with large leaves and large fruits. You can leave only 30 cm between bushes.
- Single row placement.
In small greenhouses, cucumbers are often planted in the garden in one row. Varieties that are distinguished by friendly fruiting grow well with this scheme. You can leave only 25 cm between plants; they will already be well lit.
Necessary equipment
To grow cucumbers indoors, two conditions are important: a suitable greenhouse and its equipment. When choosing a shelter, please note that polycarbonate greenhouses have more advantages than those based on film or frame. They are easy to transport, rearrange and assemble, wear-resistant, have minimal influence of weather conditions, and are more airtight.
The size of the shelter must be at least 10 square meters. m, and the height is about 2 m. It is not recommended to build a higher greenhouse, since maintaining the microclimate in it will be problematic due to the large layer of air. But a lower height when growing cucumbers is also unacceptable. This is due to the fact that cucumber vines, if placed vertically, will not have enough space; their length can exceed 3.5 m.
The choice of location for installing the greenhouse is of great importance. It should be a flat surface or a small hill so that groundwater does not flood it and cause mold to appear.
The greenhouse should be installed in a north-south direction to optimize the receipt of natural sunlight and heat.
Choosing a greenhouse for growing cucumbers
First of all, in order to grow a good early spring harvest of cucumbers, we need to think about the availability and quality of a greenhouse. Today, there are many options for greenhouses on the market, ranging from their shapes, sizes and designs to the actual covering material from which they are made.
Thick polyethylene film, glass and polycarbonate are most often used as covering materials for the manufacture of greenhouses. All of the above materials have both pros and cons. For example, dense polyethylene film, for example, is the most economical material for making a greenhouse, but its durability and heat retention are much worse than, for example, glass or polycarbonate, but they, in turn, have a much higher cost.
The choice of material from which to make the greenhouse, of course, remains yours. And in this case, there are only two options6, the first is to save at the first stage and build a greenhouse from dense polyethylene, or to purchase, albeit at a higher cost, glass or cellular polycarbonate, which will last you much longer, namely from 5 to 15 years at proper care, which will allow you to retain maximum heat in the greenhouse and grow plants in it not only in spring, but also in late autumn and even winter.
Also, when creating a greenhouse for growing cucumbers, you should take care in advance of creating vents for ventilation, an irrigation system, subsequent staking of plants and additional heating of the greenhouse in case of frost. For heating, potbelly stoves or ordinary 200 liter metal barrels, which are heated with wood or coal, are most often used.
To tie plants into the ground along a row of cucumbers, wooden stakes or metal rods are dug into the ground and then twine is pulled at a height of one, two and one and a half meters.
Greenhouse preparation
After choosing a location and installing the shelter, preparatory work should be carried out. They consist of the following activities:
- Inspecting the greenhouse for cracks and eliminating them. This will protect the cucumbers from the negative effects of drafts.
- Be sure to treat the inside of the shelter with an antifungal compound to avoid contamination of the soil and seedlings.
- Consider the location of the beds and choose the method of their formation. Most often, longitudinal rows are placed along the shelter. Their width is approximately 50 cm, and the passage must be left at least 90 cm. If the size of the shelter allows, you can use a location method that involves building a shortened bed in the middle with a circular passage and 2 rows along the length of the sides of the greenhouse.
- Cucumbers are a heat-loving crop, so depending on your plans for growing them, you may need to organize a heated floor under the beds to warm the soil when growing cucumbers year-round.
- It is advisable to install containers with water in the shelter, which will perform 2 functions: warming up during the day, giving off heat at night and being a source for irrigation with warm water.
- Provide a ventilation system. These could be additional windows or an automatic ventilation system. Moreover, the location of the vents on the roof and along the walls under the ceiling makes it possible to ventilate the room without drying out the soil, as happens when opening a door and a vent on the opposite wall.
Harvesting
Oddly enough, the regularity of harvesting affects the harvest itself. If cucumbers are not picked on time, they grow and develop further. The plant spends nutrients on them. Especially a lot of microelements go into the formation of seeds.
Therefore, the greens are collected when they reach a size of 10-15 cm. They are picked carefully, holding the whip with one hand so as not to damage them.
During the period when plants begin to bear fruit en masse, cucumbers are harvested once every 1-2 days, depending on the area of the greenhouse.
All diseased, dry and crooked fruits are removed without waiting for them to grow, as they deplete the plant.
Choosing the right variety
Growing cucumbers indoors means that pollinating insects will not have access to the plant's flower stalks. Therefore, for this case, choose varieties that can self-pollinate or those that do not need pollination at all - parthenocarpic. These properties are indicated on the seed package.
It is important to distinguish cucumber varieties from their hybrids. When planting varietal types of vegetables, their properties will be repeated from year to year, and it is possible to obtain your own seeds from the most successful harvest.
When using hybrids, self-collected cucumber seeds do not carry the properties and qualities of the previous harvest. This means that hybrid seed must be purchased annually.
Let's consider some varieties and hybrids suitable for growing in shelter:
- Adam F1. A hybrid from Holland with the ability to self-pollinate and obtain a rich, early-ripening harvest. The first vegetables can be harvested after 1.5 months, and the fruiting period is quite long. Under favorable conditions, cucumbers are tied in 5-7 pieces. in one node. The fruits are small in size, dark in color with small spines. Suitable for preparation and fresh consumption.
- Herman F1. A wonderful hybrid of Dutch selection. Very early, with a long fruiting period. Small cucumbers develop in bunches of 6-7 pieces. The fruits are juicy and dense. The hybrid is resistant to temperature changes and diseases. Good fresh and canned. Planting in open ground and greenhouses is possible.
- Son-in-law F1. Parthenocarpic hybrid. Fruits develop in nodes of 3-7 pieces. up to 10 cm long. Can be harvested at any stage of maturity. Cucumbers are delicious, yield up to 6 kg per plant. Resistant to powdery mildew and root rot. Adaptable to sudden changes in weather conditions.
In addition to the presented species, it is possible to sow seeds of the following cucumber varieties: “Metelitsa”, “Prestige”, “Ararat”, “Tatyana”, “Fed Papa”, “Everyone is Envy”, etc.
The nuances of pollination
Among the many cucumber varieties and hybrids, there are those that pollinate independently or do not need it at all. The latter include parthenocarpic varieties that do not form seeds and therefore reproduce vegetatively.
Today we’ll talk about pollinated varieties and how to influence the process. Luring bees into a greenhouse is not as easy as it seems. They are not too attracted to the smell of heated polycarbonate, so gardeners use bait. One of these is water with leftover jam or a small amount of honey. The beds are sprayed with it and the greenhouse windows are left open.
Winged pollinator of cucumber flowers.
If the bees are in no hurry, you can pollinate the plants yourself. To do this, take a fluffy brush and transfer pollen from male to female flowers. There is an alternative way:
- pluck an inflorescence that has no signs of an ovary at the base;
- The petals are carefully torn off, and the stamens are placed on the stigma of a flower of the opposite sex. It is better to perform the manipulation early in the morning, using several male specimens at once for reliability.
Important! Before pollination, you should make sure the pollen is ripe. To do this, use a simple test: touch the back of the hand with the flower stamens. If the yellowish dust remains on the skin, you can start.
Soil preparation
For sowing cucumber seeds, it is preferable to use peat pots rather than reusable containers. This is due to the fact that the crop does not like replanting when its root system is disturbed.
Soil for filling seed containers can be purchased in specialized stores and departments. This soil mixture will be disinfected and has a special composition suitable specifically for growing cucumbers.
The second option for obtaining soil for planting seeds is to prepare it yourself. To do this, take the following ingredients and mix them thoroughly:
- turf - 1 part;
- compost - 2 parts;
- peat - 1 part;
- sand - 1 part.
Such a soil mixture should be subjected to a disinfection procedure before use. To do this, you can use one of the options:
- heat it in the oven at a temperature of 170-180 degrees for 20 minutes;
- process in a special steam generator for half an hour;
- dilute 15 ml of Fitosporin in 10 liters of water and pour over the soil.
After processing, it is necessary to add fertilizer to the planting mixture to enrich it with nutrients and elements. For 10 kg of soil add:
- wood ash - 200 g;
- phosphorus fertilizers - 50 g;
- potassium sulphide - 35 g.
After thoroughly mixing the mixture, it must be moistened. High-quality soil is ready for sowing cucumber seeds.
Watering cucumbers
As already mentioned, the best watering is drip irrigation. It provides the best option for supplying moisture to plants. The water should be settled and warm.
In addition to using a special device for drip irrigation purchased in a store, you can do this watering yourself using plastic bottles.
If the weather becomes especially hot, then watering must be increased. If the water you use is hard, then it must be softened by adding wood ash: 5 tsp. for 10 liters of water.
If it is not possible to organize drip irrigation, then using a hose, it is advisable to make a spray of water, like in a watering can.
It is recommended to combine watering with fertilizing.
Properly preparing seeds for sowing
Seed material purchased in factory packaging does not require additional preparation. If the seeds are collected independently or purchased in another way, then the following preparatory procedures must be carried out:
- Selection. From the total mass, select the largest and most identical in shape. Prepare a saline solution from 1 tsp. salt and a glass of water. Dip the selected seeds into it. Remove those that remain on the surface. The rest - rinse with clean water and dry until flowability is restored.
- Disinfection. Prepare a slightly pink solution of manganese and dip cucumber seeds in it for 15-20 minutes. You should not make a more concentrated solution or keep the seeds in it for longer than the prescribed time. This will lead to burns of the seed and render it unusable.
Instead of manganese solution, you can use Fitosporin-M or Gamair-SP.
After processing, rinse the seeds with running water and dry.
- Impact of temperature. To speed up germination, place the seeds in a bag and warm them near a heating device. The reverse method is also good - place the seeds in the refrigerator for a day.
- Germination. Line a shallow plate with several layers of gauze. Distribute cucumber seeds over its surface and moisten well. Cover the top with a wet cloth. Make sure that the lower and upper material does not dry out.
Sowing seeds: step-by-step instructions
It is better to plant cucumbers immediately in individual containers so as not to expose the sprouts to picking. The process of planting seeds consists of the following steps:
- Prepare containers - yogurt cups with 3-4 holes in the bottom work well.
- Pour soil into containers and water it generously with warm water.
- A 2 cm depression is made in the middle, 2 seeds are placed in it (in case one does not hatch; if both sprout, the weaker one is removed or planted in a separate glass).
- The seeds are sprinkled with peat, sand or loose soil. It is important that the soil has good air permeability.
- The plantings are watered a little again and covered with plastic film, glass or plastic lids.
- Place in a warm (25-27 °C) place.
- After germination, the temperature is reduced to 20-22 ° C, the lid is removed.
A greenhouse is a covering material (polyethylene film) stretched over semicircular arcs made of plastic or metal. In this article you can find out how to build one correctly and why a greenhouse is better than a greenhouse.
Growing seedlings
After selecting the container, preparing the soil and seeds, you can begin directly planting the seed material for seedlings. To do this, follow the work algorithm:
- Place a drainage layer on the bottom of the peat pots and fill 3/4 of the pot with prepared soil on top. Place the container in the tray and moisten.
- Make a hole in the middle of the pot, about 1cm deep, and place a couple of seeds in it. Cover them with soil, slightly compacting it.
- Using a sprayer, moisten the soil surface with water and cover with glass or plastic film.
- Transfer the pots to a sunny windowsill or other place with a temperature range of 25-28 degrees.
Remove glass or film daily, moistening and ventilating the crops. This will prevent mold from appearing on the surface of the soil.
Moisten the soil not by watering, but by spraying water using a spray bottle.
Correct temperature conditions are important for seed germination. Shoots appear after 5-6 days at a temperature of 27-28 degrees. When leaves appear, you should adhere to a daytime temperature of 19-22 °C, and at night - 15-17 °C.
When the first leaf forms on the seedlings, fertilize with a solution of complex fertilizer.
Make sure that the plants do not stretch towards the light source. To do this, rotate the containers periodically. As the plants grow, move them away from each other so that the shadow created does not interfere with their quality development.
How and when to plant cucumber seedlings is described in more detail here.
Permissibility of planting cucumbers and tomatoes in the same greenhouse
It is not always possible for a gardener to install his own structure for growing each type of vegetable. However, there is a desire to get a harvest, for example, of tomatoes and cucumbers. In this case, it is necessary to place both types of crops in one greenhouse. Despite the fact that the requirements of plants for environmental conditions are somewhat different, by following certain rules, you can get a good harvest of both vegetables.
Table. Requirements of two vegetable crops
| Requirements | Tomatoes | cucumbers |
| Watering, l/1 sq.m | 10…15 (1-2 times a week) | 8…15 (1 time per day) |
| Temperature, degrees | +20…+25 | +25…+28 |
| Daylight hours, hours | 10…12 | 10…12 |
| Humidity, % | 60…75 | 85…90 |
The main differences in the conditions that crops like are temperature and humidity. If tomatoes love constant ventilation and dry air, then in cucumbers with a humidity of less than 80% the ovaries stop appearing.
However, it is no secret that gardeners have the opportunity to plant both crops in one greenhouse.
To do this you need:
- choose varieties of tomatoes that are resistant to fungal infections and high humidity, and cucumbers that are resistant to cool climates;
- place the crops in the greenhouse at a distance from each other.
Preparing soil in a greenhouse
Cucumbers grow well on loose and fertile soil, which retains moisture and is breathable. This is why fruits cannot be obtained on clay or sandy soils. The former are not able to allow the necessary air to pass inside, and the latter soils dry out too quickly, conducting water into deeper layers.
Things to consider:
- If the predecessors of cucumbers in the greenhouse were melons or pumpkins, then it is better to replace the soil with a new one, because it is depleted in nutrition and there is a high probability of common diseases and pests. It is advisable to plant cucumbers after cabbage, carrots, potatoes, onions, and peppers.
- It is necessary to prepare greenhouse beds in the fall. Remove all plant debris and dig up the soil, adding humus or compost 1 bucket per square meter. m. With this option, you can forget about organic fertilizing for 2-3 years, using only mineral fertilizers.
- Another solution to replenish nutrients when digging up beds in the fall is to distribute them per square meter. m of land 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate and 1 tbsp. dolomite flour (can be replaced with wood ash). In the spring, 2 weeks before planting seedlings, add peat, sawdust, humus to the soil, and dig shallowly again.
- To prevent cucumber diseases, be sure to treat the surface of the beds with a solution of copper sulfate. To prepare it, dissolve 1 tbsp in 10 liters of water. l. drug. Consumption rate - 1 liter per 1 sq. m.
- A good solution is to plant green manure in the fall, such as leaf mustard. Before frost, dig up the beds along with the plants. Over the winter they will undergo decomposition, enriching the soil with nutrition and disinfecting it.
An important nuance for growing cucumbers is warming up the soil. If there is a warm base of the beds, seedlings can be planted at any time of the year. If there is no such equipment in the greenhouse, then there are 2 solutions: wait for the soil to naturally warm up or insulate it with organic matter:
- To do this, remove the top soil layer to a depth of 15-20 cm, lay down straw, spread humus and compost on top, and fill the soil layer back.
- Spray the beds with hot water and cover with dark film. As organic matter decomposes, it releases not only nutrients, but also the heat the seedlings need. These events are carried out several days before planting the seedlings.
When to plant cucumbers for greenhouse seedlings
The optimal age of cucumber seedlings for planting in a greenhouse is 25...30 days. Overgrown and underdeveloped specimens will not take root well. In addition, when choosing the timing of sowing seedlings, you should take into account the climatic conditions of the region and the recommended dates for planting in a permanent place. For example, in the conditions of the Moscow region and the central zone, planting work in unheated structures begins in mid-May. In the Urals and Siberia, as well as in the Leningrad region - at the end of May.
Taking into account all the nuances, you can easily calculate the optimal sowing time: from the date of planting in the greenhouse, count back 30 days (the age of the seedlings) and several days before the emergence of seedlings (if seedlings were planted, then determine the optimal time for germination, not sowing; dry seeds germinate in 4 …6 days).
Transplanting
In greenhouses, without additional heating, plant seedlings no earlier than the end of May, when the soil temperature inside reaches 14-16 degrees, so that the weak roots do not freeze, but can adapt to new conditions. To measure the level of soil warming, lower the thermometer into the soil to a depth of 20 cm for 30 minutes in the morning.
Cucumbers can be planted in heated shelters as soon as 4 leaves have formed on the seedlings. This occurs approximately 35 days after sowing the seeds.
The most commonly used scheme for planting cucumbers in a greenhouse is:
- two rows of cucumbers are placed in a longitudinal bed;
- the distance between neighboring bushes in a row is maintained at 30-40 cm;
- seedlings in one bed, but in adjacent rows are planted in a parallel or staggered order, keeping a distance between them of at least 50 cm;
- the hole should be strictly under the trellis, or stretch a cucumber net between the rows.
Algorithm for planting seedlings in a greenhouse:
- Moisten the soil in the beds with hot water.
- Make holes and distribute peat pots with seedlings over them. The recess should be such that the upper edge of the container protrudes above the surface of the ground. Lightly compact the soil.
- Sprinkle a 2-centimeter layer of peat with sawdust on top, mulching the root part of the plants.
- Do not water the planted seedlings for 2 days.
Watch a video about planting cucumber seedlings in a greenhouse:
What are the benefits of a polycarbonate greenhouse?
Its advantage is that:
- the cellular structure of the material transmits light and retains heat, and also allows you to create and maintain a microclimate that is optimal for the growth and ripening of cucumbers;
- ventilation occurs due to the flow of air, without overcooling the plants and the risk of sunburn of the leaves;
- the structure is not dismantled for the winter, as it normally tolerates the cold season, as well as the heat.
You can read more about polycarbonate greenhouses in our article.
In a polycarbonate greenhouse, seedlings are not afraid of temperature changes.
Important! An additional advantage is that you can grow a crop of excellent cucumbers in a plastic greenhouse not only using seedlings, as in open ground, but even through seeds.
How to choose a polycarbonate greenhouse
Optimal conditions for the growth of cucumbers
For high-quality growing season of cucumbers, it is necessary to create and maintain a microclimate with certain conditions, as well as carry out agrotechnical work in a timely manner.
Watering
Cucumbers need regular watering of the beds, but make sure they do not become waterlogged. Warm the water for the procedure in the sun or take it from containers located inside the greenhouse. If you water with cold water, the crop will become infected with rot and spots.
If the temperature of the irrigation water is too low, a narrowing of the middle part is noticed on the fruits, and the cucumbers become deformed.
After watering, loosen the soil to prevent the formation of a crust on the surface. It will become an obstacle to the path of air to the root system and will serve to more quickly lower moisture into the lower soil layers. This procedure will also help cover the roots washed out as a result of moisture with soil. Mulching helps to retain moisture in the beds for a long time.
Sprinkling is very important for the crop. It consists of generously spraying the green part of the plant with water. Thus, the liquid flows slowly to the root system, allowing the cucumbers to better saturate themselves with moisture. In addition, the humidity inside the greenhouse increases, which has a beneficial effect on the plants.
Feeding
Be especially careful when fertilizing the soil in a greenhouse, since the formation of ovaries and the ripening of fruits directly depends on this. Keep in mind that an excess of mineral components in the soil is just as undesirable as their deficiency. Calculate the total volume of fertilizer applied per season, including limiting substances and mineral supplements. The number of procedures for adding nutrition to the soil for cucumbers should not exceed 5.
With a lack of nitrogen on the fruit, a narrowing of the tip and a change in its color to yellow are noticeable. If there is a deficiency of potassium in the soil, pear-shaped cucumbers are formed.
Cucumbers respond especially well to the addition of infusions of chicken manure, humus and mullein. To prepare food, mix 150-200 g of organic matter and 10 liters of water. Leave in a warm place to ferment for 2-3 days, stirring the mixture occasionally. Add 30 g of superphosphate. The distribution rate of the infusion is 1 liter per 1 sq. m of beds or for 4-5 plants.
During flowering, add 30 g of potassium salt to this infusion.
The amount of mineral nutrition per 10 liters of water (per 1 sq. m) in different phases of cucumber growth is slightly different:
- before fruiting: ammonium nitrate - 5-10 g;
- superphosphate - 20 g;
- potash fertilizers - 10 g.
- ammonium nitrate - 20-25 g;
Fertilizers can be applied by root and foliar methods. It is advisable to carry them out in the evening or in cloudy weather.
Light mode
A 10-hour daylight hours is sufficient for the growth and development of cucumbers. When the amount of light decreases, the growth rate decreases significantly. Therefore, in the absence of sunlight, due to weather conditions, it is impossible to do without the use of phytolamps or other sources of artificial lighting.
Temperature
Cucumbers are very dependent on the temperature in the greenhouse. So, in different phases of growth it is necessary to maintain different levels of heat:
- planting seedlings - 20-22 degrees;
- flowering - 25-28 degrees;
- fruiting - 25-30 degrees.
At temperatures from 17 to 19 degrees and from 35 to 40 degrees, the formation of ovaries does not occur.
Critical temperatures for cucumbers:
- growth cessation - 15 degrees;
- cessation of growth - 10 degrees;
- death - 7-8 degrees.
Humidity
Cucumbers are very demanding on the level of air humidity, so it should be maintained between 90 and 95%. When this indicator decreases, the ovaries stop forming and the cucumbers slow down their development.
Ventilation
The ventilation procedure is necessary to prevent the spread of diseases, especially rot, which develop in a humid, warm environment. In addition, this provides additional access to clean air into the greenhouse. Ventilation helps reduce the air temperature on hot days to the required level.
Bush formation
Shaping helps to avoid bush thickening and optimize its productive qualities. Cucumber plantings become not only beautiful, but also evenly illuminated by the sun, accessible for aeration, and convenient for various agricultural work. This procedure involves pinching the shoots and tying them with the further direction of the head lash.
It is important to remember that all manipulations to form a cucumber bush are carried out strictly before the onset of the flowering period. When the first flowers appear, any work related to moving the lashes is prohibited.
The need to form a bush is explained by the following arguments:
- If there is excessive branching, the root system cannot cope with saturating the entire plant. As a result, the fruits become deformed and their taste deteriorates.
- Dense vegetation does not allow air to penetrate through the greenery. This negatively affects fruiting and creates a favorable environment for pathogens of various diseases.
- Weeding, loosening, spraying and watering are more convenient when cucumber bushes are formed.
Pinching (pinching)
Pinching helps reduce leaf mass for a more active and longer fruiting period. Removing canes with male flowers that do not bear fruit stimulates the development of female fruiting inflorescences. The quantity of harvest and its quality increases.
To perform the procedure correctly, you need to be able to distinguish male and female flowers from each other:
- female inflorescences are formed in pairs, and barren flowers are formed in 6 pieces;
- the stem of the female flower is longer than that of the male;
- ovaries are present only on female inflorescences.
Pinching is not carried out only on specially bred hybrids that have a single-wattle development or do not produce an excessive amount of barren flowers.
For self-pollinating varieties, leave enough male flowers so that their number with female ones is approximately equal. For parthenocarpic varieties, the presence of male inflorescences is not required.
The pinching procedure after tying cucumbers goes like this:
- When forming the 5th leaf, all shoots and tendrils located below it are removed.
- When 7-8 leaves appear, a pair of shoots are left from the central stem.
- After the 11th leaf, the tips of the shoots are pinched, provoking their peripheral development and ovaries. On each shoot, 3 leaves and 3 ovaries are left.
- Parthenocarpic varieties are formed, leaving one stem. When it grows to 50 cm, the tendrils, flowers and branches are removed, and the lateral shoots are pinched down to 1 leaf.
Pinching forms the bush in the form of an inverted pyramid.
Tying up
Tying cucumbers is done to:
- the lashes did not interlock with each other using whiskers;
- the process of plant care and harvesting was simplified;
- the bush had enough sunlight for the entire plant part.
These measures make it possible to horizontally grow cucumbers and form a bush. Mechanical damage to vines and fruits and their rotting on the ground are prevented. You should start tying when the seedlings in the greenhouse grow to 30-40 cm. At this time, the vine is still flexible and does not break when its position changes.
To carry out garter work you will need:
- wooden or iron supports;
- strong, taut wire;
- trellis net for cucumbers;
- garters made of long strips of cotton or nylon fabric about 3 cm wide.
You should not use thin laces or wire to tie cucumbers, as they will pinch the stem as they grow. Disinfect all garter material by boiling or bleach before use.
You can purchase special plastic garters. Their clamping is adjustable with notches and can be used repeatedly.
Formation of a cucumber bush
Any plant produces additional shoots or branches during its growth. For plants growing in the wild, this determines their branchiness or bushiness. In cultivated plants, side shoots also create the size of the bush. However, as these plants subsequently bear flowers and fruit, the growing additional shoots begin to take away nutrients, which can lead to a poor harvest. Therefore, during growth it is necessary to form a bush. The most commonly used method is pinching, i.e. removing emerging shoots.
In addition, when constructing a greenhouse, the installation of special devices for tying cucumbers is also organized. These could be trellises, or they could simply be ropes descending vertically from the ceiling to which plants cling.
The process of forming a bush can begin after 8-9 new leaves appear on the stem.
In order for growing cucumbers to be even and large, it is necessary to leave the most well-developed fruits somewhere in the 5-6 axils, and remove the rest. In the 7th sinus the entire ovary is removed, and in the 8th sinus a few fruits must again be left.
When the stem reaches the roof of the greenhouse, it is pinched. This is done over the second or third leaf on the main stem, which are located after the fruit. But many gardeners, in order to get a larger harvest, do not pinch the plant that has reached the top of the greenhouse, but lower it down. As a result, the bush grows towards the ground, where it is then pinched.
The video below shows the entire process of correctly forming a bush.
Diseases and pests
It is reckless to assume that closed soil protects cucumber plantings from pests and various diseases. This means you need to know what dangers threaten the harvest and how to deal with them. The following diseases are common:
- White rot. A fungal disease characterized by the presence of a light, almost white, coating not only on the fruit, but also over the entire surface of the bush. It spreads quickly, destroying plants. The fungus persists in the soil. Control measures involve destroying affected plants and changing the soil.
- Gray rot. Identified by slippery gray spots on the surface of fruits, flowers and ovaries. At the first stage of infection, spraying with a solution of copper sulfate 1 tsp is carried out. and 1 tbsp. ash per 5 liters of water. The drug "Barrier" is effective. When the disease is in an advanced state, only radical methods can help.
- Root rot. Drying leaves, changing the color of the plant, and the appearance of cracks on the stems are all signs of infection. Rot can be caused by planting seedlings too deeply, excessive watering, or cold water when moistening. Sprinkle the areas affected by the fungus with crushed chalk or wood ash and dry. Do not allow moisture to enter the plant when watering. Dead plants are destroyed by fire, and soil is removed from the holes by spilling a solution of manganese or copper sulfate. Afterwards, the hole is filled with new soil.
- Powdery mildew. It is characterized by the appearance of a white coating, first on the leaves of cucumbers, and then on the stems. The fungus actively spreads in warm and humid conditions, so if it is detected, treat the cucumbers as soon as possible. The preparations “Topaz” and “Zaslon” have an effect against powdery mildew. Their use when preparing the solution must be in accordance with the instructions.
- Downy mildew. It is determined by the appearance of spots on the leaves of cucumbers that resemble burns. In a couple of days the sheet dries completely. To stop the spread of the disease and destroy it, spray with Quadris (5 g per 10 liters of water). You should stop watering and ventilate the greenhouse more often, avoiding excessive air humidity.
- Brown spot. When infected, fruits develop wine-brown spots oozing from the inside. Then the rot spreads to the entire plant. Spots of the same color are seen on leaves and stems. Within a week the plants die. Control measures come down to the destruction of diseased plants and reducing the level of soil and air moisture in the greenhouse.
- Black mold. Manifestations of the fungus are noted in the appearance of spots on the leaves, which over time merge into one and become covered with black spider mold. Preventive measures include the use of treated seeds and disinfection of the soil and premises.
In addition to diseases, insect pests can attack the greenhouse crop. Some of the most common are:
- Melon aphid. The negative impact of aphids is manifested in twisting and wrinkling of leaves on the vines. If you turn them over, you will notice a cluster of small insects on the underside of the leaf blade. They feed on plant sap, which leads to a lack of nutrients, stunting of development and drying out of the crop. In small areas, it is recommended to use traditional methods of control against aphids. This can be an infusion of onion peels or an ash solution with laundry soap. Large greenhouse farms use chemicals.
- Greenhouse spider mite. It is difficult to detect due to its small size, but cobwebs on the plant are a sign of the presence of a mite.
The appearance of insects is associated with the presence of weeds in the greenhouse and conditions suitable for the parasite. It is recommended to fight it only using chemicals, so as not to waste valuable time. The following drugs can be used: “Plant-pin”, “Aktellik”, “Fitoverm”, etc. They must be processed strictly in accordance with the instructions for the drug.
Problems with plants
When growing cucumbers, many gardeners encounter various troubles: flowers fall off, leaves and ovaries turn yellow, and plant growth stops. This can be caused by many factors.
- Poor quality seeds. You should always check the seeds in a 5% salt solution - seeds that float are unsuitable for sowing and should be thrown away. You can also check the seeds for germination by wrapping them in a damp cloth - if more than 60% do not germinate, the seed is rejected.
- Lack of nutrition. In this case, the leaves turn yellow and dry out, and the ovaries fall off or do not grow. Plant growth stops. It is necessary to apply complete mineral fertilizer to stimulate growth.
- Overmoistening of the soil. Plant growth slows down, they look rickety, stunted, and oxygen supply to the roots is poor. You should give air to the root system, that is, “dry” the soil: loosen and mulch - add dry soil and peat.
- Low night air temperatures. The symptoms are the same as with excessive soil moisture. It is necessary to control and maintain the optimal (22–26o C) air temperature in the greenhouse.
- Plants are not pollinated. In the absence of pollinating insects, cross-pollination is carried out manually. One male flower pollinates no more than 5 female flowers.
- Plant disease or pest damage. The leaves dry out and curl up, brown or yellow spots appear on their surface, and the fruits take on an ugly shape. It is necessary to carry out regular measures to protect plants from pests and diseases.
Leaves turn yellow due to lack of nutrition
Problems and their solutions
It happens that infection with diseases is excluded, but some problems still arise on the plantation. Let's look at some of them.
No ovaries
Reasons for the problem of ovary formation on cucumbers:
- insufficient ventilation;
- deficiency of minerals in the soil;
- impossibility of pollination (on pollinated varieties);
- unfavorable temperature conditions, or microclimate in general.
The lower branches dry out
Such manifestations are possible for several reasons:
- scorching sun rays;
- contact with leaves of mineral root fertilizers;
- waterlogging or moisture deficiency in the soil;
- deficiency or surplus of nutrients;
- lack of light and air.
Fruits grow slowly
Slow fruit growth is due to:
- low-quality seed material;
- failure to comply with the deadlines for planting seeds or planting seedlings;
- microclimatic disturbances;
- lack or excess of nutrition;
- dense planting without bush formation.
Cucumbers are bitter
A bitter taste (exceeding the cucurbitacin level) in cucumbers can be observed due to plant stress for several reasons:
- too bright scorching sun rays;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- violations of the temperature regime necessary for fruiting;
- lack of nitrogen and phosphorus in the soil;
- interruptions in watering or cold water;
- plants interfere with each other due to their close proximity.
Growing cucumbers in greenhouse conditions is not easy. The quality of the harvest and its quantity depends on many factors that need to be considered from the preparation stage to the fruit harvesting stage. By following all agricultural techniques and creating the necessary conditions for the crop, you will enjoy growing, and cucumbers will delight you with fragrant fruits for a long time at any time of the year.
0
0
Copy link
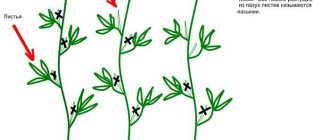
How to form lashes and is it always necessary?
The greenhouse should not resemble a jungle. Dense thickets are predictable when the gardener did not take care of the timely formation of the vegetable. To avoid getting a forest of cucumber grass instead of a harvest, you need:
- Find the first three true leaves and remove the buds and shoots from them. This will give impetus to the growth and formation of a large number of ovaries.
- At a height of up to half a meter, break off the side shoots completely, leaving each of them with a single leaf over the next 50 cm. Three leaves are left at a distance of 100 to 200 cm from the root.
- All lateral mini-shoots found on the second row must be pinched onto one leaf. The taller the plant is, the greater the number of shoots allowed. We throw the main trunk over the trellis and pinch it again, leaving 40 to 60 cm.
A proper greenhouse with cucumbers does not look like a tropical forest.
Table 1. Requirements for the formation of lashes in cucumbers of different varieties.
| The need for manipulations to form a bush | general characteristics | Variety |
| Frequent | Hybrids prone to forming a large number of branches, bred for cultivation in a greenhouse. | Moscow greenhouse; Yuventa and Rodnichok; Epic and Ritual; Topolek and Vilina; Malachite and NIIOH 412. |
| Rare | Hybrids with little branching on the sides. | Zozulya and the Golden Cockerel; April and Understudy; Gribovchanka and TCXA 3707. |
| Absent | Varieties with flowers in one ovary. | Brigadier and Neroshimy; Muromsky and Libelle; other. |
Additional information about cucumbers - useful to read!!!
Attention: Notes on the last tip. 1. Rinse and dry the shell thoroughly so that later you do not have the disgusting smell of decomposition. 2. The method requires exceptional dexterity due to the fragility of the shell.