To grow cucumbers, many owners of suburban areas install protected ground structures: greenhouses and greenhouses. The result of cultivating vegetable crops in such structures is almost always high yields of healthy fruits. However, to achieve results it is necessary to follow a number of agrotechnical rules. Planting cucumbers in a greenhouse should also be carried out using a certain technology.
Growing cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Even those who have never been involved in vegetable growing before, having studied its basic aspects, are able to achieve success. But planting and caring for cucumbers in a greenhouse requires certain labor costs. First you need to build a shelter, which needs to be taken care of in advance, and prepare the beds. Polycarbonate greenhouses are the optimal solution; cucumbers grow and bear fruit well in such closed ground. Purchasing high-quality planting material is also an important stage of preparation. It is recommended to choose seeds of crops that are suitable for growing in the region, do not require pollination by insects, can withstand unfavorable climatic conditions (drought, cold spells and frosts) and are immune to the most common diseases. You should also pay attention to the timing of fruit ripening. Cucumbers can begin to bear fruit a month or two after germination. It is best to plant plants with different characteristics in a greenhouse. This approach will help produce crops over a long period of time.
Depending on your preferences, climate and capabilities, you choose the method of planting cucumbers.
How to plant cucumbers with seeds correctly
Seeds can be planted directly in the greenhouse (this method is usually practiced in the southern regions). However, you should do a little preparation beforehand.
First, the seed material is checked for germination, for which it is placed in a container with a saline solution. The floating seeds can be thrown away; nothing will grow from them. After this procedure, disinfection should be carried out. This operation is especially indicated if you use your own planting material, since producers most often carry out disinfection. For processing, you need to prepare a solution of potassium permanganate, in which the seeds are kept for about half an hour.
Experienced gardeners also use a little trick - bubbling. The procedure consists of placing the seeds in water for a day, into which air is supplied (for example, with a hose connected to an aquarium compressor). This measure allows you to saturate the seeds with oxygen, which improves their germination.
Soaking seeds for several hours (the exact time is indicated in the instructions for the specific product) in a growth stimulator accelerates their germination. Today, manufacturers offer a sufficient range of such compounds; Epin and Zircon are in great demand.
To treat seeds, you can also use natural growth stimulants, such as aloe juice or honey.
You can start planting seeds, but pre-germination guarantees early germination. Otherwise, it is possible that after some time it will be necessary to re-sow. The easiest way to germinate cucumbers is in wet gauze, folded in several layers, or in fabric made from natural fibers. The seeds remain in the material, which will have to be periodically moistened, for several days. After about a week (sometimes grains germinate in 2 days), small sprouts should appear. You can also use wet sawdust for germination, covering the container with polyethylene.
Seeds with sprouts that have appeared can be planted in closed ground.
Recommendations for planting seedlings
Pre-growing seedlings helps to get an earlier harvest and save planting material. Its preparation is carried out in the same way as described above.
It is recommended to plant sprouted seeds one at a time (maximum two) in a separate container with a volume of 300...500 ml. Soil for seedlings can be used purchased (for growing vegetables) or you can mix it yourself from peat, humus, turf soil (in equal quantities) and sawdust (half as much as the main ingredients). It is recommended to disinfect the soil either in the oven, or with boiling water, or with a solution of potassium permanganate. You can also purchase peat cups or tablets for seedlings.
Seeds are placed in a container with soil (at an angle, the spout should be on top). Having sprinkled them with earth (a layer of about 15 mm), it is necessary to water the future seedlings. Until the sprouts appear, the seedlings should be covered with film.
Caring for seedlings is not difficult: they need to be watered and fertilized. Plants will need nutrition two weeks after germination.
Properly preparing seeds for sowing
Previously, before germination, gardeners performed a procedure such as heating the seeds. This is long-term heating of dry seeds near heating devices at a temperature of 30-35 degrees.
Such events have a positive effect on increasing the formation of female flowers in all pumpkin plants.
When preparing self-pollinating and parthenocapic hybrids for sowing, the seeds do not need to be heated, since they do not have the problem of forming barren flowers.
Nowadays, seeds that have already been treated with thiram are often sold. Information is contained on the packaging. The seeds are colored poisonous green as a warning about the toxicity of the applied substance. Thiram is a fungicide that is used against a complex of diseases. Such seeds are not soaked or germinated.
If you have ordinary seeds, then they need to be treated with some kind of fungicide or a saturated solution of potassium permanganate. When there are many varieties, you need to put them in gauze bags and place them in the prepared solution for 15-20 minutes.
After this, you need to wash the seeds and start germination. Germination does not affect the yield, but avoids planting empty seeds.
Before germination, the seeds should be placed in a small amount of water for several hours or overnight to swell. The water should cover the seeds a little so that they do not “suffocate”. There is no need to harden cucumbers because they do not have the cold tolerance gene.
Advantages of the seedling method:
- allows you to get results earlier than when sowing seeds;
- the plant will grow and become stronger in comfortable conditions;
- sorting is possible: you can see which plants develop better and which worse;
- some seeds do not germinate immediately or freeze during seedling growth.
Plants of the same height will be easier to care for. The rest can be planted in a corner so that plants of the same type grow in one place. Such measures will allow you to get an early and healthy harvest.
When to sow cucumber seeds for greenhouse seedlings
When determining the timing, it should be taken into account that seedlings are transferred into closed ground approximately 3-4 weeks after sowing the seeds (when 4-5 true leaves grow). By this time, the greenhouse should have suitable conditions for young plants.
The climate is different in different regions. Therefore, if we are talking about structures without additional heating, you should focus on approximately the following dates for planting seeds in the spring:
- southern Russia: early March;
- northern Russian Federation, Siberia: mid-April;
- center of Russia: early April.
Preparing soil and beds in a greenhouse for planting cucumbers
Cucumbers are demanding about soil quality. Everything matters: temperature, acidity level, air saturation, humidity, nutritional value. Before planting cucumbers in a greenhouse, you need to prepare a shelter. It is best to do this in the fall, after harvesting. It is recommended not to postpone the operation until spring, when there is already a lot to do in the garden.
The work is carried out in several stages:
- Cleaning up plant debris. It is necessary to clean the greenhouse from plant residues (both cultivated and weeds).
- Disinfection. It is necessary to disinfect the soil by spilling it with a solution of copper sulfate, and the structure itself by treating it with a spray solution of bleach infused for several hours (0.3 kg/bucket of water). You can also use fumigation with a sulfur smoke bomb, after which you need to ventilate the building.
- Soil preparation. The soil in a greenhouse or greenhouse should be loose and neutral acidity (chalk or dolomite flour should be added to acidic soil). It is recommended to replace the top layer about 5...7 cm thick. A month before planting cucumbers, it is necessary to add humus and fertilizers, which contain phosphorus and potassium. Two weeks before transferring the seedlings, it is better to cover the ground with polyethylene, so it will warm up well. If vegetables were attacked by insect pests last season, you need to spill the soil with an insecticide solution that will destroy the beetles that survived the winter.
- Installation of supporting structures. To form grown plants, it is necessary to place trellises or stretch guides under the ceiling, to which the stems will subsequently be tied.
It should be noted that gardeners must take into account the rules of crop rotation. Suitable predecessors can saturate the soil with the elements necessary for cucumbers. These crops include: legumes, root vegetables, cabbage. Tomatoes, pumpkins, zucchini and melons should not grow in the greenhouse before cucumbers.
Timing for planting cucumber seedlings in greenhouses made of different materials
It is important to transfer seedlings to a permanent place on time, taking into account several factors.
The air in the greenhouse should warm up to +16…+20 degrees. Soil temperature is also of great importance. It should not be less than +15 degrees. Otherwise the plants will not grow. Normal humidity level: 75...85%.
Different regions have their own timing for planting seedlings. Optimal conditions in unheated greenhouses are established at different times. If in the south seedlings are planted in the first ten days of April (although there the vegetables do well in open ground), then in the Moscow region the seedlings usually cannot be tolerated before the beginning of May. In the Urals, this operation is carried out only in the middle of the last spring month.
It is also important what type of greenhouse is installed on the site. If it has a heating system, then crops can be grown all year round. Seedlings are planted when the plants are about a month old, regardless of climatic factors.
The material from which the structure is made should also be taken into account. In polycarbonate and glass greenhouses, seedlings are planted approximately 2 weeks earlier than in film structures. That is, if plants are transferred to buildings of the first type in early April, then they can be planted in film shelters in the second decade of this month.
Many gardeners are guided by the lunar calendar when carrying out work. This celestial body is capable of influencing plant growth. It is recommended to plant cucumbers (like other crops that grow primarily above the ground) when the Moon is waxing. At this time they take root better.
It is not recommended to plant cucumbers during the full moon.
Schemes for planting greenhouse cucumbers in narrow beds
Cucumbers are demanding when it comes to lighting and nutrition. Therefore, although all greenhouse owners want to plant as many plants as possible, plantings should not be too thick. In addition, if the bushes grow too closely, they are more susceptible to diseases and pests. And it becomes difficult to care for vegetables. But even in narrow beds you can place enough plants to get a good harvest.
Planting density depends on the crop variety. Weakly branched bushes require less space for growth and development. You should also take into account the saturation of the soil with nutrients. Plants are planted less often on poor soil than on soil rich in microelements. Usually per 1 sq.m. The beds contain 3-4 plants.
Most often, long narrow beds with a passage between them are arranged in greenhouses. The plants on them are easy to care for. They are convenient to control, which helps to detect signs of disease or beetle infestation in time.
Horizontal method of planting seedlings
When growing cucumbers in this way, there is no need to install supporting structures. The stems grow along the ground and grow in different directions. In this case, they receive a sufficient amount of sunlight, but caring for the plants is difficult. Weeding the plantings, treating them from diseases and pests, and picking cucumbers is very inconvenient. The distance between seedlings in this case should not be less than 40...60 cm. As a rule, this method is rarely used in greenhouses.
Vertical method of planting seedlings
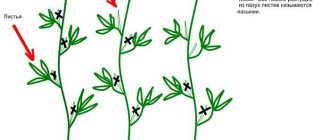
Installing various kinds of supporting structures that help the plant cling to them and stretch upward allows you to plant cucumbers more compactly. You can leave only 30...40 cm between the bushes. Tied cucumbers develop well, they are sufficiently blown with air. Cutting crops, watering, feeding, forming bushes is easy. Supports can be: trellises, ropes lowered from above, mesh or several rows of wire.
Diseases and pests
Most often, greenhouse cucumbers are affected by fungal diseases:
- anthacnose (scarp);
- white rot (sclerotinia);
- gray mold;
- powdery mildew;
- downy mildew;
- root rot.
Among bacterial infections, bacteriosis caused by the bacterium Pseudomonas lacrimans should be noted.
The main greenhouse pests of cucumbers are aphids and greenhouse whiteflies.
To combat diseases and harmful insects, modern industry produces effective drugs. An important part of the fight is preventive treatments and soil rotation.
Optimal distance between greenhouse cucumbers
In protected ground, several plant placement schemes are used. The frequency of planting seedlings also depends on the method chosen.
- Two-line method.
In this case, the seedlings are planted in 2 rows. Cucumbers are located opposite each other. A distance of about half a meter should be maintained between rows, and 40 cm between sprouts. A row located near the wall of the greenhouse should be no closer than 25 cm from it. For crops that do not have large green mass, this method is preferable. In order for the bushes to be illuminated by the sun and ensure their aeration, it is important to promptly remove lateral shoots and excess foliage.
- Chess order.
If you move the holes of the second row by half the step that is maintained between plants, the cucumbers block each other from sunlight less. This planting method is used when growing crops with large leaves and large fruits. You can leave only 30 cm between bushes.
- Single row placement.
In small greenhouses, cucumbers are often planted in the garden in one row. Varieties that are distinguished by friendly fruiting grow well with this scheme. You can leave only 25 cm between plants; they will already be well lit.
Collection of greens
When there is a wave of fruiting, the gardener cannot relax. At least 2–3 times a week, the plantings need to be inspected and harvested for the production of winter preparations, and larger cucumbers for salads and pickling.
The shelf life of fruits is different for each variety. Labels indicating the variety will help you determine where each variety grows and how it can be used. Many people make the mistake of planting salad and canned hybrids next to each other: salad cucumbers in the marinade spoil its quality.
What problems do gardeners face?
Greenhouse owners, especially those who grow cucumbers for the first time, are not immune from mistakes that lead to deterioration of the growing season of the crop and a decrease in yield.
Common mistakes when planting seeds and transplanting seedlings
Sometimes the time and effort spent on growing plants does not bring the expected results.
Why gardeners cannot grow seedlings or subsequently get a high yield of vegetables:
- Due to poor preparation of seed material, plants become weak and sickly.
- Early planting of seeds leads to the fact that by the time the cucumbers are transferred to the greenhouse, they become too elongated. Such weakened seedlings do not take root well and may even die.
- If you plant seeds too deep in containers with soil, they may not sprout. The thickness of the layer of earth above them should not be more than 20 mm.
- When planting seeds not in individual containers, but in a common container, the sprouts that appear are often too thick and cannot develop normally. It is necessary to maintain a distance between plants within 40...50 mm.
- A lack of sunlight becomes one of the reasons for excessive stretching of seedlings. For normal development, it requires light for at least 12 hours a day.
- Cold slows down the growth of seedlings, and too high an air temperature also leads to elongation of sprouts. Optimal values for growing cucumbers: +20…+25 degrees.
Plants also need moderate watering, fertilization, and timely picking. If you don’t do this, you won’t be able to grow strong seedlings. However, even having received healthy and well-developed seedlings, without proper care for them in a greenhouse, you cannot expect a decent harvest.
Choosing a variety for indoor soil
Self-pollinating or parthenocapic cucumber varieties are suitable for indoor soil. Both do not need bees. Plants set fruit in closed ground conditions without external intervention. But the process of ovary formation itself occurs in different ways.
Self-pollinating cucumbers are those in which pollination occurs as a result of pollen being transferred from the stamens to the pistil within one flower. In this case, the plant does not have female and male flowers, and accordingly, there are no barren flowers.
Parthenocapic is translated as “virgin”, that is, the cucumber sets without pollination. In adulthood, parthenocapic fruits are always distinguished by their appearance. They have virtually no seeds. And if they exist, they are very tiny, in their infancy.
Among self-pollinating varieties there are varieties and hybrids. The variety differs from a hybrid in that it is a fairly stable form that transmits its basic qualities through the seeds. If you buy a variety of cucumber once, you can plant it year after year, collecting the seeds yourself. Its varietal characteristics will be preserved.
Currently, hybrids are more common; they are designated in their names as F1. Such cucumbers do not transmit their qualities through seeds, so gardeners have to buy them every year. If this is not done, then splitting occurs in the second generation, and it is not known exactly what characteristics will appear as a result.
Let's consider several popular varieties and hybrids for greenhouses and greenhouses:
- Adam F1. Dutch self-pollinating high-yielding hybrid. Valued for setting fruit very early. In just a month and a half you can start harvesting. The second undoubted advantage is the extended fruiting period. Cucumbers are arranged 5-7 together. With insufficient care, 2-4 fruits are tied in the knot. Cucumbers grow not only beautiful in appearance: dark, small, with small thorns. They are delicious both prepared and fresh.
- Zyatek F1. A very popular parthenocapic hybrid. It is loved for its early ripening, the first fruits appear already on the 40th day. The bouquet arrangement of the ovaries is also appreciated. The cucumbers of this hybrid are gherkin-type, cylindrical in shape. They do not grow large; growth stops at 14-16 cm. The fruits of this variety are tasty and productive.
- F1 is the envy of everyone. Despite the fact that this hybrid appeared relatively recently, it has already become popular among gardeners due to its super-yielding and bunched arrangement of fruits. The variety's lashes are powerful. They develop right up to frost and produce an excellent harvest on the side shoots. The thin skin makes it possible to use these fruits both fresh and pickled.
- Well-fed dad F1. One of the salad varieties for indoor soil. Long, smooth, cylindrical fruits are suitable for salad and fresh consumption. This variety is not suitable for whole-fruit canning, but it is just right for preparing lecho and other preparations where chopped fruits are needed. Just like the previous ones, this variety has bunched ovaries, is early ripening and disease resistant.
- Ecole F1. One of the new, very successful parthenocapic hybrids. This cucumber is suitable for those who can preserve pickles (greens 3-6 cm). That is why it can be picked within 35-38 days after the first shoots appear. Ecole's greens are smooth, cylindrical, and grow in bunches. They are collected every day so that they do not overgrow.
- Chinese cold-resistant F1. From the popular series of long and sweet cucumbers. It is suitable for growing in greenhouses, where it is easier to tie it up. Its lashes are powerful and grow quickly. The fruits themselves reach half a meter in length. Smooth and tasty cucumbers can be used in salads or prepared into slices for the winter.
The labels on the bags of cucumbers “Parthenocapic (self-pollinating)” are incorrect. A variety or hybrid can be one or the other. Most often we are talking about parthenocapics.