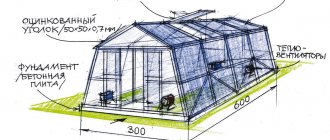
A greenhouse according to Mittlaider is a structure characterized by an unusual design of roof slopes and windows, which creates optimal conditions for gas exchange. The roof of the greenhouse has two slopes placed at different heights with a hole for ventilation. This layout promotes air circulation. The design of the “American” is usually carried out taking into account its localization to the cardinal points. The most widespread are greenhouses in the form of arches.
Advantages of a greenhouse according to Mittleider
Comparison of various greenhouses
The advantages of the structure include:
- simplicity and practicality, you can assemble the structure yourself with your own hands;
- a frame that is resistant to increased loads and can withstand a significant mass of snow;
- the wooden frame can, if necessary, be disassembled and transported to a new location;
- efficient and uniform gas exchange thanks to thoughtful ventilation:
- air openings and roof slopes have an original optimal location;
- it is possible to easily automate the process of opening and closing transoms;
- possibility of growing a variety of crops:
- absence of drafts that can have a negative impact on plant metabolism;
- structural elements made of wood, as well as a ventilation system
- prevent the appearance of condensation;
- the greenhouse is characterized by an optimal height, which provides
- the ability to grow vigorous cultivated plants;
- high horizontal beams create convenience for gardeners, providing the opportunity to tie up climbing crops (for example, tomatoes);
- a significant internal volume and a well-functioning microclimate control system ensure its relative stability and greater resistance to fluctuations in outside air temperature.
Advantages and disadvantages
Speaking about tent greenhouses, one cannot fail to note their undoubted advantages.
Advantages of awning structures for gardening:
- relative lightness and mobility of the structure;
- excellent ability to retain heat;
- possibility of long-term operation;
- protection of plants from ultraviolet radiation;
- provision and creation of the necessary microclimate for plants;
- the presence of ventilation holes, due to which you can regulate the air temperature and humidity;
- speed of frame assembly;
- the coating does not break or crack;
- no foundation is required to install the structure.
To install a tent greenhouse you do not need a foundation
Disadvantages of tent greenhouses:
- the greenhouse coating will not withstand heavy hail;
- You cannot use such a greenhouse in winter;
- for the winter, the awning must be removed, even if the frame itself remains to spend the winter outside;
- the tent greenhouse is afraid of fire, and therefore you cannot smoke in it;
- the structure “sails” in strong winds and can fly away.
By the way, the last point is quite easy to solve by pressing the awning at the bottom of the greenhouse along the perimeter. A tent greenhouse is also perfect for those summer residents who are worried and afraid about the integrity of the structure during the winter. The fact is that the coating from polycarbonate greenhouses is usually not removed for the winter; it has to cope with a significant snow load. And in an awning greenhouse, the covering material must be removed, therefore it is protected from the effects of snow and wind.
Prices for tent greenhouse
tent greenhouse
Modifications of greenhouses according to Mitlider
A special feature of the structure is the different angles of inclination of the opposite parts of the roof.
As a result, they are not adjacent to each other. This feature allows the gardener to build a vertical transom window along the entire length of the greenhouse. It is attached to the top ridge using piano hinges.
During its existence, the greenhouse has undergone a number of modifications:
- Traditional (canonical). It has vertical walls and a flat roof with two slopes. In the classic version, the width of the structure is 6 m, the length is 12 m, the height of the walls is 1.8 m. Ventilation openings are located on the south side.
- Arched. It is distinguished by a semicircular roof.
- With two transoms. This is the classic “American” type. It differs from the canonical model by the presence of a window under the southern slope. Its purpose is to enhance ventilation.
Transparent polycarbonate is used as a covering. Film can also be used. The use of polyethylene reduces the cost of construction.
Other features of the greenhouse
The design has the following features:
- the rafters are fixed on the topmost beam;
- the wide part of one slope goes to the top;
- the rafters on the south side are fixed to a ridge located 45 cm lower from the other ridge;
- the formed opening of 45 cm allows for easy installation of the ventilation system;
- this opening is equipped with film, glass or polycarbonate.
The greenhouse design helps optimize all costs associated with growing seedlings and using the greenhouse. Thanks to this idea, the American specialist was able to gain well-deserved attention to his technology.
Greenhouse according to Mitlider: drawings
When creating a project, not only the size of the greenhouse is taken into account, but also its orientation to the cardinal points. The correct location is the higher side on the north side, and the ventilation holes on the south. This allows you to protect the crops grown from the cold air masses of the north. The air is heated mainly through a flatter roof oriented to the south.
The classic Mittlider design is intended for a small farm, so when building a greenhouse on a summer cottage, they try to reduce its parameters. At the same time, they try not to change the vertical dimensions, the length is chosen arbitrarily, the width is selected taking into account the number and expected size of the beds, as well as the paths between them. Usually the width is limited to one meter. When determining the dimensions of the paths, they try to take into account the need to use garden carts and other mechanisms or devices. Practice shows that their sufficient width is ½ meter.
When performing drawing work, the following nuances are taken into account:
- The frame can be made using wood and/or metal elements. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the likely wind and snow load on the profile.
- The bottom trim is made of 10*10 cm timber made of hardwood or from a profile pipe with a cross-section of more than 5*5 cm. In order to increase wear resistance, wood elements are treated with an antiseptic and painted with kerosene-bitumen mastic, and metal profile elements are coated with anti-corrosion compounds.
- Vertical posts must be made of timber with a thickness of more than 6 cm, or, when using a metal profile, with a cross-section of more than 4*4 cm.
- The braces are installed using pipes or slats with a cross section of 4*2 cm.
- In order to prevent roof deflection, beams are made from boards 10*4 cm in diameter, or from a profile pipe with a cross-section of 4*2 cm.
- The greenhouse is most often covered with polycarbonate or polyethylene film.
Gardeners' opinions
The Mitlider greenhouse has extremely positive reviews. It can withstand heavy snowfalls and gusty winds. This is achieved by a strong frame and placing beams every two meters. Sloping beams in corners and ceilings secure the effect.
Gardeners also note the following positive aspects when using an American greenhouse:
- the greenhouse can be made collapsible, which is extremely convenient;
- support beams help in tying up tall plants;
- you can work in a greenhouse without bending;
- extensive greenhouse area;
- thanks to the stable microclimate, there is no need to monitor the plants every day;
- If necessary, repairs are simply carried out on the desired fragment.
In general, the construction of American greenhouses differs little from the construction of traditional structures. Mitlayder greenhouses have earned a worthy reputation due to their versatility and efficiency of the elements they contain.
Choosing material for the greenhouse frame according to Mittlaider
The selected material determines the service life of the greenhouse and its properties in terms of maintaining the required microclimate. When making a frame, gardeners most often choose wood, PVC or polypropylene, or metal.
Made from wood
Hardwoods are most often used: oak, hornbeam, beech, spruce, pine.
In this case it is necessary:
- determine the moisture content of varieties, not exceeding 20-22% (determined with a moisture meter);
- make sure there are no traces of insect pests feeding on wood;
- exclude the presence of cracks, chips or knots in the selected samples (there should not be many).
Made from polypropylene or PVC
When choosing plastic pipes, their rigidity and wall thickness are assessed. This is important for keeping fit.
Made of metal
The use of pipes allows the construction of structures of any shape.
Comparative characteristics of materials used in construction
A comparison of various materials is shown in the table:
| And the material used | pros | Minuses |
| Wood | Environmentally friendly, easy to process and install, inexpensive material that can last 10-15 years with proper care. | Low resistance to fungi and bacteria (preliminary and regular treatment with oil-based ingredients is recommended). |
| Polypropylene or PVC | It is distinguished by its environmental cleanliness, increased resistance to corrosion, low and high temperatures (open fire), moisture, the action of microflora, as well as durability. Plastic pipes are easy to install. The design is lightweight, making it easy to transport. | The relative lightness of the structure makes it vulnerable to strong wind gusts and prone to deformation. |
| Metal | Ease of installation work, durability and long service life (more than 25 years). | Relatively high cost, untreated ferroalloys are prone to oxidation (corrosion). |
Choosing material for covering a greenhouse according to Mitlider
Typically, cellular polycarbonate or polyethylene film is used to cover a greenhouse.
Polyethylene film
The choice of PVC film or polyethylene film allows you to operate the greenhouse for 2-3 seasons (or even 5 years). When choosing film materials, preference is given to thermally stabilized samples with reinforcement. They are characterized by increased strength and resistance to solar radiation. The recommended thickness of film materials is at least 200 microns.
The original “American” has a double film coating, with layers located at a distance of 5-7 cm from each other. Compliance with these conditions improves the thermal insulation properties, preventing the formation of condensation.
Coating is carried out in the following sequence:
- The film is attached from the “north” to the bottom trim of the side wall; wooden planks are used for this.
- The material is tensioned by nailing the top edge to the beams of the top trim and the roof ridge.
- In a similar way, the film is attached on the “south” side to the bottom of the transom.
- The ends of the greenhouse are lined in the same way.
- The remainder of the film is used for upholstery of doors and windows.
Cellular polycarbonate
This material is more expensive, however, it is stronger, more durable and heat-resistant. It is recommended to use sheets with a thickness of 6-8 mm. For regions with cold climates, it is recommended to increase it to 1 cm. In order to increase the wear resistance of polycarbonate with respect to temperature fluctuations, as well as the effects of water and solar radiation, a protective film is applied to the material. When choosing sheets, you should take into account their guaranteed thermal insulation properties, as well as flexibility, which is especially important for arched structures.
In general, the advantages of the material include its transparency (90% of the transparency of glass), lightness combined with flexibility and strength, and good heat-insulating properties.
At the same time, polycarbonate is not without its drawbacks. This is its relatively high cost, vulnerability to direct mechanical impact, sensitivity to the ultraviolet range of solar radiation (without the use of a protective film).
The sheets are fastened using self-tapping screws. In this case, their orientation should favor the drainage of condensate.
Construction of frame racks
Frame construction is a demanding task that requires detailed precision. Before starting independent work, prepare beams for vertical posts, horizontal top trim, and parts for fastening the side walls of the greenhouse.
It is better to mount the support box on the ground and then move it to the prepared foundation. All parts are pre-treated with moisture-resistant oil, and metal corners are used for connections.
Using the same corners, the frame is attached to the foundation. Additionally, side fixing posts are installed. The entire work process should be controlled using a building level.
It is better to assemble the roof (to obtain an optimal result) strictly according to the instructions. To do this, you can use training video lessons, which outline the main nuances of operation and assembly.
Construction of a greenhouse according to Mitlider: calculation of the necessary material and tools
Before starting work, a preliminary calculation is made to eliminate unnecessary costs or shortages of building materials.
As an example, a structure with a wooden frame and a polycarbonate covering with a height of 2.7 m, a width of 3 m and a length of 6 m will be used.
Foundation
To lay the foundation, you need roofing felt, reinforcement, sand and concrete grade M 200. The calculation is carried out on each side of the perimeter (3 m and 6 m).
The planned height of the sand cushion trench is 10 cm, and its width is 20 cm. The approximate required volume of sand will be 0.344 m3.
To lay the foundation strip, a height of 30 cm and a width of 20 cm are taken into account.
Calculations are carried out in a similar way. A volume of concrete equal to 1.032 m3 will be required.
Cellular polycarbonate
The calculation is made based on determining the coverage area on each side of the greenhouse.
Taking into account the initial assumptions, a total of 61.44 m2 of material will be required. In this case, it is recommended to purchase polycarbonate with a reserve.
Fittings
To strengthen the structure and form the frame, 8 mm thick metal rods are used, which are fixed with connecting elements located at a distance of 30 cm from each other. Considering that each side of the perimeter is reinforced with 4 horizontal rods, the total length of the required reinforcement will be 120 m.
Wood
For installation work you will need the following bars:
for foundation Walls, slopes, door, transoms, longitudinal roof beams Roof rafters
- 10*15*220 cm No. 18 for creating vertical racks;
- 10*15*270 cm No. 4 to support the roof;
- 5.5*8*200 cm No. 5 and 5.5*8*140 cm also No. 5 for creating a rafter system;
- 10*15*600 cm No. 2 and 10*15*250 cm No. 2 for making the bottom trim;
- 10*10*600 cm No. 2 and 10*10*250 cm No. 2 for making the top trim;
- 6*6*150 cm No. 14 and 6*6*30 cm No. 14 for making vents;
- 6*6*200 cm No. 4 and 6*6*75 cm No. 4 for making doors.
Tools
To complete the work you will need tools for:
- taking measurements: measuring tape, plumb line, building level, large square, pencil or marker;
- wood and metal work: hacksaw, hammer, screwdriver, grinder or sandpaper, molar brush, hammer drill, grinder, jigsaw, fine-toothed file, sharp construction knife, cord with stakes;
- working with soil and concrete: shovels (bayonet and shovel); concrete mixer, water tanks, hose for pouring concrete.
What you will need during the work process
To build a Mittlider greenhouse measuring 3x6 m with a wooden frame you will need:
- beams with a section of 100x100 mm for the manufacture of racks: central - 5 pcs. length 3.05 m, side - 10 pcs. 2.15 m each;
- board 100x40 mm for rafters: 5 pcs. 1.9 m long and 5 pcs. 1.31 m each;
- slats for door frames and side frame elements with a section of 50x75 mm;
- boards for the bottom trim - 24 m with a section of 25x200 mm;
- beams 50x50 mm for the construction of windows;
- plywood 7 mm thick for window and rafter wedges;
- boards 25 mm thick for the construction of corner struts;
- support bars with cut corners - 5 pcs. 327 mm each;
- piano hinges;
- beams with a cross-section of at least 75x50 mm - for window sashes and beam guides;
- covering material - polyethylene film or polycarbonate;
- wood screws or nails.
If polyethylene is used to cover the frame, then thin slats should be prepared for attaching the rolled material to the frame. Polycarbonate sheets are best mounted using special self-tapping screws with washers and deformable spacers.
A pre-prepared tool will save more than one hour of the time allotted for installation, so make sure in advance that during work you do not have to look for:
- garden auger;
- shovel and bayonet shovel;
- medium-sized hammer and sledgehammer;
- hacksaw;
- electric jigsaw;
- drill with a set of wood drills;
- screwdriver;
- bubble or laser level;
- roulette;
- carpenter's square;
- pencil.
Some of the work will have to be done at height (best with an assistant), so you will need stepladders or a pair of strong, stable stands and a wide, thick board.
Step-by-step instructions for making a greenhouse according to Mittleider
Making a greenhouse is a multi-stage process that requires a number of sequential steps.
Site selection
Before starting construction, select a bright area on a flat surface or hill. If necessary, resort to terracing.
Diagram of the most favorable location of the greenhouse relative to the cardinal directions
It is important to take into account that the structure should be oriented from east to west. The selected area is marked using stakes and rope.
The structural elements are: base, walls (side and end), door, roof and transom windows. They are strengthened using self-tapping screws, angles (corner connectors) and connecting plates (rectangular and T-shaped).
Laying the foundation
A trench with a cross section of 20*20 cm is dug along the perimeter of the site, the walls and bottom of which are compacted, after which sand is poured onto the bottom.
Its layer should be 10 cm high; for this, it is better to first apply marks to the walls of the trench. The sand must be compacted.
A layer of waterproofing is applied on top of the sand, the role of which can be played by roofing felt or polyethylene film. Waterproofing ideally covers the bottom and walls of the trench. Formwork is made from available materials, such as boards or sheets of plywood, the height of which should be 25-30 cm. Spacers are usually used to stabilize it.
Reinforcement is carried out in order to strengthen the strip base. A frame with parameters of 15*20 cm is formed from steel rods 8 mm thick with connecting elements located at a distance of 30 cm from each other. Fixation is carried out using welding or anchors. When performing work, it is necessary to avoid contact between reinforcement elements and waterproofing elements. For this reason, the metal frame is installed on bars 3.5-4.5 cm high.
Next, M 200 grade concrete is fed into the formwork using a hose. A shovel is used to evenly place it inside the trench. The steel structure must be completely cast. When poured correctly, the concrete base should rise 20 cm above the ground surface (with a height of 30 cm). As an option, preliminary walling of metal embedded elements is allowed.
After pouring the concrete, it is covered with waterproofing. In order to ensure its uniform hardening over 48 hours, the concrete should be uncovered every 12 hours for approximately 25 minutes. After the mixture has hardened, the formwork is removed.
Frame installation
After laying the foundation, wooden elements are installed.
The wood is pre-treated.
The bars in the trench are reliably waterproofed. A layer of roofing material is laid on top of the concrete slab.
Foundation waterproofing
The construction of a wooden frame is reminiscent of assembling a barn:
- The frame of the lower frame (lower frame) is made, for which beams with a cross-section of 10*15 cm with ends made using the half-tree method are used. To strengthen the connection, it is recommended to make gashes.
- The wood is fixed using nails (self-tapping screws, nails or bolts can be used for connection in the corners), after which the strapping is installed on the foundation. Holes are made in the corners for anchor bolts. Holes are drilled in the same way at intervals of 130-140 cm.
- In the corners, as well as at a distance of 65-75 cm from each other, racks are installed along the entire perimeter, including the doorway (a beam with a cross-section of 10*15 cm is used); mounting corners are used for reinforcement; In order to stabilize the frame, jibs are placed between the racks.
- Prepare the top trim from beams with a cross-section of 10*10 cm. In this regard, complete cutting grooves are formed in the beam every 75 cm.
- 4 support posts are being installed to support the roof.
The vents for the transom are made from a profile of a smaller cross-section. For the manufacture of doors, a profile with a cross-section of 2*2 cm, a width of 70 cm and a height of 180 cm is usually used. It is recommended to stitch the door with polycarbonate on both sides to form an air gap, which plays the role of future thermal insulation.
When installing a frame made of metal pipes, the connecting elements must be welded.
Roof installation
The rafter system is being installed. The assembly of components is carried out on the ground, and the number of rafters coincides with the number of racks. The role of the starting materials is performed by bars 5.5 * 8 * 200 cm and 5.5 * 8 * 140 cm. The “northern” slope should be steeper and higher than the “southern” one by about 40-47 cm. Next, the elements are lifted onto the frame.
The finished rafters are secured to temporary struts. Wood rafters are fixed using nails, metal plates and mounting angles.
Metal elements are welded to the steel frame structures or secured with bolts. After the structural elements are fastened, the spacers are removed.
Greenhouse covering
Typically, polyethylene film or cellular polycarbonate are used.
When choosing a polyethylene coating, you should pay attention to:
- stability – the ability to maintain physical properties against the background of prolonged solar radiation; Availability:
- reinforcing insert that increases the strength and wear resistance of polyethylene; antistatic coating, which slows down the settling of dust and increases the transparency of the film;
- a hydrophilic coating that ensures free drainage of condensate (not all plants like water dripping on them).
Due to the fact that polyethylene is much lighter than polycarbonate, a strip foundation is not required for the installation of such a greenhouse.
The order of plating is as follows:
- a fragment of film is stretched over one of the sections of the greenhouse;
- slats are applied on top of the material and fixed with self-tapping screws;
- in a similar way, a fragment of polyethylene is applied and fixed from the inside -
- in this case, a thermally insulating air layer with a thickness of 5-7.5 cm is formed; Then all sections of the walls are covered in a similar way.
Choosing cellular polycarbonate as the covering material, the greenhouse is sheathed on the outside, using self-tapping screws for fixation.
Polycarbonate sheathing
It begins with cutting the material, for which a jigsaw and a file with fine teeth are used. Fixation points are marked and holes are drilled using an electric drill.
The sheets are laid with a small gap provided in case of possible expansion of the polycarbonate. Self-tapping screws with a rubber gasket are used to secure them. Their joints, as well as the ends, are covered with a joining profile. It is important to remember that you should not press polycarbonate with self-tapping screws, since the material is fragile, and also make sure that the side covered with the film is on the outside.
After covering the roof, they begin to work on the walls. It is important to remember that the sheets must be oriented when fastening so that the internal cells have a vertical direction.
After the walls, they begin to cover the end surfaces, transoms and doors.
Interior arrangement
The interior arrangement includes, first of all, electrical wiring, autonomous water supply, as well as the installation of artificial lighting lamps.
Particular attention is paid to the location of beds and paths. Access to the beds should be convenient.
Regarding heating, it all depends on the purpose of the greenhouse and the gardener’s plans. For year-round operation, a heating system is necessary.
Prices for an arched greenhouse according to Mittleider of different sizes
Approximate prices for an arched non-assembled greenhouse structure with a distance between the arches of 1 meter, a width of 3 meters, a height of 2.3 m, depending on the length of the structure and the thickness of the polycarbonate, are shown in the table below:
| Non-removable arched structure | ||
| Length, m | Cellular polycarbonate, Russia, mm | price, rub. |
| 4 | 3,5 | 25 510 |
| 6 | 32 730 | |
| 8 | 40 594 | |
| 10 | 48 495 | |
| 4 | 4 | 26 122 |
| 6 | 33 517 | |
| 8 | 41 644 | |
| 10 | 49 772 | |
| 4 | 6 | 29 010 |
| 6 | 37 230 | |
| 8 | 46 594 | |
| 10 | 55 959 | |
Reviews of the greenhouse according to Mittleider
Natalya Sergeevna Shestopalova, 52 years old, Semiluki
My husband and I made the Mittlider greenhouse from wood and covered it with film. We need it to grow peppers and tomatoes. We manage without heating. In spring and summer we regularly go to the dacha, so we manage to avoid problems with air exchange. We open transoms as needed. The harvests are good, we are happy.
Dmitry Anatolyevich Veshnyakov, 60 years old, Moscow
I assembled Mittlider's greenhouse three years ago. I decided that for reliability it would be better to build the frame from metal and make the casing from polycarbonate. Air exchange is noticeably better compared to conventional greenhouses. I use the greenhouse to grow tomatoes. When there was an outbreak of late blight, I tried not to open the transoms too much.
Denisova Larisa Nikolaevna, 34 years old, Tver
The greenhouse successfully complements the interior of our garden plot. Its parameters are 270*300*540 cm with an arc step of 90 cm. The design is strong, reliable, and resistant to gusts of wind. And she is also very comfortable.
Ratnikov Alexander Vladimirovich, 61 years old, Moscow
I think that the design of the greenhouse was chosen well. Construction did not take much time and was, in general, uncomplicated. The task was significantly simplified by the initial availability of building materials. The greenhouse is durable and spacious, retains heat very well.