Columnar apple tree is a natural clone of an apple tree that does not have side branches. In British Columbia, in the village of Kelowna (located in Canada), an unusual branch was found on an old McIntosh apple tree, which was 50 years old, or rather, it had an unusually large amount of foliage and fruits and there were no side branches at all. This happened in 1964. This spontaneous mutation did not go unnoticed by breeders and was propagated. Over time, with the help of it, experts created columnar apple trees. At the same time, both English breeders from Kent and specialists from other countries worked on this plant. In 1976, the first samples of this type of apple tree were obtained.
Features of a columnar apple tree
Scientists have found that such unusual characteristics of the columnar apple tree directly depend on the special Co gene. In these plants, the branches extend from the trunk at an acute angle, and they grow almost along the conductor. In this regard, such apple trees are similar in appearance to pyramidal poplars. Such an apple tree has a thickened trunk on which many small branches grow, and flower buds are located at their tops. The skeletal branches of simple apple trees are much more powerful than the lateral branches of columnar apple trees. Often they are replaced by spears, fruits or ringlets. The shoots of such a plant are quite thick, and they have shortened internodes. Dwarf varieties are less prone to branching compared to medium-sized varieties (1.5-3 times) and tall varieties (3-4 times). After the tree is 3–4 years old, its side branches stop growing. In the event that the apical bud is injured, the plant’s growth will stop, but the side branches will begin to actively grow. In this regard, those gardeners who want to grow a columnar apple tree must do everything to ensure that the plant’s growth point is maintained at least for the first 2 or 3 years. Such an apple tree will begin to bloom and bear fruit at the 2nd or 3rd year of life. The harvest in the first 5–6 years becomes more abundant every year, but already from the 7th–8th year of the plant’s life it is consistently high, but this is only the case when the apple tree is properly cared for. A columnar apple tree bears fruit for no more than 15–20 years; after this period, most of the ringlets die off. But if you are growing strong or medium-growing varieties or a tree that has been grafted onto seed rootstocks, then in these cases anti-aging pruning can be used, which can significantly extend the life of the apple tree.
Apple trees such as columnar ones are ideal for owners of small gardens. So, instead of one ordinary apple tree, you can plant several dozen columnar ones. There are 2 different types of columnar apple trees:
- varieties that have the Co gene;
- simple varieties that were grafted onto superdwarf clonal rootstocks (they are formed as columns).
Columnar apple tree. How to avoid fakes?
Harvest
Harvesting is not difficult, since the height of columnar apple trees does not require special equipment. Harvesting begins according to the variety. Immediately after sorting, the harvested crop is placed in storage (basement, cellar) in separate small containers, boxes and other containers. For winter storage, the optimal temperature is +2.. +3 °C. Varieties with a short shelf life are used for processing (juices, compotes, jams, etc.).
- Part 1. Columnar apple trees - features and best varieties
- Part 2. Features of growing columnar apple trees
Planting columnar apple trees
What time to plant
Experts advise planting this kind of apple tree in the spring, but you need to have time to do this before the buds begin to open. If desired, you can plant a seedling in open ground in the autumn in the last days of September or the first days of October, the main thing is that the weather is warm. For planting, it is recommended to purchase annual seedlings rather than biennial ones. The fact is that such plants take root relatively easily and begin to grow and bear fruit much faster. When choosing a seedling, you need to pay special attention to its roots, so there should be no rot on them. Trees with overdried roots should also not be purchased. It is best to buy a seedling in a container; it can be planted even in the summer. A suitable area should be open and sunny, but it should be remembered that such an apple tree requires protection from strong gusts of wind. The soil needs to be saturated with nutrients and well-permeable to water. Groundwater on the site must lie at a depth of at least 200 centimeters.
Planting a columnar apple tree in autumn
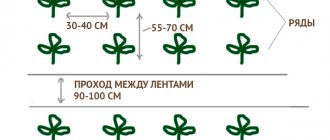
If you decide to plant a large number of columnar apple trees at once, they should be arranged in rows. Thus, the distance between seedlings in a row should be at least 50 centimeters, while the row spacing should be 100 centimeters. Planting holes, which must be at least 90x90x90 centimeters in size, must be prepared half a month before planting. If this is not done, then after planting and settling the soil, the root collar will be located underground, and this can lead to the death of the seedling.
When digging a hole, you need to discard the top layer of soil, which contains a larger amount of nutrients, separately from the bottom layer, preventing them from mixing. If the soil is heavy, then at the bottom of the hole it is necessary to place a layer of crushed stone mixed with sand for drainage. After this, add 3 to 4 buckets of humus (compost), 100 grams of superphosphate and 50 to 100 grams of potassium fertilizer into the fertile soil and mix everything. It is also recommended to add 100 to 200 grams of dolomite flour into acidic soil. This soil must be poured into the planting hole and its surface leveled. After half a month, the soil will settle and become compacted.
After 2 weeks, you need to pour the remaining soil mixture into a heap into the planting hole. After this, you need to install the root system of the apple tree directly on this “hill” so that the root collar of the seedling rises slightly above the surface of the area. After the roots are straightened, you need to pour infertile soil (from the bottom layer) into the hole and compact it well. Step back 30 centimeters from the trunk and form a roller around it, the height of which should be from 10 to 15 centimeters. The planted tree should be watered, using 10–20 liters of water. After the liquid is absorbed into the soil, its surface should be sprinkled with a layer of mulch (sawdust, peat or chopped grass). If desired, you can install a support next to the seedling and tie it up.
How to plant a columnar apple tree in spring
If the planting of columnar apple trees is planned for the spring, then it is recommended to prepare the planting holes in the autumn. During the winter, the soil will settle, become compacted, and the applied fertilizers will dissolve. Apple trees planted in such holes take root much faster, and they may even bloom in the same year. You need to plant a seedling in the spring in the same way as in the fall.
Planting a columnar apple tree
Conditions for good growth
When purchasing a seedling, you should determine the location on the site and choose the right variety. An apple tree requires the following conditions:
- Fertile soil.
- Lots of warmth and light.
- Well drained soil.
- No drafts.
- The location of groundwater is no closer than 2 meters above the soil surface.
In order for the seedling to develop quickly and bring a generous harvest, it must be looked after. It should be planted in the spring, before the buds open, or at the end of September, 1-2 months before the onset of the first cold weather.
Caring for columnar apple trees
Care in spring
In spring, it is necessary to prune apple trees and treat them for the purpose of prevention against various harmful insects and diseases. You need to have time to perform these procedures before the kidneys open. At the same time, fertilizers containing nitrogen must be added to the soil.
From apple trees planted this year, you need to pick off all the buds that form. In plants of the second year of life, only 10 buds are left. Starting from the third year of life, the load on the tree should not be increased immediately, but gradually, so that 2 times more buds are left on the plant than the number of fruits that should ripen. So, on each fruit link there should be 2 inflorescences, and thinning is done again in the summer.
Also, columnar apple trees must be watered in a timely manner and the top layer of soil around the trunk must be loosened. However, in the case when the tree is grown on a columnar rootstock, the roots of the plant may be injured in the process of loosening the soil. In this case, it is recommended to tin the tree trunk circle rather than sprinkle it with a layer of mulch. To do this, you need to step back a quarter of a meter from the trunk and sow green manure grasses in a circle, which will need systematic mowing.
Summer care
By mid-June it is necessary to carry out complex fertilizing, for which mineral fertilizers are used. After the ovaries form, it will be necessary to thin them a second time. As a result, ½ of the ovaries should remain on the tree. After the fruits are similar in size to cherries, you need to make sure that there are only 2 ovaries in each inflorescence. When the apples are similar in size to a walnut, you need to remove one of the two remaining ovaries. As a result, only 1 fruit should grow on 1 fruit-bearing link.
In the summer, do not forget to carry out preventive inspections of apple trees. If any harmful insects are found or the plant becomes sick, then it is simply necessary to take timely measures to treat it or get rid of pests, otherwise you may be left without a harvest. 4 weeks before the scheduled date of fruit harvest, all treatments of the plant against harmful insects and diseases should be stopped.
With the onset of August, organic fertilizers, as well as those containing nitrogen, cease to be applied to the soil. At this time, it is recommended to apply only potassium fertilizers to the soil, because they promote faster ripening of young shoots. To ensure that the upper parts of the shoots do not suffer from frost in the winter, it is necessary to shorten the 4 leaves located at the very top by 2/3.
Autumn care
In the autumn, when the fruits are harvested, it is necessary to add fertilizer to the soil and carry out treatment against harmful insects and fungi that have taken refuge in the bark, as well as inside the soil around the trunk. If necessary, it is necessary to prune for sanitary purposes, and then prepare the trees for wintering.
Processing columnar apple trees
At the beginning of the spring period (before sap flow begins) and in the autumn (when the leaves fall), these apple trees must be treated to prevent diseases and harmful insects. The surface of the tree trunk circle should also be treated. Most often, gardeners in this case use a solution of Nitrafen or Bordeaux mixture (1%). This treatment will help get rid of harmful insects and pathogens of various diseases that are found in the soil of the tree trunk and in the bark of the apple tree. There are those gardeners who use a urea solution (7%) for treatment in the spring, which acts as a fungicidal and insecticidal agent, as well as a nitrogen fertilizer.
Watering
Due to the fact that this kind of apple tree does not have a tap root, which goes deep into the soil, and at the same time the root system is surface and is located within a radius of a quarter meter from the trunk, then young plants need to be watered in the summer in normal weather once every 3 days . In dry and hot weather, columnar apple trees should be watered every day or once every 2 days. Watering mature plants should be carried out 1 or 2 times every 7 days. From the second half of June, watering is slightly reduced, and from the beginning of August these plants stop watering altogether, the fact is that they must have time to complete the formation of flower buds, as well as growth, and also prepare for wintering.
To prevent the soil from drying out too quickly and to prevent a dense crust on its surface, the tree trunk circle is sprinkled with a layer of mulch (straw) or it is seeded with green manure. It is recommended to water such apple trees using the drip method, and the supply of moisture to the root system should be dosed. However, once every 4 weeks it is necessary to water abundantly so that the soil can get wet to the depth at which the roots lie. Once every 2 weeks in the evening after the sun has set, you need to thoroughly water the crowns of the plants with a hose.
Fertilizer
Since this tree produces a very large number of apples, it absorbs a lot of nutrients from the soil. In this regard, such a plant should be fertilized throughout the entire period of intensive growth. In spring, organic fertilizers need to be added to the soil. For this purpose, both fermented chicken manure and slurry are used. In order for the tree to receive the required amount of nitrogen, you can spray it with a urea solution (7%), but this must be done at the beginning of the spring period, before the buds begin to open. After this, before the beginning of the second half of the summer period, if desired, the plants can be fed 2 more times using the foliar method and also use a urea solution (0.1%).
During the peak of intensive growth (from early to mid-June), trees need complex mineral fertilizers. From the beginning of August, organic fertilizers should no longer be used for fertilizing. During this period, columnar apple trees need potassium, as it promotes rapid ripening of the upper parts of the shoots.
Wintering columnar apple trees
At the beginning of the autumn period, the trunks of young columnar apple trees must be thoroughly covered with spruce branches or wood shavings. It should be remembered that only dry covering material should be used, and it should be protected from the penetration of rodents. You cannot cover plants with straw. If the tree trunk circle is mulched with straw, then it should be removed in the fall, because various rodents simply adore it. When the snow cover appears, you need to hill the base of the apple tree trunk with snow.
How I cover columnar apple trees for the winter
The history of the appearance of “speakers”
Apple trees with a crown in the form of a “column” or a narrow inverted “pyramid” have been cultivated relatively recently. It is known that the original form was found in the mid-60s of the 20th century in Canada. One of the gardeners discovered an actively fruiting branch on the Mekintosh apple tree, practically devoid of side shoots. The breeders assumed that this interesting specimen was the result of a random mutation and used the branch to grow self-rooted and grafted seedlings. As it turned out later, the fruits that ripened on the grown trees carried in their seeds the gene responsible for the manifestation of “columnarity.” In addition, it turned out that about half of the seedlings obtained by pollinating the flowers of “ordinary” apple trees with columnar pollen have similar properties. It was these facts that made it possible to breed all currently existing plants of this type.
The name of the first of the varieties, “Wazhak”, according to the most common version, comes from the surname Wazhak or Wazhek, which was borne by the owner of the “original” plant, a Pole by origin
The first variety of columnar apple tree was named “Wijcik McIntosh” or simply “Wajak”. British scientists became interested in the new variety of crop, and by 1976, several varieties were bred at the East Malling experimental station: “Trigen”, “Taskan”, “Tileimon”, etc. In the USSR, the selection of trees with a similar type of crown began in 1972, when Pollen of the “Vazhak” variety was brought into the country. The famous breeder, Professor V.V. Kichina managed to pollinate the flowers of the “Cinnamon Striped” apple tree with it. Work on breeding large-fruited, winter-hardy and weakly affected by diseases plants was carried out for 30 years and resulted in the production of more than 20 winter, autumn and summer varieties of columnar apple trees.
Currently, the selection of “columns” continues in many countries. New, successful varieties are constantly appearing, bred in the USA, Czech Republic, England, Holland, Sweden and even China. In the post-Soviet space, not only Russian, but also Ukrainian, Belarusian and Latvian scientists are actively engaged in such work.
Today, the apple tree is the only garden crop that has varieties with a columnar crown shape. The efforts of breeders aimed at obtaining similar varieties of other fruit plants have so far remained unsuccessful. Sellers of seedlings offering “columns” of pears, cherries and plums are simply deceiving gullible buyers.
Pruning columnar apple trees
What time is pruning done?
A real columnar apple tree should not have branches; therefore, pruning to form the crown is not required. Only the side branches are pruned at the very beginning of the summer period or after all the leaves have fallen.
How to prune a columnar apple tree
You should remember one of the main principles of pruning an apple tree - the more branches you trim, the more intense their growth will be. So, for example, you cut a branch by about ½ part, and at the same time there were 3 or 4 eyes left on it. After some time, 3 or 4 strong shoots will grow from these eyes. If you cut off 1/3 of the branch and there are 7 or 8 eyes on it, then 7 or 8 medium shoots will grow from them. If pruning is done correctly, then every year the apple tree will grow by 10–15 centimeters, and 2 or 3 lateral buds will appear.
When you prune the branches, do not forget that you should not touch the central conductor. Otherwise, having lost its growth point, the tree will begin to actively grow branches.
At the beginning of spring, all the side branches of a tree of the first year of life should be cut off so that only 2 buds remain on each of them. In the next 2 or 3 years, it is necessary to form fruit links from young shoots. It is recommended to carefully trim those side shoots that are not needed while they are still green. The fact is that healing of wounds on woody shoots takes relatively longer.
Spring pruning
Pruning a columnar apple tree
Before sap flow begins, formative pruning should be done. For plants of the first year of life, all lateral branches must be pruned, leaving 2 buds on them. Sanitary pruning is also carried out, during which diseased, intersecting branches, as well as those affected by severe frosts in winter, are removed.
The tree of the second year of life is pruned to form fruit links. To do this, of the 2 shoots that grew on last year’s cut branch, you need to cut off the one that is more vertical, leaving only 2 buds on it. A horizontally located shoot will begin to bear fruit this year, and from a pruned shoot 2 powerful shoots will appear.
In the third year of life, those branches that bore fruit in the previous year must be removed. With the remaining branches, the same pruning procedure should be performed as last year. It should be remembered that the fruit link can function for no more than 3 or 4 years. After this period, it should be cut into a ring.
If the apical point of growth dies, it is recommended to trim the conductor, leaving only 2 buds. Wait until lateral branches grow from them. Of these branches, only 1 should be left, and it should be located vertically. This branch will become a replacement for the conductor. The remaining side branches must be cut into a stump (not into a ring), and the stumps must have the same length as simple ringlets.
Autumn pruning
In autumn, pruning should be done only when it is really necessary.
Reproduction of columnar apple trees
To propagate columnar apple trees, the method of grafting a varietal cutting onto the rootstock that is most suitable is used. However, in order to successfully perform such a procedure, experience is required. You can also propagate by seeds, but this will take too much time and require a lot of effort. And not all apple trees that grow from seed are columnar. Experts advise propagating such a plant by air layering. Select a branch at the very beginning of spring, the thickness of which should be similar to a pencil. Then a circular cut of the bark is made at the base, the width of which should be 5 mm. After this, you need to moisten the cotton wool in Heteroauxin and wrap it around this incision for 24 hours. Next, moistened peat should be used to wrap the incision, while this place is covered with a black polyethylene bag, it is fixed so that no air gets under it. Do not let the peat dry out completely. In autumn, roots should grow at the site of the cut. After this, the branch is separated from the parent plant and planted in the soil. The probability of success of such reproduction is 50:50.
Growing seedlings of this type of apple tree is not an easy task. In this regard, it is recommended to buy them from trusted nurseries, and the seedlings must be transported correctly.
Selection of seedlings
In autumn, you have a better chance of buying quality seedlings of good varieties. If it is too late to plant the plant in a permanent place, you can simply bury it in the garden for the winter.
It is possible to save a seedling if you plant it in a large pot and place it in a cool cellar. The soil in the pot must be moistened periodically.
A seedling purchased in late autumn can be buried in the garden for the winter.
Purchase 1-year-old seedlings for planting (their height is usually 60–70 cm, 5–6 buds are visible on the stem) without leaves, with elastic bark, and intact roots. The survival rate of one-year-olds is significantly higher than that of two-year-olds.
It is better to purchase seedlings with a closed root system. When planting, the change of soil goes unnoticed for them and they are practically not exposed to stress. If you bought a seedling with an open root system in the spring, do not let the roots dry out. They can be wrapped in damp burlap and wrapped in plastic, or placed in a bucket of damp sawdust and watered periodically.
Pests of columnar apple trees
Columnar apple trees may well be inhabited by green and plantain aphids, sawflies, glass beetles, red mites, codling moths, moths, leaf rollers, copperheads, comma scale insects, currant, fruit and subbark leaf rollers, fruit and fruit moths, various cutworms, rowan moths, gypsy moths, oakleaf and ringed silkworms, blood and red gall aphids, goose weevils, western gypsy bark beetles, sapwood, pear pipeworms, as well as other pests. In the fight against harmful insects, you can use insecticidal agents, and catching belts made of corrugated paper are also useful (they prevent pests from going up the trunk).
Diseases of columnar apple trees
Such apple trees suffer from exactly the same diseases as ordinary ones. Most often, the columnar apple tree suffers from diseases such as: proliferation, or witch's broom, bitter fruit rot, mosaic, mosaic ringing, fly beetle, powdery mildew, milky sheen, tinder fungus, common cancer, scab, dying branches, fruit rot, subcutaneous viral spotting, rubberiness, rust, glassiness of fruits, flattened branches, black cancer and cytosporosis.
Main varieties with photographs and descriptions
The division of varieties is carried out depending on their growth, namely, they are divided into vigorous, medium-sized (semi-dwarf), and also dwarf. They are also divided according to the time of fruit ripening into late (winter), mid-season (autumn) and early (summer). Below are varieties divided by ripening time.
Summer varieties
On these plants, ripe apples can be harvested from the last days of July to the first days of September. Such fruits are eaten fresh or used to make preserves, jams, compotes, etc. The shelf life of such apples is relatively short.
The most popular varieties:
Nectar
This semi-dwarf variety is characterized by high yield and resistance to frost, diseases and harmful insects. Yellowish-white apples have a fairly thick skin, as well as juicy and grainy flesh with a distinct honey taste. On average, each apple weighs 100–250 grams. Plant height can vary from 200 to 250 centimeters.
The president
This semi-dwarf compact variety is characterized by high yield and resistance to frost, harmful insects and diseases. The fruits are very fragrant, pale yellow or pale green, in some cases they have a slight light pink blush. On average, apples weigh from 150 to 200 grams. The fine-grained pulp is juicy and tender.
Vasyugan
This productive variety is resistant to frost, harmful insects and diseases. The shape of the red-striped fragrant fruit is conical, the taste of the pulp is sourish-sweet, and it has clearly visible subcutaneous points. The cream-colored flesh is distinguished by its softness and juiciness. On average, the weight of the fruit is 140–200 grams.
Dialogue
The medium-sized variety is characterized by productivity and resistance to frost, pests and diseases. The deep yellow apples are not very large in size, but they are quite juicy. The shape of apples is flat.
Ostankino
The medium-sized variety is resistant to harmful insects and diseases. The fragrant, sour-sweet fruits have a light green color with a blush that has a fuzzy, blurry shape. Juicy apples can weigh from 100 to 220 grams.
Also quite popular among gardeners are such varieties as: Chervonets, Luch, Ideal, Raika, Flamingo, Gala, Cheremosh, Iksha, Green Noise, etc.
Autumn varieties
Fruit ripening on plants of these varieties occurs throughout the autumn period. They are eaten fresh or made into various preparations for the winter. Such apples are stored for a relatively short time (maximum until January). Popular varieties:
Malyukha
This dwarf variety is one of those that have the highest taste. The truncated-conical shape of dessert apples is large in size. They are painted orange-yellow or deep yellow and weigh from 150 to 250 grams. The durable, glossy skin is quite thin, and the yellow, fragrant flesh is fine-grained. This variety is high-yielding and early-bearing.
Gin
The variety is characterized by productivity and resistance to frost. The rich red fruits can weigh 80–200 grams. The sweet and sour pulp is firm and juicy. Apples can last until January.
Triumph
Medium-sized variety. The apples have a rich dark red color and have a striped blush on their surface. The shiny peel is quite dense. Snow-white crispy fine-grained pulp. It has a dessert sweet taste with a slight sourness. On average, apples weigh 100–150 grams.
Arbat
The variety is characterized by high yield and resistance to frost, harmful insects and diseases. The fruits ripen in the last days of September or the first days of November. Rich cherry color, medium-sized glossy apples with sour-sweet juicy flesh. The average fruit weight is from 100 to 120 grams.
Iedzen
This vigorous variety is resistant to scab and is winter-hardy. There are red streaks on the surface of yellow apples. The average fruit weight is 150 grams. The fine-grained, dense yellowish-green pulp has a sweet and sour taste. The taste is high.
Also quite popular are varieties such as: Kumir, Ladoga, Titania, Teleimon, Melba, etc.
Winter varieties
The ripening of apples of these varieties occurs in mid-autumn. They can last until spring. The following varieties are popular:
Amber necklace (amber)
The medium-sized variety is characterized by productivity and resistance to frost. Large greenish-yellow apples have a blush. The fine-grained, fragrant pulp is juicy and sour-sweet.
Currency
A medium-sized, early-fruiting variety, characterized by high yield, resistance to frost and scab. The fruits are large (weighing approximately 200 grams) and have a rich yellow color with a red side. The snow-white, sweet, juicy pulp is quite fragrant.
Moscow necklace
This self-sterile variety is characterized by high yield and resistance to frost, harmful insects and diseases. The fruits are quite large and dark red. The peel is dense. The sweet, juicy pulp has a slight sourness. On average, apples weigh about 170 grams.
Bolero
The fruits are large and their average weight is about 200 grams. The firm white flesh is juicy.
Varieties for the Moscow region
The Moscow region is characterized by a temperate continental climate. It clearly defines the seasons. Warm summers and moderately cold winters. The spring and autumn periods are characterized by a sharp change in temperature.
The following columnar varieties for the Moscow region are suitable for cultivation in such climatic conditions:
- Bogatyr;
- Arbat;
- Vasyugan;
- Nectar;
- Ostankino;
- Gin;
- Moscow necklace;
- Bolero;
- The president.
These species tolerate low temperatures well. Therefore, they are not afraid of sudden frosts.