The need for ventilation in a greenhouse
Elevated air temperatures in greenhouses and excess humidity have a detrimental effect on vegetable crops. To maintain a balanced microclimate inside, the building must be equipped with ventilation. It helps to normalize the greenhouse microenvironment, maintaining the level of humidity and temperature within normal limits.
Also, the need for established air exchange is determined by the mandatory pollination of plants for their productive growing season.
The acceptable temperature range is small – +24⁰ – +30⁰ C. You can monitor it using an alcohol thermometer placed at the planting level. The humidity indicator is recorded by a hygrometer (regular or automatic), which is also preferably installed inside the structure. These simple devices will allow you to monitor changes and respond to them in a timely manner, regulating the inflow and removal of air masses.
Home greenhouse structures. Peculiarities
Constructed from various materials. If possible, a transparent material that does not allow air to pass through is attached to the metal or wooden frame. Thick polyethylene film, polycarbonate, glass, etc. are widely used. They allow sunlight to pass through, warming the air, but at the same time retain heat inside.
The main feature is the heating of the internal space due to the heat generated by the soil and sunlight. This allows you to plant vegetable crops and harvest 1-1.5 months earlier. As a rule, they are built for tomatoes, cucumbers, herbs, zucchini, eggplant, etc.
In order for a greenhouse structure, the effort spent, and time to be worthwhile, it is necessary to competently organize the planting of plants, determine their compatibility, correctly distribute them throughout the space, taking into account the conditions of their germination, formation, vegetation, etc. In addition, proper care of plants is important: a mechanism for controlling the temperature and humidity levels of the air in the building, loosening, replacing soil, weeding, the correct watering and ventilation scheme.
Types of ventilation
If a fruit-bearing plant is not properly cared for, it will not bear fruit and will die. Currently, there are two types of ventilation of artificial structures:
- automatic;
- manual (mechanical)
Automatic ventilation can be done:
- bimetallic;
- electrical;
- hydraulic
The manual version of ventilation (ventilation) involves the presence of a different number of vents and doors; it is simple and accessible.
Attention! Regardless of the ventilation system, it is assumed that manual ventilation is possible by closing and opening the vents.
The advantages of such air ventilation for homemade greenhouses:
- No costs for special devices.
- Saving electrical energy.
The disadvantage of manual ventilation is the mandatory presence of the greenhouse owner.
Those who do not have the opportunity to constantly care for plants try to use automatic greenhouse ventilation made by themselves. Advice! It is not necessary to look for a specialist to create ventilation; it is quite possible to cope with such a task on your own, using a ready-made algorithm of actions.
Among the advantages of the automatic ventilation mode, we note the chance to create the necessary climate regime for certain plants.
Let us consider in detail the algorithm for creating automatic ventilation of a structure.
How to place windows
To equip a polycarbonate greenhouse with high-quality natural ventilation, it is necessary to correctly place the window openings. In many ways, ventilation will occur through them, so when constructing it yourself, it is recommended to adhere to the basic rules for placing vents:
- The number of vents depends on their size and greenhouse parameters. The smaller the openings, the more often they are located.
- Placed at the top of the structure, the vents will draw out moist heated air well, creating rarefied pressure inside. This in turn will contribute to a better flow of fresh air flow.
- Inlet openings are best located inside the side walls of the building, at a level just above the beds and shelving. This way the plants will be well ventilated and air exchange will occur effectively.
- A good location option is to equip the greenhouse with window openings at different levels for the most complete change of air masses.
- Vents can be located in the end walls. As a rule, there is a doorway at one of the ends of the building. When weather conditions do not allow opening the side windows (for example, strong wind), ventilation is carried out through the end windows. This will ventilate the greenhouse and avoid strong drafts.
Electric ventilation
This is the most budget-friendly ventilation option. If you decide to make such ventilation in the greenhouse yourself, you will need an electric fan and a thermostat. It is the thermal relay that will become the main element of the circuit. It allows the summer resident to adjust the function of setting the ventilation system to a given temperature regime, and to send a signal to the fan about the need to start working. Immediately after receiving the signal, the fan begins to function, cooling the air inside the greenhouse. What are the main advantages of such a cooling system?
- Budget, availability of the device. Such ventilation in a polycarbonate greenhouse can easily be done with your own hands.
- Install the desired number of fans and relays along the entire length of the greenhouse.
- Correct installation of such greenhouse ventilation with your own hands makes it possible to adjust the air flow density. In case of significant overheating or sudden cooling of the air, you can change the fan operating mode. The exhaust fan, when creating a slight vacuum, removes hot air outside, instead of it a fresh air flow enters the greenhouse.
- Thermal relays are considered reliable devices that give clear readings. Modern thermal relay models require setting parameters that allow them to turn off and on at certain times.
Advice! To increase the efficiency of such a ventilation system, you can install a window at opposite ends of the greenhouse that opens when the fan is running. Unfortunately, alternative energy sources (sunlight, wind energy) are not enough for the uninterrupted operation of the system.
We also recommend watching
| A greenhouse is a closed structure designed for growing early or heat-loving plants. A distinctive feature of the greenhouse is the presence of heating. Thanks to this, plants can be grown in it all year round. The heat source for the greenhouse can be gas, water, or electric heating. Moreover, both the air in the greenhouse and the soil must heat up. Again, constant heating tends to dry out the air in the greenhouse. This means you should monitor the humidity level in the greenhouse and ensure constant watering. |
| Despite the fact that the concept of “greenhouse” comes from the word “heat,” heating is not the only condition for creating favorable conditions for growing plants. An important condition for obtaining a good harvest is to ensure a constant supply of fresh air. This allows you to avoid overheating of plants, regulate humidity levels, and harden seedlings. |
| Most of the territory of the Russian Federation cannot boast of ideal conditions for growing plants. Therefore, both farmers and summer residents are forced to resort to installing artificial lighting systems in the greenhouse. They are a kind of equivalent of sunlight. But, only if the lighting source is chosen correctly and the amount of incoming light is regulated. |
| Various closed ground structures help to harvest vegetables and herbs all year round or grow seedlings and vegetables in early spring. We talked in detail about what they are like in the articles: “Structures of closed ground. (Part 1) Insulated soil, greenhouses” and “Structures of closed soil. (Part 2). Greenhouses - overview of species." But simply building a greenhouse or a greenhouse is not enough; you need to maintain a special microclimate favorable for plants. |
Methods of ventilation in greenhouses
The disadvantage of the system is the difficulty of supplying uninterrupted power in the event of a power outage and the need to use expensive additional equipment. This is relevant during the hot summer season. When the ventilation system is turned off for 2-3 hours, the risk of plant death increases.
Advice! To partially solve this problem, you can use solar collectors fixed on the roof of the greenhouse.
Hydraulic ventilation
It is this method that can be considered a brilliant invention of our time. The hydraulic option for ventilation of greenhouses is considered the most durable and reliable system. Such a system includes the following elements: levers connected to each other by a transom.
The essence of the arrangement and functioning of such a scheme:
- Pour liquid into a certain container. In the process of heating, gradual expansion occurs, and upon cooling, partial compression occurs.
- As the volume of liquid increases (when heated), the window opens. When the volume of water decreases, ventilation stops. The thermometer is a vessel installed inside the greenhouse. The compensator is a container fixed outside the greenhouse structure. In order for the containers to become communicating vessels, hydraulic hoses are used (they connect the outer and inner containers to each other). When the pressure in any container increases, an instant reaction occurs - normalization of the indicator, leading to an upward movement of the transom.
- The transom will never reach its maximum position, so ventilation is carried out smoothly and leisurely.
Disadvantages of hydraulic ventilation
- This process is inertial, that is, in the event of a significant decrease in the outside air temperature, closing is performed very slowly. For plants sensitive to cold, this is enough for their complete death.
- In such a system there are no windows, which is inconvenient when growing many garden crops.
Advantages of hydraulic ventilation
- Easy to install.
- Reliability of the system, its durability.
- Inexpensive maintenance, there is no need to constantly monitor the process.
Advice! When choosing a hydraulic opener, it is important to take into account the opening angle; it is selected individually for each system. You can use machine oil for this method.
Climate control
To control temperature and humidity, you will need at least two devices:
- Thermometer
- Psychrometer
You should buy an alcohol thermometer, because a mercury thermometer only shows the maximum temperature and “does not fall down.” You should have several of them in different places in the greenhouse. The thermometer should not be hung at eye level, but at the level of green plants. (See also Thermostat for greenhouse)
A psychrometer (also known as a moisture meter or hygrometer) is needed to measure the humidity in a greenhouse.
This product consists of two thermometers - dry and wet. To measure relative humidity, read the difference between the dry and wet bulb readings. If you don’t want to spend money, you can make such a psychrometer yourself.
To do this, you need to buy two alcohol thermometers. One of them must be placed in a container of water (just a glass). The table below is used to measure relative humidity.
Psychrometer
In addition to the complexity of calculating relative humidity, this hygrometer has one undoubted advantage: there is nothing to break, it is practically eternal.
Humidity determination table
Humidity determination table
If you don’t want to repeat a high school physics course, you can buy a digital hygrometer, and even one with a remote temperature and humidity sensor. To determine humidity, you simply need to read the data from the display.
Digital hygrometers can be of various types and designs.
Types of ventilation systems in greenhouses
There are two ways to arrange high-quality air circulation in a confined space in greenhouses: manually or automatically. In the first option, this requires labor, because you need to constantly monitor the state of the microclimate inside, but for small greenhouses this method is quite effective. In the second case, you can set up a fully automatic system, which will only need to be inspected occasionally. How to make greenhouse ventilation with sufficient functionality, and what type to choose?
Manual ventilation
This air exchange is also called natural ventilation in a greenhouse. It occurs by unlocking doors, vents and transoms in the walls of the greenhouse. These openings can be of different sizes with different distances. The basic principle of natural air exchange states that the smaller the window, the more often they need to be placed.
The second rule of this type of ventilation: the outflow of air masses must be equal to their inflow. That is, the number of openings should be the same.
But their location should be at different heights. Inlet transoms are located lower near the ground surface, and outlet openings are located higher, preferably in the roof.
With the opening of the same number of vents, air exchange occurs naturally, due to the temperature difference. Warm heated air rises and leaves through the upper openings, and fresh, colder air penetrates through the lower transoms.
Forced air exchange
But such ventilation can be arranged if the greenhouse is small in size; with large greenhouses you will have to constantly tinker, controlling the microclimate. In order not to settle for permanent residence next to the vents, forced ventilation of the greenhouse would be an excellent option.
The system is organized by installing suitable fans powered by electricity.
This option provides many advantages for greenhouse farming:
- You can arrange high-quality ventilation for relatively little money.
- By installing the required number of fans, ensure full ventilation throughout the entire greenhouse space.
- By installing the system taking into account the technology, you can completely control the microclimate in the greenhouse by changing the operating mode of the supply and exhaust fans from a stronger option to a weaker one and vice versa.
- Installing temperature sensors with relays will allow you to fully automate air exchange and turn it on/off at a certain time for a limited period.
Unlike natural ventilation, its forced counterpart is more productive and greatly simplifies work in the greenhouse, freeing up time.
Forced ventilation is necessary if natural ventilation cannot reduce the temperature below +28 degrees. It is characterized by the artificial movement of air masses. This method is recommended for use in large greenhouses. Standard buildings measuring 6x3 m are ventilated naturally.
Fan selection
The main element of a forced ventilation system is a fan, most often an axial “axial” one with blades, designed for installation on flat horizontal or vertical surfaces. To operate the device in autonomous mode, a thermostat is used. The fan is selected depending on the area of the greenhouse and power. When purchasing, pay attention to the following points:
- The speed of air movement in the room should not exceed 1.9 m/s.
- The normal frequency of aeration is 50-60 times per hour. When making calculations, you can use the following proportions: with a room volume of 40 m3, the fan should have a capacity of 2000 m3 per hour.
- Always buy a product with a power reserve.
- In smaller buildings, appliances such as those used in toilets can be used. They are available in a waterproof version.
- It is advisable that the unit be equipped with a speed controller, with which you can adjust the performance depending on the temperature and humidity in the room.
Fan power determination
When calculating ventilation in a greenhouse, the following points must be taken into account:
- The degree of ventilation depends on the season and weather.
- In summer, the air in the greenhouse should completely change within 1 minute.
- In winter, 20-30% fresh air is enough for ventilation, and the plants will not freeze.
To determine the fan power, there are many formulas that differ in accuracy and complexity. The following calculations are considered the simplest method: A = V * C * K, where: A is the productivity of the apparatus (m3/hour); V is the volume of the greenhouse (m3); C - frequency of air exchange (hour), usually one change per minute, 60 per hour; K - loss coefficient (if there is a filter on the fan), in the case of using a carbon filter K = 1.25, because the device efficiency drop is 25%. As an example, let's calculate the fan power for a greenhouse measuring 1.2x2.4x2.5 m. Multiplying the values, we determine the volume V = 7.2 m3. A = 7.2 * 60 * 1.25 = 540 m3/hour This value determines the minimum productivity of the unit. In order to have a reserve for unforeseen situations, it is recommended to take the product with 25% more power. For winter ventilation, a low-power fan is required, so the selected device must be multi-speed to be used at any time of the year.
Rules for installing a forced ventilation system
In order for the fan to work with the greatest efficiency, you need to know the rules for placing the product and the structure of the entire system. The greenhouse will quickly ventilate if the following conditions are met:
- The fan should be located at the highest point of the room, to which warm hot currents rise. This could be the roof or side wall.
- In large greenhouses, products are placed at the ends of the room. In country houses they are mounted above the door.
- It is recommended to purchase products with blinds for protection from external influences, as well as for closing openings when the electric motors are not working.
- The room where you plan to install the fan must have an opening for air circulation. Perform it on the opposite side. In winter designs, this may be a window that opens manually. In summer, a small opening is left, which is covered with a wet rag.
- The quality of ventilation is monitored by several sensors placed in different places in the greenhouse.
- In larger buildings the fan can be installed indoors. It mixes cold and warm air, creates laminar movement, which prevents a number of diseases in plants.
- To automatically turn on the electric motor, thermostats or humidity sensors are introduced into the system. A moisture-resistant thermostat should operate at a temperature of +28-30 degrees.
Hydraulic systems
Forced ventilation is the best option, but it has one drawback - it requires a constant supply of power. If it is turned off, a problem will arise, especially in the already warm season, when the air temperature in the enclosed space of the greenhouse can rise to a critical level in a couple of hours.
An excellent analogue of automation would be the installation of a hydraulic system. Its operating principle is based on the physical properties of liquids, how does it function?
A system of rods, which are hydraulically driven, is mounted to the transoms. Its performance is as follows. There are two containers with liquid installed outside and inside. The internal one acts as a temperature sensor, and when heated, the liquid, expanding through the hoses, moves the lever, opening the transom. The outdoor container serves as a compensator, that is, when the liquid cools, it contracts, moving the second lever, closing the window.
But such a system has one drawback: the liquid changes its properties, gradually heating up or cooling down, and when sharp frosts occur, the windows may simply not have time to lock the openings. However, hydraulic ventilation is very easy to maintain and cheap to install.
When choosing a factory-made hydraulic design, pay attention to the following points:
- The product is designed to carry a certain weight, so before purchasing, find out from the seller whether the mechanism can raise your window and at what angle.
- The frame of the greenhouse often cannot withstand heavy loads, so you need to find out if it can support a hydraulic device.
- You should also determine the temperature adjustment range on the device and compare it with your requirements.
- Pay attention to the price. Good quality devices are not cheap, and you need as many of them as vents.
You can make a hydraulic device yourself. To assemble the device you will need: 2 glass jars of 3 and 0.8 liters, 2 lids - seaming and plastic, tubes - hard (copper) and soft (rubber or plastic), a small rail, soft wire. Perform the following operations:
- Pour water into a three-liter jar and seal it with a tin lid. Pass the copper tube through the hole and lower it until there is a 3mm gap above the bottom.
- Secure the container above the window.
- Pour liquid into a smaller container and cover with a plastic lid. Insert a copper tube into it and carefully seal all the cracks.
- Secure the container to the top crossbar of the transom using wire and a nail. Nail a block on the outside that will serve as a counterweight. It must balance the load on the window from the can of water.
- Connect the copper tubes on the containers with a soft tube. As the temperature changes, the air will begin to expand and displace water into the lower container. The weight of the can will increase, it will press on the lever and open the window. The hydraulic system is quite reliable and does not require constant supervision. However, it works 20-30 minutes late after a change in temperature, which can be detrimental to the seedlings.
Bimetallic structures
The functioning of the system is based on the same principle as hydraulic analogues. Only the work is based on different expansion when heating two different metals.
Typically, steel and brass are used as sensors. When the metal heats up, it expands, opening the window slightly, and when it cools, the system closes the transom.
The design of such a ventilation system is very reliable and durable because there are no power sources or parts that can break. However, it can only be used on small windows, and it is also quite difficult to obtain a structure precisely tuned to a certain temperature.
Calculating the size and performance of an exhaust fan
In small greenhouses it is recommended to install fans on the end side, and in large greenhouse structures they are also placed on the side walls. In this case, a small distance is maintained between the installations.
The fan blades are oriented parallel to the walls. It is advisable to install blinds in the wall instead of glass, which occupy a horizontal position when exposed to the air flow blown out by a fan.
Ventilation in industrial greenhouses is an integral part of the design
Length x Width x Height = Greenhouse volume (m3) AxB x H = V (m3).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Eggplant with the fabulous name Nutcracker
In our example, the dimensions of the greenhouse are as follows: length (A) – 3.65 m, width (B) – 2.4 m, height (H) – 2.5 m. The resulting volume was 21.9 m3. By the way, the better the insulation of the greenhouse, the better, since in such a room it is much easier to control the environmental parameters.
Room ventilation must solve two main problems: removing warm exhaust air (after CO2 extraction) and supplying fresh cool air. An axial exhaust centrifugal fan is used to remove warm exhaust air.
In turn, cool fresh air can be supplied either passively (through ventilation openings) or actively using a centrifugal axial supply fan. which can also work as an extractor.
Required exhaust fan capacity (m3/h) = Volume of the active growing zone (m3) x air exchange rate (hour) x Loss coefficient on the carbon filter.
The volume of the active growing zone refers to the volume occupied by light sources and plants.
To calculate the volume, multiply: length x width x height. In our example with two 600 W lamps, the room dimensions are 1.2 m x 2.4 m x 2.5 m. Thus, the volume of the active growing zone is 7.2 m3.
Multiply the resulting volume by the air exchange rate per unit of time. Therefore, to calculate the amount of air exchange per hour, it is necessary to multiply the volume of the active growing zone by 60.
Finally, when using a carbon filter on an exhaust fan, consider the 25% drop in fan efficiency. This value may vary depending on the manufacturer and service life of the filter, the length and shape of the air ducts between the fan and the filter, and many other factors. To take this factor into account, simply multiply the resulting value by 1.25.
Required exhaust fan capacity (m3/h) = Volume of active growing area (m3) x 60 x 1.25. Required exhaust fan capacity (m3/h) = ((1.2 x 2.4 x 2.5) x 60) x 1.25 = 540 m3/h.
This final value will determine the minimum performance of the exhaust fan. If the site is located in a place that receives a lot of sunlight, then you may need an exhaust fan with a capacity of 25% more.
— The ventilation hole must be located closer to the floor, diagonally opposite the exhaust fan. Remember that the exhaust fan should be mounted high, close to the ceiling, so that a stream of cool, fresh air crosses the greenhouse, picking up hot, moist air along the way.
When installing exhaust fans, use proper mountings to prevent vibration.—Some crops may produce unpleasant odors. Installing a carbon filter on an exhaust fan removes up to 90-95% of unpleasant odors, allowing you to grow almost any crop without complaints from neighbors.
However, in this case, the correct selection of the filter depending on the fan used plays an important role. Odors have a measurable “lag time” that must pass before they are completely absorbed.
Thus, for an exhaust fan with a capacity of 750 m3/h, you will need a carbon filter with a similar capacity of 750 m3/h. You should not experiment with less efficient carbon filters - they will still not be enough.
— If noise is an important limiting factor, consider using flexible, sound-absorbing circular ducts. They allow you to reduce the noise level from the fan by about a third.
A minimum of 1 m of duct length on both sides of the fan is recommended. Silencers - rigid or flexible - can also help in the fight against noise. As in the previous case, the maximum effect is achieved when using silencers on both sides of the fan, and the drop in noise level can reach one third of the original one.
— For precise microclimate control in hot or cold weather, fans with a built-in automatic speed control module and a duct temperature sensor or with a remote sensor are useful. Remember: regular air exchange is the key to stable plant growth.
Automation of ventilation in a greenhouse
The automation of this process greatly simplifies work in greenhouse farming. After all, there is no need to constantly monitor the state of the microclimate: air temperature, humidity level and the correspondence of these factors to a specific crop. It is enough to install simple sensors and only periodically check the system.
Using the above types of ventilation, you can achieve high-quality air exchange in a confined greenhouse space. Which of these systems can you install on your farm?
- Electrical equipment, with temperature control sensors and relays.
- Hydraulic climate control systems.
- Bimetallic types of ventilation.
- Automate closing and unlocking of windows.
What nuances need to be known and taken into account when using such automatic greenhouse ventilation systems in order to maintain the necessary balance of humidity and ambient temperature?
Electrical automation
One of the best systems that can be used today for installation in greenhouses. The operating principle is based on the presence of a temperature sensor and a relay with its further connection to the fan.
Electric ventilation works according to the following scheme. If the temperature rises to the set limit, the relay is activated and the hood starts. The heated air mass will be removed through the exhaust ventilation duct, and fresh, cooler air will enter through the supply openings or non-sealed greenhouse cover structures.
It is important that the volume of fresh air supplied is approximately equal to the mass removed! If the natural inflow is not enough, you can add a forced supply system in the walls. In addition to a sufficient volume of fresh air, this will provide more intensive cooling, and as a result will reduce the operating time of electric fans.
Automatic ventilation of greenhouses operating on this principle allows for very precise control of the indoor microclimate.
However, like any system, there is one drawback: it must be connected to the mains. During unscheduled power outages, the entire greenhouse is at risk. This can be eliminated by additional sources of electricity.
Sometimes it is recommended to install solar panels or a wind generator. But such systems are very expensive and require certain conditions for their operation. The best thing. Install an emergency gasoline or other similar generator, with an automatic switching system in the absence of main power.
It is also quite difficult to correctly install the entire ventilation system and install fan drives without experience. But, in this case, it is best to turn to specialists who will do everything very quickly and efficiently.
Why is it important to maintain temperature balance?
By design, a greenhouse made of any material is a thermos.
Green plantings are comfortable inside, but only up to a certain point - fluctuations in humidity and heat can cause unpleasant deformations of plants and the development of diseases. Excess moisture will provoke root rot, and lack of ventilation interferes with air exchange - plants do not receive oxygen. The optimal temperature in the greenhouse is +22 C ... +26 C during the day and up to +15 C at night.
The presence of vents in the lower part of the greenhouse will not save the situation. Warm air and condensation will settle on the tops of plants and the roof. Ventilation of the lower part leads to drying out of the soil and cooling of the root system. Cutting through vents or installing removable panels at the top of the structure will help you avoid trouble.
The main danger of air overheating is pollen sterilization. To lose pollination properties, pollen only needs to be heated to +35 C. The level is achieved at external temperatures of +25 C, provided the greenhouse is tightly closed. It turns out that ventilation should be done when the outside air is heated from +20 C.
Expert opinion
Elena Pchelkina
Gardening Expert
It is extremely important to take into account the temperature in the greenhouse for the planted crops. Eggplants and peppers are comfortable at +28 C, tomatoes begin to hurt when the indicator rises from +24 C
Natural ventilation in a greenhouse
It is considered the simplest and most affordable option for ventilating a building through doors and vents. Before ventilating a greenhouse, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the most popular cooling systems.
Ventilation through doors
Circulation occurs by moving air from the warm room outside and the cold air from outside to inside. If the temperature difference is small, the flow moves very slowly, which eliminates the occurrence of drafts. To control air parameters, a thermometer and a hygrometer are used. According to their testimony, transoms are manually opened and closed many times a day. To automate the process, you can install special equipment that will do this work for you at any day and time. To do this, it is necessary to purchase appropriate electromechanical actuators and customizable sensors. Usually they are already provided in the mechanisms. The product is triggered when the temperature reaches the set value. Also popular are hydraulic and pneumatic devices that are easy to assemble yourself. The simplest way to ventilate a greenhouse is through doors located at the ends of the room. If they are opened at the same time, air movement appears in the room from one end to the other, and the building cools. However, rapid temperature changes have a bad effect on plants, and they begin to get sick. To reduce the influence of drafts, a path is made in the middle of the building along which the main air flow will pass. Crops located on the sides of the greenhouse will be less affected by the draft. It is also recommended to open the openings in calm weather and only during the day. This ventilation option may be useful for seedlings that are intended for transplanting into open ground. Landing under the open sky will be less painful.
Ventilation through vents
If the vents are located at the ends of the building, then ventilation through them is in many ways similar to ventilation in the previous way, but has its own characteristics:
- Transoms are easier to install than doors. They do not require sealing, because water does not fill the gaps between the window and the frame.
- To obtain a good result, it is necessary to place the openings as high as possible. Cool air penetrates the building from top to bottom, moving towards the center, without the formation of strong drafts.
- It should be remembered that the smaller the size of the window, the greater the flow rate. The optimal total area of openings is at least 20% of the total surface area. With these parameters, plants are subject to minimal temperature loads.
- Additional openings on the side walls also reduce drafts. Air enters from different sides, mixes, but does not move in one direction.
- The classic placement of vents is in the roof. Warm air rises and cold air sinks into the building. No drafts are formed, and the crops are not affected by temperature loads. The main advantages of this method: low energy consumption, high efficiency, and no harmful effects on plants. However, it has disadvantages associated with the upper location of the windows. They are difficult to close and open manually, so you have to use expensive mechanisms - chain drives, gear motors, etc.
In film greenhouses, the side walls can often be completely opened. This option is ideal for seedlings. During the day, almost nothing protects the plants, and they are hardened from temperature changes, and at night, after the film is lowered, the seedlings are protected from hypothermia.
Pneumatics for natural ventilation
In order not to spend money on expensive equipment, you can automate the device yourself. Let's consider a design that is designed for a window that opens horizontally. To do this, you will need the following parts: a tank with a capacity of 30 liters, a chamber for the ball, a pipe or hose, with the help of which the individual elements are connected into one system. The work is performed in the following sequence:
- Attach a lever to the window through which the force for opening and closing it will be transmitted. It should be adjustable, allowing you to fix the frame at different angles.
- Adjust the transom so that it closes on its own.
- Install a football camera between the lever and the frame of the greenhouse and secure it in such a position that the window opens when filled with air.
- Connect the chamber with a hose to the barrel, which should be located in the middle of the building.
- Seal all holes in the container.
Under the influence of high temperature, the pressure in the barrel will begin to rise and air will move into the chamber. When expanded, it will move the lever and raise the transom. After cooling, the window will close the opening under its own weight.
Other natural ventilation devices
To organize ventilation in a natural greenhouse, you can use the following devices:
- Bimetallic devices
. The design consists of a lever and two bimetallic plates with different expansion coefficients. The operating principle of the device is as follows: when the temperature rises, one of the plates is deformed and opens the window. When lowered, the element is leveled and the frame returns back. The system is very simple, but has disadvantages: it is difficult to calculate by what amount the plate is deformed when heated. - Automatic window
. This is a new direction in arranging ventilation in a greenhouse. The main element in the product is a cylinder with a piston into which oil is poured. When heated, the oil expands, moving the piston and the transom attached to it. The liquid does not compress, so when it expands, the device can move a fairly heavy structure. It differs from other designs in its simplicity and low price. - Electrical devices
. Such machines have high sensitivity, convenient adjustment and unlimited power. The adjustment devices are small and easy to place anywhere in the building. The device can be configured for any operating algorithm. However, the electrical system is unreliable and depends on the continuity of the system. A power outage for several hours in the summer can cause the destruction of the entire crop. Therefore, it is always necessary to provide autonomous power sources in the greenhouse - batteries recharged from solar panels.
How to ventilate a greenhouse - watch the video:
Methods of organization
According to the control method, ventilation systems for greenhouses are:
- mechanical (doors and transom doors open and close manually);
- automatic.
In a greenhouse, automatic ventilation (using a thermal drive) is divided into several types:
- electric ventilation system for greenhouses. Available in price. Consists of a thermostat and an electric fan. The mechanism is triggered when the set temperature is exceeded;
- hydraulic. A device based on a hydraulic cylinder, with the help of which the transoms are opened and closed. The mechanism comes into operation due to the expansion of the liquid inside the device as the air temperature increases;
- bimetallic. It works due to the different expansion coefficients of the two metals. When heated, one plate bends, opening the transom;
- automatic window.
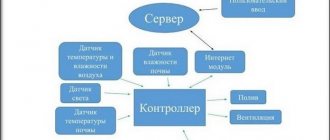
Climate control system
The greenhouse climate control system is used to maintain the optimal level of four parameters: humidity and temperature in the greenhouse, lighting and carbon dioxide content. For this purpose, the greenhouse is equipped with:
- heating and ventilation system;
- backlight;
- CO2 feeding system.
The operation of the system is monitored using a special control controller, as well as measuring sensors located inside the greenhouse. In addition, the system is equipped with a weather station, which includes a whole set of different sensors in its design.
The microclimate control system has the following functionality:
- climate control in the greenhouse;
- setting temperature and humidity conditions;
- tracking outdoor weather conditions;
- saving and analyzing the obtained indicators.
In industrial buildings
In most options, industrial greenhouse structures are equipped with a combined ventilation system.
Ventilation technology in industrial greenhouses in this case is carried out by combining natural air exchange with artificial mixing of air in the room using fans suspended from the ceiling.
Air enters the greenhouse through transoms, which are opened using a hydraulic or electric drive.
The openings open automatically, while the doors swing open not one at a time, but in a complex manner, maintaining the required angle.
The combined ventilation method can also be used in large home greenhouses.
Read the article about an automatic greenhouse ventilation system.
Polycarbonate
For ventilation in a polycarbonate greenhouse, you need to equip the structure with vents, which can have a conventional design or forum blinds. If there are vents in the form of blinds, air evenly enters the room, which helps prevent the formation of drafts.
In addition, a polycarbonate building can be equipped with various types of automatic ventilation systems.
Electrical ventilation system
With this method, air exchange occurs due to the supply ventilation system, which is turned on at a certain time in accordance with the specified settings or when the required temperature in the room changes. Air is removed using exhaust fans.
To ensure air circulation, a household fan that is installed on the wall indoors is suitable.
It is also possible to organize air exchange by automatically opening the vents, but such a system requires special drives, the installation of which is not only complicated, but also associated with considerable financial costs.
Do-it-yourself automatic greenhouse ventilation
Let's give an example of how to properly make ventilation in a greenhouse yourself.
Hydraulic system of communicating vessels . Installed for an axial window (horizontal, vertical arrangement). Two containers are needed: glass jars, plastic bottles or other containers. Manufacturing:
- One container is half filled with water.
- Placed at the top of the greenhouse. The higher it is, the faster the water will heat up and the window will open.
- The second container is attached (with twine, for example) to the top of the vertical axial window. Slightly filled with water.
- The containers are connected to each other by a thin hose, the ends of which are located at the bottom inside each bottle/can.
When heated, the liquid from the first container will move through the hose to the second, making it heavier. The window frame will gradually open as the second bottle/can moves down. When the air cools, the water will return and the window will close.
Bimetallic design . Used for light vents, it begins to act when the temperature rises significantly. Roofing iron and vinyl plastic materials are well suited for this. Manufacturing:
- Cut a long strip of each material.
- Glue the two strips together along the perimeter, slightly retreating from the edge.
- Measure ¼ of the entire length on the resulting structure.
- Attach the strip in the marked place to the bottom of the window frame.
- Install the other end of the strip through the double hinge joint on the bottom of the window itself.
The design will open the window when one of the elements warms up more than the other, bending the entire strip. When cooled, it will return to its original position, gradually closing the window frame
Pneumatic drive
The opening of the window will occur when heated air expands in the drive.
To make the mechanism you will need:
- Piston with foam rod.
- Rubber hose.
- A container for air, preferably made of metal.
- 20 - centimeter cylinder.
- Pulley.
- Durable cord.
- Wooden rocker.
- A ball made of plastisol.
Automatic ventilation of greenhouses with your own hands using a pneumatic drive is not difficult:
- You just need to make sure that the guide for the rod is fixed in the upper part of the cylinder.
- A hole is made in the bottom through which the hose is pulled.
- The mechanism starts working when the balloon is inflated.
- It lifts the rod and piston, which causes tension on the hose. When the temperature drops, the ball shrinks.
- There are also several non-standard ways to create an automatic ventilation system for greenhouses.
Note. If there are no metal plates and cylinders available, you can use what is always at hand in any country house: glass jars.
Ventilation system made from handy materials
How to make automatic ventilation yourself.
To assemble the automatic mechanism you will need the following parts:
- Jar lid used for wrapping vegetables.
- Cover made of polyethylene.
- Copper or brass tube, about 3 cm.
- IV tube, 10 cm.
- A wooden block, measured according to the shape of the window.
- Nails – 2 pcs.
- Wire on which to hang jars.
- The soldering agent is a sealant.
A ventilation system from cans is created according to simple instructions:
- In a large glass container with a capacity of 3 liters, you need to fill 0.8 liters of water. After this, the container is rolled up with a lid. A hole is made in it, the size of which is suitable for a brass tube;
- After this, the hole must be sealed with sealant;
- The same hole is made in the polyethylene lid, only a plastic tube is inserted and also sealed.
- After this, the jars are placed in the greenhouse. A beam is attached to the frame of the greenhouse, acting as a counterweight.
Note. It should be borne in mind that this method is only suitable for those greenhouses in which the transoms open along a horizontal axis. Once every three weeks you need to add water to the jars.
Recommendations
A list of some factors that help optimize the spatial environment of a greenhouse:
- It is best to glaze a heated garden with low-emissivity glass, which is characterized by the reflection of thermal energy inward. This will allow you to save on this insulation, given that the structure is completely glazed;
- a garden with passive solar heat gain can be glazed with single-chamber double-glazed windows;
- it is recommended to make the roof from safety glass;
- A shading system, artificial or natural, is required. Direct solar exposure can warm up the garden space to 70⁰ C, which is detrimental to most plants;
- ventilation is required all year round. Warm air, rising upward, will condense when touching cold glass; condensation cannot be avoided;
- when arranging natural ventilation, it is necessary to check the ceiling height, it should be more than 2.5 m;
- independent calculation of air duct outlets must be based on the principle that the total area of ventilation openings is 15% of the total area of the structure.
Conclusion
In an artificially created climate, everything must be provided for in advance, including ventilation. Thanks to it, you will be able to control the humidity in the structure and temperature, which will have a beneficial effect on crop yields. Today you learned about two main types of ventilation and now you can choose the one that is most suitable for you (see also the article “Galvanized steel ventilation - a universal solution”).
Sources
- https://foundmaster.ru/ventilation/kak-organizovat-ventilyatsiyu-v-teplitse.html
- https://bouw.ru/article/kak-sdelaty-ventilyatsiyu-v-teplitse-iz-polikarbonata
- https://AeroClima.ru/ventilyaciya/v-teplitse/
- https://tutknow.ru/building/uchastok/8899-kak-sdelat-ventilyaciyu-v-teplice.html
- https://parnik-teplitsa.ru/avtomaticheskoe-provetrivanie-teplicy-svoimi-rukami-78
- https://TopVentilyaciya.ru/ventilyaciya/teplitsy.html
- https://gidroguru.com/ventilyaciya/808-ventilyaciya-v-teplice
[collapse]
Homemade devices
A real economic effect can be achieved by installing a homemade mechanism; if you do not want to spend money on a finished device, assemble it from scrap materials. The simplest is a system of communicating vessels. For its device you will need:
- Two plastic containers of different sizes, one with a volume of 5–6 liters, the second – 1.5–2.
- A connecting hose, the length of which is the distance from the large container to the transom with free sag.
- Metal fitting according to the diameter of the hose.
- Sealant.
The volume of containers must be selected based on the weight of the window. Plastic bottles of 5 and 1.5 liters are suitable for opening a light transom. A thin rubber hose or plastic tube from a dropper will do. A large container will become an expansion tank; you need to pour water into it to a third of its volume and close it tightly with a lid. A hole is cut in the lid, a fitting is inserted into it, onto which the end of the hose is put on.
Also pour a small amount of water into a smaller container and close it with a lid, into the hole of which insert the other end of the hose. When the bottle is turned upside down with the stopper, the water should cover the inserted end of the hose. After treatment with sealant, the communicating vessels are ready for installation. The expansion tank is installed under the roof of the greenhouse, not far from the transom. A smaller bottle, which acts as a weight, is attached to the top of the window. The window opening device must provide for rotation of the frame along a horizontal axis.