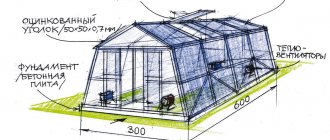
Greenhouses and greenhouses are temporary structures, and every gardener knows that it would be impractical to erect such a structure on a monolithic concrete foundation.
The current material for the foundation for a greenhouse will be timber. This is a durable and reliable material that will withstand the finished structure, and if desired, it can be moved to another location next year.
In order for the foundation to be reliable, it is necessary to become more familiar with the conditions of use of the material and the nuances of constructing the structure.
Advantages of a timber foundation
If we are talking about a structure for seasonal use, then a foundation made of bars is the best option. The main advantages of this design include the following:
- Small material and time costs.
- Possibility to assemble the greenhouse immediately after installing the base.
- Attaching the greenhouse frame to a wooden beam is quite simple.
- The wooden foundation under the greenhouse can be easily restored.
- If it is necessary to move the greenhouse, the structure is very easy to dismantle.
- Such a foundation is environmentally friendly and is perfect for a structure such as a greenhouse.
Of course, a timber foundation will last less than a concrete or brick foundation. But it will not damage the fertile layer. The minimum service life of such a foundation for a greenhouse is five years. However, in practice this period is much longer.
Choosing a wood type
The timber should be made from selected wood, but you should pay attention to its species.
Pine has an expressive pattern, but this is not the main thing when choosing a species for building a foundation.
This material has a density of 520 kg per cubic meter, it is rigid and elastic. Treating pine with impregnations will not be a problem. This is the most common lumber from which timber is made.- Spruce has a density of 430 kg per 1 cubic meter. It is light in weight, but has good stiffness and elasticity. It also lends itself well to treatment with chemical compounds. This raw material has a higher thermal insulation value and a low resin content. It is because of this that spruce is more susceptible to rotting than pine.
- Larch is often an alternative to oak, as it has good rot resistance. It is chosen for this advantage for foundations: larch is not afraid of dampness. It is strong, durable, widespread throughout the country - it is easy to find in almost any construction market, and larch is also low in cost.
- Cedar pine is not often used, since the timber made from it is expensive. The wood is dense and easy to process. This material is more suitable for decorative finishing. Than for the base for a greenhouse.
On a note. Considering the above, we can conclude that the best options for the base will be larch and pine.
Features of a timber base: installation technology
Speaking about the advantages of a columnar foundation, the following positive aspects are highlighted:
- simple technology and low cost;
- additional thermal protection is created;
- cannot be deformed due to the properties of wood.
A significant disadvantage of this design is its fragility.
The strip foundation has the following advantages:
- durability;
- can be used for the construction of winter spring greenhouses.
Minuses:
- high price and labor-intensive construction;
- If you need to move the greenhouse to another area, it is very difficult to dismantle the strip base.
Getting started right – preparation
Design calculations are a purely individual matter, but it is impossible to do without them. The wooden base must clearly correspond to the dimensions of the lower trim of the greenhouse being installed. There are no exact instructions where the greenhouse frame should be fastened: along the central axes of the timber frame, along the outer or along the inner edge.
It depends on the personal preferences of the master and on how it is more convenient for him to attach polycarbonate or polyethylene to the frame. However, this issue should be carefully thought through and carefully calculated in advance so that you do not have to resort to expensive alterations.
The timber for the foundation is selected depending on the installation method:
- material with an impressive weight of 150×150 mm (116 kg is the average mass of one coniferous element 6 m long), material with a size of 150×100 mm (the same criteria 77.47 kg) are purchased for the construction of shallow-buried wooden tape-type foundations. A large, heavy beam is used to ensure the stability of the greenhouse frame so that the structure does not overturn in gusty winds;
- lumber with a large cross-section is also preferable when building a large-sized greenhouse, if the length of the frame is more than 6 m and the height is more than 3.0 m;
- material measuring 100×100 mm (51.8 kg) and an even lighter material 100×50 mm (26.0 kg) are used to construct grillages attached to columnar supports. Because Since the main load falls on the supports, there is no point in using heavy, expensive timber.
Timber made from softwood is the cheapest and easiest to process. But it cannot be considered one of the most wear-resistant representatives of wood products. Larch will last the longest; underground and underwater structures have been built from it since ancient times, but its price is slightly higher than pine. Regardless of the species, the moisture content of lumber should not exceed 22%. Otherwise, the wooden frame will warp, and along with it, the frame of the greenhouse will be deformed. There should be no blue discoloration or other signs of damage on the purchased timber. It is not advisable to buy grade IV with numerous knots.
Before construction, it is recommended to protect the wooden foundation from destruction by fungal microorganisms and from the negative effects of ground moisture. A wide selection of bitumen mastics and antiseptic impregnations are now on sale. In addition to them, there are traditional methods:
- Copper sulfate. The prepared solution, often used in greenhouse farming, is impregnated with dry material and allowed to dry thoroughly. The timber will need to be brought to “condition” on an outdoor area protected from sunlight. It takes quite a long time to dry, at least two to three weeks, but then serves flawlessly. The readiness of lumber for laying is determined “by eye” and by touch;
- Firing with hot bitumen coating. The timber is first burned with a gas burner and then covered with heated tar. Particular attention should be paid to ends and knots. You can simply burn wood over a fire;
- Warm up working out. Cheap and easy to apply with a brush or rag. Used engine oil is not at all pleased with its environmental and fire-fighting benefits.
Greenhouse owners give justified preference to the first two of these methods. They will not upset the natural balance. However, the third option is also quite suitable for constructing a wooden foundation completely buried in the ground, installed in a trench with walls and bottom covered with roofing felt.
Next, we’ll take care of preparing the site. It is advisable to break it down before work, without relying too much on your own eye:
- According to the pre-calculated dimensions of the external outline of the frame, we will hammer in temporary pegs.
- We connect them with twine or fishing line at a height of approximately 40-50cm from the ground. We tie each pair of pegs with a separate piece of rope with a margin of 30 cm at both ends.
- Let's check the lengths of the diagonals and check the perpendicularity of the corners.
- If everything is correct, we will make a kind of cast-off. Let's kind of extend the imaginary lines of the foundation walls and hammer in two more at a distance of about 50cm from the existing peg.
- We will tie a fishing line or twine to the newly installed pegs so that the point of intersection of the two lines is directly above the planned greenhouse corner - i.e. over the first hammered peg. We do this 3 more times.
Casting for the construction of a foundation made of timber is an optional measure. Often they do without cutting at all, because the specifics of long-length lumber help to maintain dimensions. At first glance, the procedure itself takes time, but in reality it saves. After all, the master will not need to control the direction and dimensions dozens, and sometimes hundreds of times.
Tools and materials
In addition, to complete the work you will need the following tools:
- rope or fishing line;
- wooden stakes;
- building level;
- roulette;
- hacksaw;
- hammer;
- nails;
- shovel and bayonet;
- anchors for fastening the main structure.
It should be noted that this is not a complete list of tools and available materials necessary for arranging the foundation. Depending on the type of foundation chosen, you will need to add a hand drill (for a pile foundation), formwork boards (for laying a strip base), etc. to the list.
Forest selection
The base is made of hardwood timber, which is chosen very carefully. The lower part of the tree trunk (butt) is what is needed for these purposes. There should be no rotten or gray areas affected by fungus.
A greenhouse is a specific structure. The humidity there is always high, plus chemicals and fertilizers quickly render the structure itself unusable.
Therefore, the forest should have a humidity of no more than 20%, otherwise it will begin to deform over time.
Leading to undesirable consequences, subsidence, cracks and distortions of the entire structure, this is unacceptable for a polycarbonate greenhouse.
Treatment
When assembling a wooden frame base, one cannot do without special processing of such a foundation. Bioprotection with special solutions will provide excellent protection against insect pests. Antiseptics also need to be used; they provide protection against mold and fungi, which is very important when growing seedlings.
It is easy to apply it to the prepared timber with a roller and brush. If the polycarbonate greenhouse will be in a humid place, it is recommended to process the wood by immersion in a special mixture.
Making a soaking bath is not difficult. The galvanized sheet is bent so that it has two sides and a solid bottom. Then the edges are rolled. It looks like a trough.
But if you don’t have the right material at hand, use a shovel and thick plastic wrap. Dig a ditch and cover it with film. After pouring the solution directly into the hole, treat the timber by immersing it in the solution for 5 minutes. Then dry.
Moisture protection
Waterproofing with resin
When creating a wooden foundation for any greenhouse made of metal, wood or polycarbonate, you cannot do without protecting the base from moisture. Moisture is always present here, flowing down the inner surface of the polycarbonate or film.
Usually the beam lies on a concrete base, but sometimes it is laid on a compacted bed of crushed stone, laying a layer of waterproofing materials.
Oil is one of the wonderful remedies. Some impregnations contain different oils, from cottonseed to bitumen-based oils. By impregnating a timber foundation, you will significantly extend its service life. The treatment is carried out in two layers with a brush or roller with artificial bristles.
When carrying out such work, use personal protective equipment, masks, respirators, rubber gloves, an apron or a special work suit.
Marking
Having decided on the place to install the greenhouse, it is very important to correctly mark the future foundation. The use of prepared lumber greatly facilitates this process, since all elements of the base will correspond to the length and width of the structure being built. At this stage, it is important to set right angles and check the geometry of the rectangle along the diagonals. For these purposes, a measuring tape, wooden poles and twine are used.
Soil excavation
After marking the boundaries of the foundation, it is necessary to excavate the soil for lining the greenhouse. The depth of the trench is 10...15 cm. Next, along the entire perimeter of laying the timber, the sand and soil mixture is backfilled and compacted. The backfill should be 5...10 cm above the soil level. This will allow the base structure to be leveled perfectly in the horizontal plane.
If you plan to use point supports to tie the foundation of the greenhouse, then metal pillars with thrust bearings are screwed in along the marking line, or concrete blocks are laid on a sand cushion. In addition, pre-treated wooden posts can be dug into the ground. However, this option is not so popular due to the difficulty of aligning all the columns to the same level.
Laying
On a prepared and perfectly leveled base, the piping of the future greenhouse foundation is assembled. At this stage, each element is connected to each other. There are two ways to join corners:
- Connection in the paw;
- Half-tree connection.
If a greenhouse 6 meters long or more is installed, then the timber must be increased. In this situation, it is best to use a half-tree connection. Elements laid in width are built up in the same way if a greenhouse of non-standard dimensions is installed on the foundation.
Installing a wooden frame in a trench
If the area is prone to heavy winds, the above scheme is not suitable. A more complex, but much more reliable method is to install a timber foundation in a shallow trench. To form it, a breakdown is needed.
Digging a trench will not require much effort. The maximum depth of the groove is equal to twice the height of the beam, the width is equal to twice the width. A quarter of the bottom of the trench will be filled with sand or gravel. Opinions are divided regarding further actions:
- According to a large number of craftsmen, it is necessary to arrange something like a pallet made of roofing felt in the ditch in order to create a barrier between the wooden base and the external moist environment.
- According to their opponents, this is an unnecessary measure that can harm the wood. Water entering a “trough” constructed in this way will not infiltrate into the soil, which can cause the wooden frame to rot.
We admit that the second opinion is very reasonable. In addition, leveling the frame in a trench with roofing felt seems to be a difficult undertaking. And it is necessary to level it according to the spirit level readings, otherwise the skewed base will become the start of the construction of a skewed greenhouse.
The wooden base must be leveled in accordance with building codes using wooden wedges, scraps of timber, boards, etc. Minor deviations are eliminated by adding sand or gravel. If bricks or stones are used as a lifting element, there should be a spacer made of roofing felt, parchment or simply oiled paper between them and the wooden parts.
If the owner decides to build a more powerful wooden base for the greenhouse, the timber is laid in two or even three rows like well crowns. The rows are fastened together with wooden dowels or reinforcement sections. It is wiser to use reinforcement, because it will simultaneously play the role of rods driven into the ground. True, the service life of a foundation with a metal-wood combination will be reduced.
By the way, you can assemble the foundation according to the well principle, and according to it, bury the wooden foundation into the ground. First dig up the soil under the assembled walls approximately in the middle. Then place bricks or logs in the dug hole as temporary support. Then dig around the perimeter, after which these temporary supports must be removed. The foundation will settle on its own in its intended place.
Fixation
The final stage of constructing a foundation for a greenhouse is fixing the timber. All elements of the greenhouse base can be fixed relative to each other using self-tapping screws, threaded rods and metal brackets. In addition, the harness is fixed relative to the base. In one case, the frame is secured with anchors to concrete blocks. In another, they are fixed to the thrust bearings of screw piles.
When installing heavy greenhouses, a two-layer timber frame can be used as a foundation. In this case, each crown must be connected to each other with threaded rods. Using this type of connection will allow you to quickly assemble and disassemble the base structure.
If you decide to dig a foundation for a greenhouse made from wooden beams, refrain from laying roofing material in the trench. Its use will serve as a moisture storage device. In such an environment, the base frame will begin to rot very quickly.
A simple foundation for a small greenhouse
During active use, the basic strip version of a wooden foundation has acquired numerous varieties. Fundamentally, the design of its construction consists of connecting four sections of timber.
The optimal type of connection is considered to be a “toe-to-foot” connection, because it can be made without the use of metal fasteners. It is recommended to duplicate the “half-tree” notch with a bolt or smooth reinforcement driven through the joining area. The reinforcement is driven into a pre-drilled hole with a diameter slightly smaller than the pin being driven.
An inexperienced contractor who has decided to build a timber foundation for a country greenhouse for the first time with his own hands should not bother with the cutting. Frame parts can only be fastened with two anchor bolts screwed into the end of the beam, iron brackets or metal corners.
A frame assembled from timber can be installed on a pre-leveled platform without unnecessary fuss. In this case, the breakdown of the site is excluded from the work cycle without any qualms. Assembly accuracy is checked by measuring the diagonals. If the values of the diagonal dimensions coincide, it means that the strip wooden foundation is assembled impeccably.
All that remains is to secure the base by:
- driving reinforcement into the ground from the inside of each corner and through 1.0-1.5 m of the long walls of the greenhouse;
- screwing screw supports with a length of no more than 70 cm at the same points;
- fastening by driving reinforcing bars into the ground through areas of corner and linear connections.
Lengths of reinforcement and screw supports driven from the outside or inside of the foundation frame are screwed to it using metal mounting plates. Instead of reinforcing bars, wooden stakes can be driven into the soil. They do not need to be screwed, just nailed. The stakes are pre-fired and treated with tar.
After fastening, the wooden foundation is sprinkled with sifted coarse sand without foreign inclusions or gravel. The standard algorithm for the construction and installation of a wooden base with the assembly of a miniature greenhouse is demonstrated by a photo selection:
Let's consolidate our knowledge by watching a video about constructing a timber foundation for a domestically produced greenhouse:
Recessed option
Recessed columnar foundation for a winter greenhouse
A greenhouse or greenhouse is built on a wooden foundation even if it is necessary to grow vegetables and seedlings in the winter. It is usually buried 1 meter. This makes it possible to save on resources, taking advantage of the warmth of the earth. Despite the fact that the area of the walls transmitting light is reduced, this option allows you to save fuel.
The technology of the polycarbonate surface version differs not only in the design of the frame, but as for the base, it is created much more powerful. Using logs or semi-tips, semi-logs. Having removed the bark and carried out pre-treatment.
In these basics, the work goes like this:
- They excavate the soil to a given depth and level the walls. Lay a waterproofing layer of roofing felt on the outer wall.
- Drive the pointed end of the log into the ground around the perimeter. Pre-treating them with bitumen or mastic.
- Along the lower and upper parts of the finished log walls, staples 40-50 cm long are driven in and tightened.
- Level the top edge using a chainsaw. Then they place the top beam, screwing it to the ends of the logs.
- They compact the base near the pillars.
Every 5th log should be 50-60 cm longer than ordinary logs. For example, the burial height is 1000 mm. The row post is 1400 mm long, and the corner and intermediate post is 1800 mm long.
To build greenhouses made of wood or polycarbonate, you can use any of these technologies. The main thing is to determine the direction and purpose of the greenhouse. And to build a base from wood means choosing the optimal ratio of price and service life.
If a grillage is constructed from timber
In the case of using timber as a grillage, the layout of the site is carried out taking into account the installation of supports, which can be:
- low posts made of timber dug around the perimeter, the size of which is similar or larger than the lumber used to construct the frame;
- screw supports with disks whose diameter is equal to the diagonal of the beam;
- point concrete supports, for pouring which it is not necessary to make formwork. Concrete is poured in two steps into a miniature pit with sides 25 cm, 30-40 cm deep. First, the hole is filled to about half, then a piece of metal mesh is placed on the set mortar and the pit is filled with concrete flush with the ground;
- brick pillars, in front of which a 5cm concrete base is poured. Its area should be larger than the area of the brick support. The bricks are laid two in a row, in two or three rows.
The frequency of support placement depends on the weight and dimensions of the greenhouse being constructed. For a light, small-sized structure, only corner posts are often sufficient; row posts are installed at a distance of 1.2-1.5 m from each other.
In the process of preliminary calculations, it is necessary to take into account that the timber is laid exactly in the middle of the support column. Between wood, brick, metal or concrete, a roofing material is required. The timber frame is attached to the supports with anchor bolts and washers, and a greenhouse frame can be erected on it without any difficulty.
These are all the subtleties of constructing a wooden foundation for a personal greenhouse, the construction of which the owner will devote a minimum of time, money and effort.
What will you need for the job?
To arrange the supporting structure, you need to prepare the following tools:
shovel;- roulette;
- level;
- hammer;
- drill;
- screwdriver;
- jigsaw or saw;
- screwdriver.
You also need to purchase screws or other fasteners that will secure the frame. The materials you will need are timber of the selected species; it should have a moisture content of about 22%.
There are also nuances when choosing the thickness of the boards. For example:
- For a lightweight greenhouse frame, 5x5 cm beams are suitable.
- For a medium-sized structure on metal rods, it is important to take a beam of 5x10 or 5x15 cm.
- If the greenhouse frame is created from profile pipes or thick wooden boards, then it is better to take raw materials with a cross-section of 10x10 or 15x15 cm.
Step-by-step installation of a greenhouse on a wooden support
It is advisable to install a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall. At this time there are still no frosts, so there is every chance of getting a rich harvest and using this design comfortably.
Assembly instructions, fixing fasteners
The process of correctly installing a polycarbonate greenhouse is carried out in accordance with the following step-by-step instructions:
- Decide on the area where the greenhouse will be located. It is advisable to place it at a distance of about 10 m from buildings and about 3 m from plants. Remove the top fertile layer of soil from the surface of the outer area and prepare the site for installation. The removed soil must be cleared of roots. It must be placed in a special place for a year, and then used when planting vegetation.
- The process of assembling the greenhouse frame must begin from the ends. Their installation is carried out one by one.
- Ensure that the end arc for the greenhouse is secured from above using bolts on the door frame. Fasten the end struts in the same way.
- Attach the end posts to the spacers and arch. Thus, further installation of the metal frame can be continued. The intermediate spacers are fixed at the end using bolts.
- Install intermediate arches and posts using bolts with longitudinal struts. The greenhouse ends must be installed in a horizontal position. The arcs are connected to the ends using longitudinal struts. When the installation of all parts is completed, the greenhouse sheathing is completely ready.
- After preparing the required area, the dimensions of which coincide with the dimensions of the base of the sheathing, secure the metal product using self-tapping screws. Now you can use polycarbonate sheets. They are put to work when covering the sheathing from above. In this case, this must be done in such a way that the size of the sheets coincides with the dimensions of the perimeter of the base of the sheathing.
Installation of a metal frame
The frame for such a design must be used in the form of a constructor. Thanks to this, you can easily replace damaged parts with high-quality and new ones. To do this, you just need to remove the screws and fix the new elements. Read how to make a greenhouse with your own hands from PVC pipes here.
Methods for installing polycarbonate panels
The process of fastening polycarbonate to the frame can occur in several ways.
The simplest is considered to be a profile fastener, which is characterized by the shape of the letter H lying on its side. The profile is fixed to the sheathing itself, and then polycarbonate sheets are inserted.
The second method involves laying special rubber gaskets. The polycarbonate panel is fastened to the gasket. After this, you can install metal nozzles. To fasten them you need to use screws. After that. Once the greenhouse is assembled, it is also important to think about heating it in the cooler part of the day, and infrared heating of greenhouses is suitable for this.
Video about installing polycarbonate with your own hands and the intricacies of attaching it to the greenhouse frame:
Material processing
Before using timber from the timber to lay the foundation, it is recommended that it be properly treated. It is worth considering several important nuances:
- the antiseptic must be intended for external use: compositions for internal use will be washed off at the first precipitation;
- the impregnation should be “friendly” with polycarbonate and not damage it during use;
- there should be no poison in the impregnation: it can penetrate the soil and infect the plants;
- the most optimal composition is water-based, which creates an invisible film on the surface of the raw material and protects it from rotting;
- Sometimes, instead of ready-made products, you can use a folk method: burning with a blowtorch, heated bit or machine oil works well.
You can also use copper sulfate - it is harmless to plants. For processing, each part is soaked in a solution and left to dry, but without exposure to sunlight. Drying usually takes about 3 weeks.
Tips for installing a greenhouse
The installation of polycarbonate panels is carried out in such a way that the ribs are vertical and water can flow freely from them.
Panel manufacturers recommend making a small hole in the bottom trim for drainage. Its diameter should be 6 mm. The distance for the moisture accumulated at the bottom of the panel to escape should be 30 cm.
The panels can be attached to the wooden frame using screws. In this case, the seams can be masked with overlays, and the point load exerted by small-area sheets screwed in with screws will be evenly distributed.
Installation errors, tips on how to install correctly
The process of installing a polycarbonate greenhouse has many features, so the following mistakes should not be made, and you should listen to advice on how to install it correctly:
- When you start making a frame, it is very difficult to make identical arches yourself. Therefore, it is better to use ready-made products at affordable prices, which are sold in specialized stores.
- You must always monitor the inclination of the surface relative to the rays of the sun.
To solve this problem, you need to use flat surfaces. They are able to transmit light inside rather than reflect it
- It is known that polycarbonate greenhouses are completely transparent structures. For this reason, the greenhouse loses thermal energy and light. As a result, one side of it receives light, and the other releases it. A large flux of light can eliminate this problem. For these purposes, it is necessary that the northern part of the building reflects light and is opaque. What mistakes all gardeners make when heating a greenhouse in winter and how to heat a polycarbonate greenhouse in winter are detailed here.
If a polycarbonate greenhouse shines when exposed to sunlight, then the light is reflected from the surface of the greenhouse. This phenomenon has a negative impact on the plant, since then they do not receive enough light.
You can install a polycarbonate greenhouse on a beam with your own efforts. But for this you need to know the main technological stages. It is very important not to make a mistake in choosing polycarbonate sheets and their correct location. Particular attention must be paid to the construction of the frame and wiring of lighting and irrigation systems.
Sources
- https://TalbaMas.ru/tipy-i-montazh/kreplenie-teplicy-k-zemle-shtyryami.html
- https://2Gazon.ru/postroiki/teplizu/montazh-na-derevyannyj-fundament.html
- https://vasha-teplitsa.ru/karkas/fundament-dlya-teplicy-iz-brusa.html
- https://teplica-exp.ru/fundament-dlya-teplicy/
- https://FundamentClub.ru/ustrojstvo/fundament-dlya-teplicy-iz-brusa.html
- https://pcarbonat.ru/fundament-iz-brusa-dlya-teplicy-iz-polikarbonata.html
Terms of Use
The greenhouse must be installed on a frame, and if timber was chosen as the base material, then it is worth remembering several conditions for its use:
the weight that such a foundation can support is from 70 to 120 kg;- fastening of parts must be provided in such a way that in the future it can be disconnected and the greenhouse can be moved to another location;
- the greenhouse frame must ensure the rigidity of the entire structure;
- the timber must be treated appropriately to protect the soil inside from being washed away by rain;
- raw materials must be treated with antiseptics and impregnating materials to avoid rotting, attacks by rodents and insects;
- processing of the material should take place on a separate site to avoid chemicals getting into fertile soil;
- all cuts, places where beams and boards are fixed must be treated with antiseptics - this is done at the assembly site.
Important! To process the material, not only impregnations and antiseptics are used, but you cannot do without them. If you abandon the processing stage, then with constant rain and watering inside the greenhouse, the timber frame will become unusable very quickly.