In modern individual and industrial construction, the issue of high-quality glazing is one of the first places. The glazing material must be transparent, durable and inexpensive. Today, these requirements are fully met by polycarbonate - a viscous polymer plastic obtained using the organic synthesis of carbonic acid. Depending on the intended purpose of the building, the type and thickness of polycarbonate are selected individually, based on specific conditions and requirements.
Features of the material
Cellular polycarbonate is called transparent sheets, inside of which there are small cells with long partitions. This structure gives the material truly unique properties. Cellular polycarbonate transmits sunlight no worse than glass. That is why it is often used in the construction of greenhouses. This material is almost 200 times stronger than glass.
Among other things, cellular polycarbonate is elastic and can bend along the cell partitions. Therefore, it is easy to assemble complex curved structures from it. These can be arched greenhouses and canopies, round gazebos, etc.
The disadvantages of this type of polycarbonate include only the ability to expand and contract with temperature changes, as well as instability to ultraviolet radiation. To prevent the sheets from being destroyed in the sun, manufacturers have to cover them with a special transparent protective film.
Do you need UV protection?
When choosing polycarbonate, it is important to think about whether it will be protected from ultraviolet radiation.
On a note! By the way, a material coated against this part of the spectrum lasts much longer than polycarbonate, which does not have such protection.
With constant exposure to UV radiation, microcracks gradually form on the plastic - the so-called photoelectric destruction begins. Gradually, these cracks increase in size, grow together and thereby destroy the polycarbonate sheet.
To prevent this destruction and increase the service life of the material, polycarbonate is coated with a special layer that protects against UV rays. The coating is applied on one side, on which there will be a mark indicating that the material is not afraid of this type of impact. It is with this mark facing out that the sheet is mounted during installation work to cover the greenhouse.
Polycarbonate effectively protects against ultraviolet radiation
Attention! Polycarbonate without a protective coating begins to deteriorate within the first year of operation. That is why it is generally unsuitable for greenhouses.
By the way, on some types of polycarbonate such coating can be on both sides. But for greenhouses this will be a waste of money.
UV protection of polycarbonate
Length, width and thickness of material
The sizes of polycarbonate sheets sold in hardware stores are standard. Their width is 210 cm. The length can be 6 or 12 meters. When purchasing, it is important to pay attention not only to these parameters, but also to the thickness of the material. The choice of polycarbonate based on this parameter depends mainly on where exactly it is intended to be used. The most popular sheets at the moment are 4, 6, 8 and 10 mm thick.
Types of Polycarbonate Sheet
Polycarbonate is produced in two main types:
- monolithic;
- cellular or cellular.
The simplest structure is that of a monolithic type of material. It is produced with a thickness ranging from 2-12 mm, sometimes it reaches 20 mm.
The properties of monolithic polycarbonate make it possible to use it to create structures with complex surface topography. It is convenient to hot mold, and the thickness of the material after processing remains the same over the entire area. Due to the high density of monolithic polycarbonate, it does not require an additional frame.
This type of plastic is characterized by high strength characteristics and anti-shock properties. You can purchase material of any color that remains transparent in any climatic conditions. In addition, such polycarbonate is very convenient to work with, and it does not weigh down the structure due to its low weight.
Using polycarbonate of different thicknesses
The first two types of material (4 and 6 mm) are most often used when assembling arched greenhouses or walls of buildings with a pitched or gable roof. In this case, polycarbonate with a thickness of 6 mm is considered more preferable. The fact is that the material is too thin and requires very frequent lathing, which makes construction more expensive. Sheets of 8 mm are usually used for a gable or pitched roof. This material is also used to make the walls of semi-professional greenhouses, where vegetables are grown even in winter. The roof of such structures is usually made of polycarbonate 10 mm thick.
For even more serious buildings, including gazebos and verandas that are subject to heavy snow and wind loads, you can use material with a thickness of 16, 20, 25 and 32 mm. The cell size of cellular polycarbonate does not exceed 16 mm. Therefore, thick sheets may have several layers.
Why polycarbonate?
Most private developers and construction organizations prefer to deal with polycarbonate. This is due to the fact that this material has unique positive properties at a relatively low price.
So, it has the following properties:
- Ecological cleanliness. Polymer plastic can be used both indoors and outdoors. It is chemically neutral and does not emit harmful substances even when heated.
- High strength. Monolithic 1 mm polycarbonate is much stronger than 3 mm silicate glass. Due to the viscosity of the plastic, the panels do not break, but bend under impacts.
- Nice appearance. The use of dyes allows you to create products of various colors and shades. The ability to bend allows you to create coatings of the most fantastic shapes.
- Durability. An important factor for construction. The polymer is not susceptible to rotting, mold, moisture and temperature factors.
- Insulating qualities. Cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of 16 mm, 20 mm, 25 mm can compete with single-chamber and double-glazed windows in terms of thermal and sound insulation.
- Low specific gravity of the material. This factor is very important when constructing frame structures. With the same strength as silicate glass, 10 mm cellular polycarbonate weighs 20-30 times less.
The material has a different structure and can be used almost anywhere.
Thus, polycarbonate sheets are used in the construction and finishing of such structures:
- transparent roofs. These architectural solutions are used in the construction of sports facilities, train stations and airports, shopping and entertainment centers, cowsheds and pigsties. As a rule, 32 mm polycarbonate is used for this. This material successfully resists snow and wind loads. Even large hail is not scary for him. An air gap of 30 mm serves as excellent sound and thermal insulation. This construction technique allows you to save significant amounts on room lighting;
- glazing of house facades. Panoramic windows are increasingly becoming fashionable in the construction of multi-storey residential and administrative buildings. 12mm polycarbonate panels are lightweight and durable. They are much easier to install than double-glazed windows. If damaged, they are easy and inexpensive to replace;
- canopies of various types. Thanks to its ability to bend, polycarbonate can be used to create canopies of a wide variety of shapes - smooth, domed, arched, concave and curved. As a rule, cellular polycarbonate 4 mm - 8 mm is used for this. Awnings can be installed over a car parking lot, a summer pool, a playground, a barbecue area and a table;
- canopies over the entrance doors to houses, shops and various institutions. Depending on the size, monolithic polycarbonate 5 mm or cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of 6 mm or more is used;
- greenhouses and greenhouses. The use of this material is popular both in small summer cottages and in industrial production. Polycarbonate transmits and diffuses light well, providing ideal conditions for plant development. Basically, cellular polycarbonate is used to equip greenhouses, the thickness of which varies from 3 mm to 6 mm. In conditions of increased wind load, 8 mm cellular polycarbonate is used.
In all cases, when planning glazing work or constructing various partitions, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the material, one of which is its thickness. It is on the thickness that qualities such as strength, thermal insulation, sound absorption and bending radius largely depend.
What should be the frame of a greenhouse or gazebo?
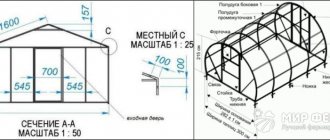
So, the dimensions of the polycarbonate sheet are fixed. Its length is 6 or 12 m, width – 2 m 10 cm. This material is mounted on a pre-assembled frame. When assembling any structure made of cellular polycarbonate, you need to take into account that the thinner the sheets, the smaller the pitch of the supporting sheathing should be. The relationship between these two parameters is presented in the table below.
| Cellular polycarbonate thickness (mm) | Lathing pitch (mm) |
| 4 | 500 x 500 |
| 6 | 750 x 750 |
| 8 | 950 x 950 |
| 10 | 1000 x 1000 |
| 16 | 1000 x 2000 |
Thus, when drawing up a project for a greenhouse or gazebo, and in particular when developing frame drawings, you should take into account not only the size of the cellular polycarbonate sheet, but also its thickness. Otherwise, the structure will not be reliable.
Advantages of polycarbonate for building greenhouses
It is not for nothing that gardeners began to choose polycarbonate if they need to build a greenhouse.
This building material has clear advantages over others:
- Retains ultraviolet radiation;
- Well transmits the light needed by plants;
- Scatters the sun's rays;
- Weighs a little;
- The plasticity of the material allows buildings to be given any shape;
- Lasting;
- Retains heat well;
- Good sound insulator;
- Not afraid of temperature changes;
- Relatively resistant to mechanical stress;
- Creates the necessary comfortable climate for plants inside;
- The average service life is more than ten years.
Weight of cellular polycarbonate
So, we found out what the usual sizes of polycarbonate sheets and their thickness are. However, when purchasing this material, you should definitely pay attention to some other indicators. For example, you should definitely find out how much weight the material has. The fact is that some manufacturers, in an effort to save money, make the stiffeners and jumpers in the honeycombs very thin. Of course, in this case the weight of the material is reduced. The same applies to strength characteristics.
For example, the weight of a standard sheet with a thickness of 4 mm is 0.8 kg/m2. Material 6 mm weighs 1.3 kg/m2, 8 mm – 1.5 kg/m2, 10 mm – 1.7 kg/m2, 16 mm – 2.7 kg/m2. Such sheets ensure maximum reliability of the erected structure.
Lightweight material is usually marked Light. Cellular polycarbonate of this type is cheaper. But even at the same time, it is, of course, less durable than the standard one, and therefore lasts less. The standard dimensions of lightweight polycarbonate sheets are no different from the length and width of conventional full-weight material.
Panel dimensions
Standard sheet sizes depend on the type and characteristics of polycarbonate. The dimensions of the sheet material and its physical characteristics (degree of flexibility) influence the choice of transportation method and are taken into account when calculating structures.
Dimensions of honeycomb material
Cellular polycarbonate is a sheet material with a thickness of 3 to 35 mm. For cellular polycarbonate, the sheet width is 2100 mm, with the exception of reinforced multilayer sheets with a thickness of 25 mm or more. Its width can be 1200 mm (depending on the manufacturer). Manufacturers produce cellular panels 12 meters and 6 meters long, the permissible deviation for transparent material is up to 1.5 mm, for colored material up to 3 mm.
The weight of a square meter of cellular sheet depends on its structure (number of layers and jumpers), as well as the thickness of the elements. The table shows the standard dimensions of cellular polycarbonate, the specific gravity at the standard density of the material and the corresponding weight of the panel.
Characteristics of cellular polycarbonate
When choosing cellular polycarbonate sheets, it is important to pay attention to the weight of the sheet. Manufacturers can supply material with reduced thickness of partitions. Its production requires less raw materials, which reduces the cost and, accordingly, the price of cellular polycarbonate. Lightweight cellular panels are not suitable for arranging roofs, canopies, and greenhouses in climates with snowy winters. They can be used in southern regions or used for the installation of structures that do not experience increased loads.
This polycarbonate is marked Light to warn the buyer about its low resistance to stress.
.
Sometimes unscrupulous manufacturers and sellers often pass off lightweight, less durable material as standard. Therefore, when purchasing, it is imperative to check the certificates for the product, evaluate the quality by pressing on the surface of the sheet - it should not be dented.
Dimensions of monolithic material
Monolithic sheet polycarbonate is produced in panels, the approximate size of which is 2x3 meters. This material has a higher light transmittance compared to cellular sheets. Typically, monolithic panels are made in single layers, but the material with a decorative effect can consist of several connected layers.
Be sure to read: How and how to cut cellular and monolithic polycarbonate at home
For solid polycarbonate, the standard sheet dimensions are
:
- width – 205 cm;
- length – 305 cm;
- thickness - from 0.2 cm to 3.2 cm (panels with a thickness of 0.8 cm are made to order).
Characteristics and approximate prices for monolithic material
This material looks impressive and can be used not only for installing canopies, canopies, roofs and fences, but also for creating advertising structures and decorative elements installed indoors or outdoors.
What could the cell structure be?
Stiffening ribs are the most important structural element of polycarbonate sheets. They determine the load-bearing capacity of the material. Moreover, their reliability may depend not only on their thickness, but also on the shape of the cells they form.
To create arched structures, a material with an orthogonal honeycomb structure is usually used. Such sheets are greatly deformed under load, but do not break and quickly return to their original shape.
Material with X-shaped and diagonal ribs is most often used to create rectangular greenhouses with a pitched or gable roof. Such sheets have low plasticity and practically do not deform. However, their maximum permissible load indicators are usually somewhat lower.
The fewer walls and partitions inside the sheet, the higher its heat-retaining qualities and the worse its strength. This should also be taken into account when purchasing material.
Whatever the shape of the cell, the dimensions of the polycarbonate sheets (width 210 mm, length 6-12 m), of course, will remain standard. The weight and thickness of the material may vary.
How to choose the right polycarbonate
As practice shows, often unscrupulous manufacturers and sellers try to pass off low-quality material as a lightweight version with high technical characteristics. In order not to be deceived, it is recommended to choose well-known manufacturers. Undoubtedly, the cost of such material will be slightly higher, but in this case you can be sure that the declared characteristics are fully consistent.
In addition, the warranty period is of no small importance. It is best if the warranty ranges from 10 to 15 years. It also wouldn’t hurt to ask to see the quality certificates of finished products. You can find out in advance what methods the manufacturer uses to protect its product from counterfeiting.
Attention! The optimal thickness of monolithic polycarbonate for a roof is 10 mm.
Why is the material width fixed?
So, 210 cm is the standard size of a polycarbonate sheet. It is clear how the width of this material is measured - based on one of the outer sheets. But why it is exactly like this and no other - this question already deserves more detailed coverage. And the point here is this: polycarbonate sheets, as already mentioned, are capable of greatly expanding at elevated air temperatures and contracting at lower temperatures. With a very wide material the difference in vibration would therefore be too noticeable. A narrow sheet is not particularly convenient to install. 210 centimeters, therefore, is the optimal option. A sheet of this size is convenient to install. The structures made from it are reliable and neat.
Recommendations for material storage and transportation
If there is a need to store polycarbonate sheets, you need to follow the basic rules:
- sheets must be smooth, without protrusions of any origin;
- Before laying, the sheets must be cleared of debris;
- the stack of sheets should not exceed 250 cm;
- the room intended for storage should not be exposed to the sun and moisture;
- for outdoor storage, the stack will need to be covered with transparent or white plastic film;
- Sheets cannot be stored curled.
When transporting material, you also need to follow a number of simple rules:
- polycarbonate sheets must be folded on a flat, flat surface;
- The surface must also be cleared of debris before storage;
- the stack in this case should not exceed 200 cm;
- the stack must be secured to the body with tapes or ties, there must be at least two of them;
- When transported in a rolled state, the radius of the roll must exceed that of the bend of the sheet.
How to cut sheets
When drawing up drawings of the frame of a gazebo or greenhouse, the standard dimensions of polycarbonate sheets must be taken into account. However, sometimes for some reason it is not possible to use the entire material. For example, there may be too little space on the site for a greenhouse, etc. In this case, cut the outer sheets. The cutting operation is also mandatory when arranging arched structures or those having some other complex shape.
In order not to spoil the material when cutting, you should follow certain rules. Recommendations for cutting cellular polycarbonate sheets are as follows:
- The center line of the cut piece should be parallel to the sides of the sheet.
- It is necessary to take into account allowances (about 5-10 cm).
- The procedure should be performed as carefully as possible, trying not to damage the protective layer.
- Any sawdust that appears from the channels should be removed.
- It is also necessary to take into account that polycarbonate bends only in the direction of the channels.
The type of tool used when cutting cellular polycarbonate depends mainly on the thickness of the sheets. Thin material is usually cut with sharp scissors or a utility knife. Thick sheets are cut using a hacksaw.
As we found out, the standard size of a polycarbonate sheet, or rather, its fixed width, is 210 cm. This gives owners of gardens and vegetable gardens another important advantage. From sheets of this size, you can cut ends wide enough to create a spacious and comfortable arched greenhouse. The material itself is used as economically as possible.
Video description
You can learn how to choose polycarbonate from the video:
Regarding installation, you must follow the following rules:
- leave gaps for thermal expansion;
- Place fasteners no closer than 4 cm from the edge and pre-drill a hole;
- maintain at least 5 degrees of slope for roofs and canopies;
- longitudinal jumpers in the honeycomb fabric should be located so that free drainage of condensate is organized;
- voids must be protected from direct contact with water, rain and snow.
Installation rules
The size of the polycarbonate sheet for the greenhouse allows you to cut the material with maximum convenience. However, the cut elements, among other things, also need to be installed correctly. Otherwise, the structure will not be durable and neat. When installing cellular polycarbonate, experts advise observing the following rules:
- The channels after fastening should be located vertically. In this case, the condensate that accumulates in them will flow out.
- The channels of vertically located sheets are covered with a special polycarbonate profile. The fact is that the moisture that appears in them will contribute to the loss of color and transparency by the sheets. Sometimes moss even begins to grow inside improperly installed material.
- When drawing up a design for a structure made of cellular polycarbonate, it is necessary to take into account wind and snow loads.
- When attaching sheets to the frame, you should use special self-tapping screws with thermal washers. Polycarbonate, as already mentioned, is a good thermoplastic.
So, we have answered the question in sufficient detail about what the size of a polycarbonate sheet is. For a greenhouse, or even a small gazebo, you usually don’t need too much of it. Moreover, cutting can be done as economically as possible. Therefore, despite the relatively high cost, if the desire is too strong to assemble such a structure in the yard, the owners of the site will not have to spend much.
Areas of application of polycarbonate
Despite the fact that polycarbonate is a rather fragile material, it still has a number of advantages. First of all, it is quite cheap and available to a wide range of buyers. In addition, it has a small mass, which allows you to build large structures without weighing them down. In this case, glass is not the best choice, and its price is noticeably higher.
The advantages of polycarbonate sheet allow it to be used in various industries. Transparent roofs, greenhouses and greenhouses, partitions, doors and canopies made of polycarbonate no longer surprise anyone. In addition, this material is actively used in the production of stands and stands for advertising, as well as in exhibition halls and galleries.
The following examples of the use of monolithic polycarbonate can be given:
- glazing of various buildings;
- installation of partitions in office, retail or other premises;
- arrangement of greenhouses, attics and summer terraces;
- installation of noise-absorbing barriers on highways;
- blocking of pedestrian crossings and transparent security posts;
- creation of covered public transport stops and telephone booths.
These are not all cases of using the material. Over time, new ways of using it are found.
Lifetime
Manufacturers of cellular polycarbonate guarantee the preservation of the basic technical characteristics of the material for a service life of up to 10 years, subject to the installation and maintenance rules. The outer surface of the sheet has a special coating that provides protection from ultraviolet radiation. Damage to it significantly reduces the service life of the panel and leads to its premature destruction. In places where there is a risk of mechanical damage to half-carbonate, sheets with a thickness of at least 16 mm should be used. When installing panels, the need to avoid contact with substances whose prolonged exposure contributes to their destruction is taken into account.
Which manufacturer to choose
There are many companies on the market that produce high-quality polycarbonate. However, there are also companies that sell a cheap analogue, passing it off as an expensive material. For example, instead of a polymer with a protective film, they often sell a fake that fails after just a couple of years. Therefore, a responsible buyer will always ask the seller for a quality certificate. If there is no such thing, it is better not to buy the product.
Among the brands of high-quality polycarbonate, the “magnificent seven” should be highlighted:
- Makrolon
This is a brand of the German concern Bayer Material Science, which has an impeccable reputation.
- Lexan
The trademark belongs to Sabic Innovative Plastics from Saudi Arabia. Known in many countries of the world.
- Trirex
Korean trademark, owned by Samyang. Domestic buyers appreciated the products of this manufacturer for a reasonable price-quality ratio.
- Caliber
Brand of the American company Dow Chemical. The quality is excellent, but the price is very high.
- Carbonglass
A Russian manufacturer that has proven itself positively. The material is durable and lasts for at least a quarter of a century, buyers note.
- Novattro
Domestic brand, owned by Safplast Innovative. The price is affordable, compared to foreign products, the service life is up to 14 years.
- "Polygal"
Trademark of a company of the same name. The Russian-Israeli manufacturer guarantees high quality and long service life, but at the same time the prices are quite attractive.
It is better to pass by Chinese goods; the service life of such a product is insignificant, less than ten years, and besides, it cannot withstand temperature changes. True, the product is inexpensive, which is why it is attractive to many buyers.
How to form cucumbers in a greenhouse step by step
Moisture resistance
This sheet material does not allow or absorb moisture, which makes it indispensable for roofing work. The main difficulty in the interaction of cellular polycarbonate with water is its penetration into the panel. Removing it without dismantling the structures is almost impossible.
Prolonged presence of moisture in the honeycomb can cause it to bloom and gradually collapse.
In order to avoid such developments, only special fasteners with sealing elements should be used during the installation process. The edges of the polycarbonate are covered with a special tape. The easiest way to clean honeycombs is to blow them with compressed air from a cylinder or compressor.
To protect the edge from moisture, the following is used: 1. - special adhesive tape, 2. - a special profile that is placed on top of the glued tape.
Specifications
For a long time, translucent structures were created using glass. However, it is fragile and unreliable. Any unfavorable atmospheric phenomenon (hail, gusty wind, snow) could result in damage to the structure. Polycarbonate outperforms glass in all performance characteristics, so it is more often used to create roofs of complex shapes. Strength and mechanical stability are influenced by thickness. Polycarbonate, selected for specific conditions of use, can last up to 25 years. Manufacturers claim the following properties of this material:
- A light weight. The sheet, in accordance with the thickness of the polycarbonate, weighs only 0.8-3.4 kg/m2, which makes it the lightest roofing covering.
- The minimum bending radius of the sheet is 0.7-5.7 m. The following trend can be observed: the thinner the material, the better it bends.
- The sound insulating ability of the sheet lies in the range of 15-36 dB.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of polycarbonate is 1.4-4.1 W/m2xK. For cellular polycarbonate this figure is lower.
- Light transmittance is 53-95% depending on the thickness and structure of the material.
Material characteristics
Professional builders claim that polycarbonate is used to perform a wide range of jobs. It is suitable for constructing canopies, covering gazebos or terraces, building greenhouses, greenhouses, and outdoor swimming pools. In order for the material to serve for a long time, you just need to choose the right type, thickness and color of polycarbonate.
No. 3. Honeycomb geometry and polycarbonate strength
The partitions inside polycarbonate form honeycombs, the shape of which significantly affects the strength of the material and its load-bearing capacity. The most common options:
- rectangular honeycomb is the most common material. The load-bearing capacity is not very high, but light transmission remains at a high level. This polycarbonate is recommended for use in greenhouses where artificial lighting is not provided;
- square honeycombs make the material more durable and suitable for the construction of medium-load greenhouses;
- hexagonal honeycomb They allow you to achieve the highest strength, but greatly reduce the level of light transmission, so such polycarbonate is rarely used for the construction of greenhouses, and if used, it requires the mandatory arrangement of artificial lighting.