Many experienced gardeners who own a plot of land are thinking about growing crops on a production scale for further sale on the commodity market. But often, one garden is not enough to create your own business. In addition, when working in open ground, you may encounter a number of problems that have a significant impact on the quality and quantity of the finished crop. In such situations, industrial greenhouses are one of the best options, thanks to which it becomes possible to grow cucumbers, tomatoes, strawberries and flowers in large quantities.
How do industrial greenhouses differ from conventional ones?
During the construction of industrial greenhouses, it is worth considering that they differ from conventional structures in size, which can be tens of times larger. The area of such structures can reach up to 100 square meters. m and more. Some industrial structures can match the height of standard fins, but the length and width are significantly different.
Another feature of industrial buildings is the reinforced frame. Since the structure area is impressive, the materials used for the cladding are heavy, resulting in the need to strengthen the frame installation. Also, do not forget that in winter the load from snow is much greater. If for a small greenhouse the collapse of the frame due to the weight of snow is a minor problem, then for large-scale structures this is a real disaster.
Since the main goal is to obtain a large harvest, an industrial greenhouse for growing vegetables operates all year round. It is for this reason that it is necessary to take care of creating comfortable conditions - install lighting, install ventilation, and a heating system, which in most cases is not present in ordinary home greenhouses.
Various modifications of the tunnel greenhouse
Tunnel greenhouse with a straight wall, width 9.6 m x h 4.0 m, height to hanging – 2.6 m.
Arch made of galvanized pipe Ø 60 mm, thickness 2 mm.
Two-way side ventilation with manual drive,- Ends Polycarbonate 8 mm.
- Two doors on each side of the greenhouse.
- Double layer of film 200 microns. with anti-condensation coating,
- Anti-wind - mosquito net.
- Pressurization system.
Tunnel greenhouse with a straight wall, width 9.6 m x h 4.7 m, height to hanging – 2.7 m.
Arch made of galvanized pipe Ø 60 mm, thickness 2 mm.
- Two-way side ventilation with manual drive,
- Ends Polycarbonate 8 mm. -Two doors on each side of the greenhouse.
- Double layer of film 200 microns. with anti-condensation coating,
- Anti-wind - mosquito net.
- Inflation system.
Tunnel greenhouse with a straight wall, width 9.6 x h 5.5 m, height to hanging – 3 m.
Arch made of galvanized pipe Ø 60 mm, thickness 2 mm.
- Two-way side ventilation with manual drive,
- Ends Polycarbonate 8 mm.
- Two doors on each side of the greenhouse.
- Double layer of film 200 microns. with anti-condensation coating,
- Anti windy mosquito net.
- Pressurization system.
]
Arched tunnel greenhouse, width 9.6 m x h 4.5 m, height to hanging – 2.7 m.
Arch made of galvanized pipe Ø 60 mm, thickness 2 mm.
- Two-way side ventilation with manual drive,
- Ends Polycarbonate 8 mm.
- Two doors on each side of the greenhouse.
- Double layer of film 200 microns. with anti-condensation coating,
- Anti wind mosquito net.
- Pressurization system.
Greenhouse construction "Households" Blok" connects and forms greenhouse complexes
Greenhouse construction "Households" Block" width 9.6 m or 6.4 m.
- Stoic Prof. pipe 80*60*2 mm.
- Arch made of galvanized pipe Ø 60 mm,
- The ends and sides are 8 mm polycarbonate. - Two doors on each side,
- Dome Polycarbonate 8 mm.
Greenhouse construction "Households" Blok" connects and forms greenhouse complexes
Covering, fastening and pressurization system
The greenhouse is covered with a double light-stabilized polyethylene film protected from destruction by UF radiation with an anti-condensation coating, the warranty period is 60 months.
Galvanized aluminum profiles with PVC clamps and locks are provided for fastening. Air is supplied between the layers of film through the turbine; the periods of operation of the turbine are controlled by a control unit.
The created air cushion guarantees savings in thermal energy and reduces the amplitude of temperature fluctuations, increasing structural rigidity and resistance to wind.
Ventilation
As standard, manual ventilation is provided along the entire length of the greenhouse by twisting the film onto a shaft using a handle connected to the shaft by a cardan.
Greenhouse construction "Households" Blok" connects and forms greenhouse complexes
- Double Sided Nozzle - Greenhouse Wall/Roof Intersection Flange
- Sealed (electrical protection level IP 55)
- Thermostat with sensor for installation in a greenhouse to save fuel consumption
- Axial Fan.
- Electricity consumption
- Gas air heater 1.65 kW (fan 1.2 kW, burner 0.45 kW)
- Gas consumption
- 17.23 m3/hour (or) Diesel fuel 13.7 kg/hour (or) Propane 6.66 m3/hour, Butane 5.05 m3/hour.
Top sprinkler irrigation system
- Connection node 1”,
- Dispensing line made of PVC pipe 32 mm,
- Sprinklers have PE pipes 20 mm,
- Sprinklers Modular Group 43 l/hour with anti-leakage devices,
- Electrovalve 1”,
- Cable production.
Automatic control:
- Complete control panel including 4-channel Galcon 4AS controller.
Watering and nutrition system for plants grown using the hydroponics method
The watering and spraying control unit (mixer with a capacity of 12 m3/hour) includes a microprocessor controller; EC and pH control sensors; injection dosing pumps for fertilizers and acids; water meter; bypass; control disk filters (120 microns) at the inlet and outlet of the mixer; chemical-resistant filters ¾” for fertilizers and acids; tanks for stock solutions of fertilizers and acids; piping and fittings; cable production;
The drip irrigation system includes main and auxiliary lines made of PVC pipes; sprinklers made of PE tubes 16 mm; droppers with anti-leakage devices, pressure compensated, with a capacity of 2.2 l/hour, for each plant at the rate of 2.5 plants/m2; field solenoid valves and cables for them; a complete set of fasteners, connections, accessories, etc. necessary for installation.
Artificial lighting system
Aluminum tables
Popular posts
- Greenhouses for a summer residence How to choose inexpensive but effective greenhouses for a summer residence A greenhouse for a summer residence is a great way to get…
- Frames for greenhouses Plot -16 votes + Vote for! - Vote against! The frame is the main element of the greenhouse. Exactly…
- Installing a greenhouse according to the cardinal directions How to choose soil for a greenhouse All these are the main factors for installing a building according to the cardinal directions.…
- Automatic ventilation of greenhouses Automatic ventilation of greenhouses There are two types of devices that automatically ventilate greenhouses: mechanisms and automatic systems,…
Types of industrial greenhouses
If we consider the types of industrial greenhouses, it is worth noting that they can be seasonal or year-round. This is what further determines the presence or absence of a heating system.
Seasonal greenhouses, as the name suggests, are used exclusively during the summer season. In the spring they are engaged in planting planting material and caring for the crop. After the harvest is harvested, and this will happen in late autumn, the greenhouse begins to be prepared for winter. The arrangement does not require large investments of funds. In most cases, such buildings are practically no different from home greenhouses, except for their global size.
Year-round structures are designed to grow crops throughout the year. In such cases, you will need to take care of a strong foundation in advance, which will further prevent the process of soil freezing. In addition, there must be artificial lighting and a heating system inside the greenhouse. Additional equipment can compensate for the lack of heat and sunlight during the cold season. Although such structures require large investments, the costs will pay off quite quickly. This is due to the fact that the cost of vegetables in winter is much higher than in summer.
Attention! In some cases, you can find not only polycarbonate, but also industrially produced film greenhouses.
Which greenhouse to choose
Industrial greenhouses with heating. The most budget option is to order a tunnel, arch-type model, with a metal frame, covered with a 150 micron film, with an air lock. Install heating, drip irrigation and windows for ventilation in the greenhouse. The frame will last for at least 20 years, and the film for no more than 5 years, then you will need to change it. It will be cheap, and if you have just started getting into the greenhouse business, and have limited funds and experience, it will probably be suitable. In five years, industrial greenhouses (photos confirm this) can be transferred to another level.
A structure covered with glass will last much longer than a film structure, it is heavy, and it is not afraid of the wind. A glass greenhouse allows sunlight to pass through best. The disadvantage of this model is that due to the heaviness of the glass, a more powerful frame is needed, which means that the project is much more expensive, and glass is much more expensive than polyethylene film and can break.
Industrial greenhouses made of polycarbonate are the best purchase option. The frame is as light as a film. Cellular polycarbonate, of course, is expensive, but will last at least 15 years. It transmits sunlight well and has a protective layer against harmful radiation. Polycarbonate retains heat well, is lightweight and soft enough to be transported in rolls. Covering a greenhouse with cellular polycarbonate is much easier and more convenient than with film or glass.
Drawings and projects of industrial greenhouses
In the process of carrying out installation work, it is simply impossible to do without drawings of an 8 m wide industrial greenhouse. In such cases, you can draw up a project and the necessary drawings yourself if you have skills in this area. Otherwise, you can use ready-made models, which will significantly save time and money.
Choosing a location for an industrial greenhouse
If you plan to build a large industrial greenhouse, then the choice of location should be given due attention. Thus, many experienced gardeners recommend adhering to the following recommendations:
- the site must be level, the number and size of existing irregularities must be present in a minimum amount, the permissible slope angle is 0.004%;
- since during the growing process the crop needs a large amount of moisture, the optimal solution is to choose a plot of land in close proximity to a water supply or reservoir, and close proximity to rivers is considered a violation of sanitary standards;
- construction on an industrial scale is not allowed in the area where factories operate - this is due to the fact that emissions into the atmosphere have a negative impact on the level and quality of the finished product;
- It is worth considering that if the distance to the road is quite long, then transportation costs will increase significantly;
- The ideal solution is to choose a plot of land that is protected from strong gusts of wind, otherwise you will need to install special protective fences yourself.
Also, do not forget about the fertility of the land, otherwise it is unlikely that you will be able to get the desired amount of harvest.
Window specification
- 3 glass roof vents - 1.125 x 3 x 1.040 mm with safety slamming rails.
- 6 glass roof vents - 1.125 x 6 x 520 mm with safety slamming rails.
The side profiles and window flashings have a rubber gasket installed to create insulation on the roof profiles and slamming rail. The vents are secured to the ridge using stainless steel roofing clips.
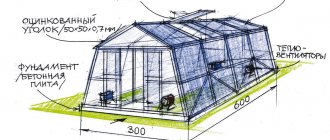
Industrial greenhouse foundation
Regardless of the design of the industrial greenhouse and the covering material used, a foundation must be present. Today, strip concrete foundations are popular. The foundation must lie below the freezing depth of the ground, which will further protect the greenhouse from the effects of cold in the winter.
Aluminum – gables – and side wall
- Roofing end profiles will have black rubber for installation.
- The top side of the rail will have black rubber for mounting.
- Glass profiles are designed for double glass in the gable.
- Staple profiles that close against the purlin, giving 4-sided support to the glass, will be supplied with closing white PVC strips.
- The bottom beam profile will be supplied with a black rubber profile at the front and will be designed to condense the drainage.
- The glazing bars will be equipped to use stainless steel bolts and locknuts.
- The gable and side wall structures are suitable for installing vertical screens.
Industrial greenhouse frame
Industrial greenhouses can be of several types according to the shape of the frame:
- Arched or arched. The cross-sectional shape of the greenhouse is semicircular. The frame arches are connected to each other using horizontal ties. The advantage is a high level of resistance to strong gusts of wind. In addition, much less building material is required to construct the frame. With the help of such arches it is possible to create structures of any size. Regardless of the time of day, sunlight falls on the surface of the roof and is then dispersed inside the greenhouse.
- Gable. Such greenhouses have a standard shape, the walls and roof are rectangular, the roof has 2 slopes. The advantage is the same height of the walls around the entire perimeter of the building. Such structures are the most durable, but their construction requires a large amount of building material.
- Lancet. This frame is a subtype of the arched version of an industrial greenhouse. In cross-section, you can observe the shape of a pointed arch, which is elongated in height and has a pointed end. The advantages are identical to those of arched structures. A special feature is the fact that snow practically does not accumulate on such roofs.
In the production process of industrial greenhouses, high quality materials are used, namely corner profiles and profile pipes made of steel.
Where to start construction?
- Choosing a location.
- Selection and preparation of the project.
- Materials.
- Greenhouse heating.
Selecting a location
To get the most out of your investment, you need to orient your building .
IMPORTANT: The best orientation of a long greenhouse building for areas located south of latitude 60° is from north to south. In the northern regions of the country, it is recommended to orient greenhouse buildings from west to east.
The construction of industrial greenhouses begins with the selection of a site. It should be as level as possible ( a slight slope of 0.04% is allowed). If hurricane winds occur in the region, provision should be made for the construction of additional shields and fences that will reduce wind speed. They will also protect the building from inflatable snowdrifts.
During melting snow and heavy rains, water should not accumulate on the site, which will flood the greenhouse and destroy the foundation. Before starting the construction of industrial greenhouses, you should think about the water supply. The soil must be fertile , and in order to obtain good harvests, it is necessary to provide for the use of soil mixtures, natural and artificial fertilizers.
Selection and design of the project
Before building a greenhouse, the farmer and the owner of a private farmstead need to decide what he will grow in the summer and winter seasons. As a result, a drawing of a farm greenhouse , as well as a list of requirements.
Experience shows that when building a critical structure that will serve for years, it is better to rely on specialists . In specialized companies, the customer is given a choice of dozens of ready-made projects that correspond to his wishes. Here you can buy a ready-made greenhouse in disassembled form and mount it on the foundation. Typically, businesses offer installation services.
Projects and drawings of industrial greenhouses:
Materials
How to build an industrial greenhouse ? In order for the greenhouse to serve for many years, it must be mounted on a foundation . The foundation allows you to securely fasten the structure, prevent the penetration of atmospheric water from the outside, and protect the crop area from weeds.
For small industrial greenhouses, any type of foundation - on piles, block, point, slab, brick. For large greenhouses, a concrete foundation is usually made; timber is less often used.
Frame
For farm and industrial greenhouses, a durable arched or gable frame is used. The frame is assembled from a hat profile, from a profile pipe or from a corner.
The hat profile frame is installed quickly and easily, but this design cannot withstand the weight of heavy snow. If you decide to build farm greenhouses from a profile pipe, then the frame can be welded. The pipe has a round or square cross-section. This design also cannot withstand heavy snow weight.
The best is a frame made from a corner (angle profile). It is assembled with bolts, without welding, the profile is galvanized and can serve for many years. This design can withstand the weight of snow up to 100 kg per square meter.
The frame is fixed to the foundation. For strength, use anchor bolts or pre-fixed studs. Such fastening will provide sufficient rigidity and strength , while the difference in the thermal capacity of building materials will not contribute to the loosening of the structure in extreme heat and frost.
The frame can also be aluminum . But the aluminum structure can be deformed under the influence of winds and heavy snow.
Winter industrial greenhouse - project:
Covering material
It is important not only to correctly calculate for modern industrial greenhouses regarding the required amount of building material, but also to choose a covering material.
In such cases, you can use the following options:
- sheets of cellular polycarbonate;
- glass;
- plastic film.
Since each material has its own characteristics, it is best to study them before making a purchase.
Cellular polycarbonate
Today, polycarbonate is actively used for the construction of a complex of industrial greenhouse structures. This material is easy to install. In addition, it is able to withstand mechanical damage, has a high level of strength and a long service life. According to the technology for constructing industrial greenhouses for growing planting material in winter, it is recommended to use polycarbonate sheets with a thickness of 3.2 mm to 6 mm.
Glass
Glass is perfect for making industrial greenhouses. In such cases, you can use window or greenhouse glass. It should be borne in mind that the second option differs from the first in its high level of strength. The light transmittance can vary from 88 to 92%, it all depends on the thickness of the selected material.
Polyethylene film
Despite the fact that the installation of industrial greenhouses under film has been practiced for a long time, this version of the covering material has a number of disadvantages. During the construction of industrial film greenhouses, difficulties arise with fixing the material, since it is very easy to damage. When there are strong gusts of wind, the polyethylene film stretches, causing it to inflate and cause damage. Arched structures built in places with strong gusts of wind have to be covered every year.
Serially produced models
Large enterprises in all regions of Russia are developing standard designs for conventional and industrial greenhouses. They have created a series of projects and offer the buyer a large selection of products.
REFERENCE: when designing industrial greenhouses, SNiP 2.10.04-85
What types of industrial greenhouses are there? There are several types of professional greenhouses for farmers:
- tunnel;
- multi-tunnel with gallery;
- block multi-span;
- garden centers.
Farm tunnel greenhouses . The series is developed by manufacturing enterprises based on existing building codes and regulations in Russia.
Industrial-scale greenhouses are produced under film and polycarbonate; different types of frames are used in the design. The cross-section of greenhouses can be arched, “Gothic”, “with straight frames” and “straight reinforced walls”. The width of the greenhouse building ranges from 3.5-12 meters .
Farmer Series
Industrial greenhouses "Farmer" are designed in compliance with SNiP 2.10.04-85 , they are intended for the industrial cultivation of vegetables, berries and seedlings. The frame of the farm greenhouse is assembled from a galvanized profile with bolts.
Arc-shaped trusses are tied together by straight beams. The cross-section of greenhouse buildings is semicircular (arched) or pointed (“Gothic”).
Dimensions of industrial greenhouses "Farmer":
The height in various models of the series is 3-4 meters . This allows you to grow both tall and short-growing crops by placing the seedlings on racks.
Greenhouses of this series are mounted on any foundation or on the ground in which racks are dug. The width of the structure ranges from 3.5 to 7.7 meters . The basic kit includes double-leaf gates, which are mounted at the ends of the greenhouse building. At the buyer's request, additional ventilation vents can be installed.
The greenhouses are covered with transparent cellular polycarbonate . The customer can choose the thickness of the polycarbonate - 6 mm (recommended), 8 mm or 10 mm. The polycarbonate is fastened with special “polyclip” fasteners, and the covering material is attached to the end walls with corner brackets. In the Farmer , vegetables can be grown all year round.
Ventilation, heating and lighting
The main system that must be present in industrial greenhouses in winter and summer is watering. Irrigation, if necessary, can be carried out in several ways - sprinkling or drip. If you choose the first option, you will need to install water sprayers in the greenhouse, as a result of which moisture gets not only to the soil, but also to the plants. This option allows you to provide watering at minimal cost. For drip irrigation there is another scheme. To do this, you need to install a drip tape or hose between the beds. Since there are a large number of holes in the hoses and tapes, water enters the ground through them.
Equally important for a winter year-round industrial greenhouse is the presence of a heating system. To do this, you can choose one of several methods:
- installation of a heated floor system;
- convection heaters;
- infrared lamps;
- air heaters.
Of all the proposed options, the installation of infrared lamps is considered the most effective, but it is worth considering that its cost is quite high.
Ventilation is mainly required in summer. In addition, it is important to understand that with a lack of sunlight, the intensity of photosynthesis is significantly reduced, as a result of which artificial lighting is required.
Important! If possible, it is recommended to automate the microclimate inside an industrial greenhouse as much as possible and the budget allows.
Engineering systems
To successfully grow vegetables, it is necessary to organize a stable microclimate in the building. To do this, devices are installed in the greenhouse that maintain optimal humidity and temperature, and also provide lighting and fresh air.
Heating system
For those who need to grow vegetables all year round, information about heating a greenhouse will be useful. It can be gas, electric or stove.
Based on the type of heat supply, the following types are distinguished:
- Steam. It operates by supplying hot water to radiators, which are located around the perimeter of the structure. Instead of radiators, you can lay pipes underground. In this case, the fertile layer will act as one large radiator.
- Air. The heating system is connected directly to the ventilation system. When turned on, warm air begins to circulate in the room. The most budget-friendly, but ineffective option.
- Infrared lamps. Large greenhouses are best heated in this way. After all, infrared rays warm the soil, not the air. The disadvantage of such a system is the cost of the equipment and the amount of electricity consumed.
Ventilation system
Air exchange is important for many crops. Due to ventilation, excess heat and moisture are removed from the shelter, and oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. Air exchange is ensured using natural and forced ventilation systems. As a rule, special openings (windows, vents) are installed in the roofs and walls of greenhouses. You can close the windows either manually or using an automatic drive. For additional ventilation, fans are installed on opposite sides of the greenhouse.
Important! The higher the ventilation hole is located, the more efficient the air exchange process is: warm air rises on its own, while lowering fresh, cooler air.
Greenhouse lighting systems
Auxiliary lighting is especially important in winter, when daylight hours are very short. The most economical option in terms of energy consumption is the installation of LED lamps. Electromagnetic waves heat not the air around them, but the soil. But such equipment is not cheap. Sodium mirror phytolamps have proven themselves to be quite good, but purchasing them will cost a pretty penny.
Irrigation system
Your own greenhouse must be equipped with irrigation. There are two main systems: drip and sprinkling. When sprinkling, sprayers are installed in the greenhouse, which will water the plants from above, falling drops onto the ground. As a result, plants receive the required amount of moisture with the least amount of water.
A sprinkler system can consist of several types of installations:
- stationary equipment fixed under the arch;
- installations fixed between rows;
- mobile devices fixed to the ceiling.
Drip irrigation is organized according to a different scenario: a hose or tape is laid between the rows, in which holes are made.
Water is released from these holes, which moistens the soil at the root zone. Ultimately, the bushes receive an adequate amount of moisture, and little water is wasted. In this case, waterlogging does not occur and weeds do not grow. The advantage of this method is that everyone can independently organize free drip irrigation using old hoses or tape. It is advisable to install water filters in professional greenhouses. This will not only rid the water of unwanted impurities, but will also increase the service life of the equipment.
It will also be useful for you to read how and how to heat a greenhouse in winter.
Interior arrangement and layout of beds
Making an industrial greenhouse with your own hands inside is not so difficult if you follow the following tips:
- it is better to make the beds of a standard narrow size; not only people should move freely along the paths, but also transport, if necessary;
- to save space, multi-tiered beds and the use of shelving would be an excellent option;
- Hydroponics can be used to obtain a high yield.
The choice directly depends on the specifics of the plants, as well as on the available budget.
Pediments and side walls
- Unless otherwise specified, the grade of steel used will be FE 360 (CT3).
- The columns will be secured to the foundation beam using anchors.
In the calculations for the ends of the gables, the following were taken into account:
- The consoles for supporting the heating pipes are located 870 and 4,700 mm below the tray.
- Screen wire level with the top of the lattice truss (“single” screen).
In calculations for the side wall the following should be taken into account:
- The consoles for supporting the heating pipes are located 4,700 mm below the tray.
Photos of industrial greenhouses
Everyone determines the size and height of an industrial greenhouse for themselves, depending on their needs and financial capabilities. Industrial greenhouses can differ from each other not only in size, but also in shape. If necessary, you can look at examples of already implemented projects, which will allow you to determine the future dimensions of the structure.
Greenhouse complex "Cold House"
The “Cold House” greenhouse block is an industrial-type structure consisting of modules, the number of which can be any. Each block is a separate room in which a special microclimate can be created, necessary for a given variety of grown plants.
Greenhouse block “Cold House”
The span width of the blocks is 9.6 or 8 m. The frame consists of hot-dip galvanized steel posts 5 m high, installed at a distance of 5 m from each other. Frame elements can be not only steel, but also aluminum. Along the horizontal blocks, parallel to each other, there are stiffening belts, which can be equipped with drainage trays and gutters. These same structural elements are the main supports during the installation of engineering systems.
Example of a greenhouse complex
The roof of the blocks is peaked, gable, glass. Equipped with a system of rafter spacer beams. It is possible to insulate structures with any of the modern thermal insulation materials. To install the Cold House complex, a reinforced concrete foundation with a height of 40-60 cm is required. The manufacturer offers the installation of a concrete floor inside the greenhouse premises, as well as the installation of a wear-resistant self-leveling coating.