About induction
An induction boiler has absolutely no advantages over conventional ones equipped with heating elements. All the talk about this is the fantasy of marketers and sellers with the goal of selling their product to gullible customers. The percentage of electricity converted into thermal form is almost the same for all types of heating devices. Do not equate boilers with kitchen stoves - indeed, an induction surface is more economical than steel “pancakes”, there are no losses in heat transfer through the surface of the stove to the dishes, the heating spot exactly matches the size of the pan, the tightness of the seal does not matter. In heating boilers, the coolant is immediately heated; there are no intermediate elements. There are no advantages, the efficiency of the boilers is the same. The rest of the “arguments” regarding reliability and safety are also made up. Disadvantages: increased winding wear due to interturn short circuits, increased insulation aging, vibration when heating, labor-intensive repairs.
Induction heating systems are by no means new; they have been used in industry for more than 70 years, but only a few domestic Kulibins offer their use for heating buildings
Electric boiler on heating elements, fully equipped, adequately controlled
Types of heating boilers
There are several types of boilers that can be used to heat a greenhouse.
Gas. How to connect registers correctly?
A gas boiler consists of various components, in particular a steel or cast iron heat exchanger, an atmospheric burner (sometimes), a control system, a water circulation pump, an expansion tank and a safety valve.
Photo 2. Gas boiler for heating a greenhouse. The device is quite large and is often located outside the greenhouse.
The device operates on the basis of natural or liquefied gas, is unpretentious to water quality and can be installed anywhere in the greenhouse.
Technical characteristics of the greenhouse boiler:
- Efficiency minimum 93%;
- power - from 40 kW;
- the volume of water in the boiler is at least 6 liters;
- device height is about a meter;
- width - 54-60 cm;
- length - 90 cm;
- gas consumption - minimum 5.0 kb. m/hour.
After turning on the boiler, the water flowing through it is heated in the heat exchanger to the required temperature and supplied to the system circuit by a pump. This is a single-circuit option that is used only for heating. To heat the greenhouse and supply hot water, double-circuit devices with a built-in hot water heating circuit are used. Mostly single-circuit models are used for greenhouses. Smoke is removed through a specially equipped chimney or through a steel pipe.
In order to connect the register to the water circuit, you need to find out where the hot water will be supplied and where the cold water will go. Next, holes are made at the ends of the register for threaded couplings, to which fittings are then attached that connect the heat exchanger to the water circuit. An air vent is welded on the opposite side of the supply. It can be located at the end, but it is better for the valve to be at the top.
Since the register is heavy, it is necessary to provide reliable fastenings. There are two ways to place the heat exchanger: wall-mounted and floor-mounted.
In order to install the register on the floor, you need to make legs, and also additionally fix the device against the wall.
Also, do not forget that the distance from the surface of the register to the walls and floor should be about 25 centimeters.
Advantages: the gas boiler is unpretentious in maintenance and does not require constant human intervention. It heats up instantly and ensures even heat distribution inside the greenhouse.
Disadvantages: high price for models for heating a large area, costs for gas supply, need to coordinate the connection of the boiler.
What type of greenhouse stove is on the market?
You can purchase a ready-made stove or make a stove yourself. Of course, making a heating stove yourself will be much cheaper. But do not forget that a polycarbonate greenhouse is not your home; you should not spend a lot of money on purchasing a stove. A stove for a greenhouse should be Compact, efficient and budget-friendly.
You can also make a bubafonya stove - this is an economical stove. Unlike others, this stove is distinguished by its air intake, which comes from above.
This has its advantages:
- Longer fuel combustion;
- Capable of heating the entire volume of the greenhouse;
- Improved heat retention for heating;
- It heats up well from shavings and wood chips.
When purchasing a stove, you need to take into account the area of the greenhouse and the material from which it is made.
To make such a stove, you will only need to take an iron barrel or other metal.
When firing such a stove, the ash door should be opened completely. When the stove has fully “accelerated” for operation, a slight hum is emitted from it. This is when the rocket should be loaded with fuel. Gradually, the access of air should be covered. To make your own rocket stove, you will need a 24-inch or 200-liter barrel. For the blower, bunker and firebox, pipes of different sizes, both round and profile, are quite suitable. It is better to coat the outside of the oven with a special heat accumulator - adobe. This is necessary in order to heat the vegetarian tank with solid fuel. The boiler can be made from a gas cylinder. The heating performance will not be affected.
A brick stove is a fairly massive stove for a greenhouse. However, if your greenhouse is very large, then you can use it. A brick oven is difficult to build. But a brick rocket stove can be made in 5-20 minutes.
The Kuznetsov stove is another type of stove for greenhouses, as well as large rooms. There are no barrels used here, only bricks. Such furnaces provide high efficiency and good temperature. Blacksmithing does not require special care and in some cases is not even cleaned for several years. You can easily integrate a water heating circuit into such a furnace and not deteriorate the condition of the furnace. You can also make a Kuznetsov mini-oven.
Advantages of blacksmithing:
- Excellent traction;
- Good heating;
- Pleasant appearance;
Homemade Kuznetsov stoves can often be found among summer residents who heat the greenhouse in winter.
Electric boilers
Electrical systems are used to heat the air and soil. Most often, an electric boiler is purchased to heat large greenhouses in which plants that require light and temperature grow. An electric boiler allows you to accurately set the temperature that should be maintained inside the greenhouse and use electricity to additionally illuminate the plantings.
Types of electric boilers:
- The simplest convectors will be an excellent choice for a polycarbonate greenhouse. The heating coil, through which air flows, uses little energy, but cools quickly and is not suitable for heating the soil;
- Heaters are distinguished by the fact that air circulates through the heating coil forcibly and in large volumes. The heater is equipped with a thermal fan, and the heated air goes not only into the space inside the greenhouse, but also into pipes laid underground and along the walls;
- Heating cables are laid in the soil and heat it, and this, in turn, increases the air temperature;
- Water for hydronic heating is also heated using electricity. This system is used both to heat the soil and to increase the overall temperature in the greenhouse. This heating option is recommended for use in large rooms, since electric boilers for water heating are usually sold as powerful ones, intended for farms and private homes. An alternative option is to make a wall-mounted greenhouse and install heating to it from the common boiler of a private house.
An alternative way to heat a greenhouse using electricity is to use IR heaters. These devices are shaped like regular ceiling lights, but they emit bright light that heats the objects it hits rather than the air. Infrared heaters work from the mains, and they can be used in greenhouses of any size and type. The only drawback of this heating option is the high cost of the device and the small area on which the light falls. Attaching an IR ceiling heater with your own hands is no more difficult than hanging and connecting a regular lamp.
A separate category of heating systems for greenhouses is combined boilers. They usually operate on two types of fuel at once, for example, gas and solid fuel or gas and electricity. Such complex systems are used to save one of the resources or for greater security. For example, at night electricity may cost less than during the day, and not every summer resident will decide to leave a boiler running on gas or coal for several days. Additionally, combined systems come in handy in areas where power outages occur frequently.
Choosing the most suitable boiler for heating a greenhouse is a difficult task. Its decision depends not only on the size and conditions of use of the greenhouse, but also on the preferences of the gardener. Some people choose simple gas stoves, while others choose a complex and expensive long-burning system. But in any case, installing a convector allows you to increase productivity and extend the time of use of the greenhouse by at least twice.
Soil heating system from convectors
Convectors are good for everyone, but they cannot solve the problem of heating the earth. There is, of course, a way out - to lay pipes and blow warm air through them, but these are complex systems that are developed by professionals. You can build a similar simple homemade system using any unit: dig a hole, install a stove with a convector casing in it. You lay the chimney in the ground parallel to one of the walls and take it outside the greenhouse and only lift it up there.
Heating of both air and soil with one convection oven
The idea is simple but effective. Firstly, the air and adjacent soil around the stove are heated by thermal radiation emanating from the body (it must have a convection casing, which will provide an intense upward air flow along the walls). Secondly, combustion products, passing through a chimney located in the soil, warm it too. But problems may arise with the selection of material for such a pipeline: it should not have too good a heat transfer, otherwise the soil will become hot. In addition, these pipes must be sealed - you can’t joke with combustion products - you can get caught. They must also withstand high temperatures - at the boiler outlet the smoke temperature can be 350°C or higher (depending on the boiler and the type of fuel used). Asbestos pipes are more or less suitable for inexpensive materials, but they cannot be called environmentally friendly and require care with sealed connections.
This solution also requires the presence of a smoke exhauster in the pipe - a long horizontal section of the pipe does not at all contribute to the presence of draft. Therefore, a smoke exhauster is required and its power must be decent. It needs to be installed closer to the end - the temperatures there will be lower and it will work longer. But during installation, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of frequent cleaning - soot will accumulate: with a vertically located chimney, it mostly flies away, and in our version it is deposited on the pipes and blades of the smoke exhauster. The pipes will also need to be cleaned frequently, so some kind of inspection windows are needed here too. In general, it is problematic. But if you build a couple of such pipelines, you will be able to heat your greenhouse economically.
Types of boilers for heating greenhouses
The main criteria for choosing a suitable boiler model for heating a greenhouse are its cost, the need for monitoring on an ongoing basis, efficiency indicators and availability:
- Solid fuel boilers. Firewood, sawdust or special briquettes are used as fuel material. Efficiency = 75%.
- Liquid fuel models. Gasoline, kerosene or diesel fuel are used as fuel. Efficiency = about 96%.
- Gas boilers. This includes devices running on natural or liquefied gas. Efficiency = max 98%.
- Electric boilers. Power source - electrical grid, solar panels or wind turbines. Efficiency is 95-97%.
Operation of a solid fuel boiler
The appearance of a solid fuel generator is similar to a stove, but the difference is that the functional state is ensured by the gas released during the combustion process.
The photo shows a solid fuel boiler for a greenhouse
The boiler design has several sections. One of the sections is designed to accommodate fuel. The combustion process is ensured by the supply of oxygen through the lower air supply system.
The pressurization system has an adjustable damper; when the fuel has burned sufficiently, the damper is closed, after which the flow of oxygen is reduced to a minimum. Due to the absence of air, a chemical process begins to occur and pyrolysis gas
. It enters the second compartment, where heat is generated.
Pyrolysis boilers are one of the most economical models for heating greenhouses with a small area. Thus, the recommended amount of fuel per 100 m2 of space is only 11 kg/day.
Heating a greenhouse with a pyrolysis boiler has another positive quality:
Possibility of heating not only air, but also water. This makes it possible to develop several options for the greenhouse heating system (for example, install radiators around the perimeter or place pipes under the fertile layer). Also, when using a pyrolysis boiler, the amount of smoke becomes less than 95%, and the fumes are collected in a special compartment and do not poison the atmosphere with harmful emissions.
The disadvantage of a pyrolysis boiler is its high cost.
Gas and liquid fuel boilers
Gas can be supplied to such boilers either stationary (natural gas) or mobile - that is, fuel is supplied from an installed cylinder, which requires periodic replacement.
Gas flows through the pipes
An important point when heating a greenhouse using a gas boiler is the mandatory presence of ventilation.
This is necessary to ensure normal conditions for plants and greenhouse workers, since carbon dioxide produced during the combustion process is extremely dangerous in both cases. The same situation applies to the use of liquid fuel boiler models. However, it will not be difficult to convert a gas boiler into an oil boiler and vice versa. You just have to change the burner to another one with a nozzle of a suitable diameter.
Electric boilers - their advantages and features
The use of electric heating boilers for greenhouses is allowed only if it is not possible to install another type of installation.
This is due to the cost of electricity and the availability of alternative energy sources. The only possible exception would be the use of heat accumulators. Such projects are participants in a multi-tariff electricity consumption plan and allow saving up to 60% of energy costs. At the same time, the heating, ventilation and heating system is fully automated.
The video clip shows how you can heat a greenhouse with a converted boiler (from a mine boiler to a pyrosine boiler). When the temperature outside the window is minus 21 degrees, the greenhouse warms up to + 25 degrees. Interestingly, the heat generator is literally assembled from scrap metal. We recommend watching it.
We hope that the article was useful to you. If it's not difficult, please click on the social networking buttons below.
Types of stoves + comparison of fuel options
The design features of stoves depend on the dimensions of the room.
Devices differ according to the dominant criteria for the thermal effect they provide, which include:
- infrared radiation;
- heat transfer;
- convection.
In the oven it is customary to distinguish:
- fuel combustion chamber;
- air flow channels;
- convection shirt;
- additional components.
The following can be used as fuel:
- electricity;
- wood shavings (pressed sawdust);
- peat;
- coal;
- firewood;
- oil-based fuels.
Firewood is affordable. They are a slow burning fuel option.
Coal has a high calorie content. However, its use is limited due to the presence of large amounts of waste, the formation of potentially hazardous substances during use, and the ability to spontaneously combust.
The use of sawdust is justified from the point of view of low cost, environmental friendliness, rapid combustion, minimal smoke and high efficiency. The principle of use is based on their slow smoldering, due to which the greenhouse is heated for a long time.
Burning waste oil for heating is attractive from the point of view of its low cost, but is limited by the toxicity of the compounds formed during its combustion.
The use of electricity is limited by its high cost. In this regard, the spread of electric furnaces is limited.
About the efficiency of various electric heating systems
As for heating with electricity, direct heating systems are more economical: fan heaters, convectors, heating cables and heated film floors. The lower efficiency of a water system with an electric boiler is explained by losses in the delivery of coolant: overcoming the hydraulic resistance of the liquid, the operation of the circulation pump. Warm floors have the best performance due to optimal temperature distribution. How to ensure their safe operation in a greenhouse is a separate issue. But the difference between different types of electric heating is small, we are talking about only a few percent.
https://vasha-teplitsa.ru/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/banya18430.jpg — It’s quite possible to create a warm floor using a heating cable in a greenhouse. It can be protected from possible damage by a strong mesh laid on top.
How to choose boilers for greenhouses - advice from farmers
When choosing between solid fuel, electric, coal, or steam boilers, you need to take into account the area of the greenhouse, financial capabilities, type of covering and types of plants grown.
Recommendations from experienced farmers will help you navigate and make the right decision:
- If there is a gas pipeline on the site, it is more profitable to install a gas boiler. This statement is true for buildings of any size.
- For year-round heating of areas over 50 square meters. m and if you have available firewood, it is better to choose a solid fuel unit with long combustion. The costs of purchase and installation will pay off within two to three years. Payback in small greenhouses (15-20 sq. m) is about 10 years.
- When heating is turned on seasonally (in early spring), it is advisable to use a low-power hanging electric boiler without a chimney outlet. However, during severe frosts they are not effective, since they heat the air above, but the soil remains cold - this is fraught with freezing of plants.
Homemade solid fuel stove
Some gardeners consider direct combustion solid fuel models like potbelly stoves to be the optimal heating boilers for small greenhouses. The efficiency of the system can be significantly increased by connecting a water circuit and installing a pump for pumping coolant.
Features of using the oven
Long-burning stoves are an improved version of the Russian stove, economically consuming a wide variety of solid fuels (firewood, old furniture, sawdust, pine cones, various garbage, coal). They were actively used during the Civil War and the Great Patriotic War, when even ordinary firewood was in short supply and boiler houses were idle.
In them, the fuel burns from top to bottom, and as it burns out, the fire sinks lower and lower. This increases the burning time and releases more heat. The fuel in such furnaces slowly smolders at high temperatures and burns out to the end (pyrolysis). This process is regulated by the supply of air through a vent or blower.
Did you know? Americans attribute the invention of the potbelly stove to the famous American politician Benjamin Franklin. In the USA, such stoves are called “fat bellies”.
At the beginning of work, the stove is heated well. Otherwise, the combustion process may stop. The chimney in these structures must be straight and have no bends, since it will need to be periodically cleaned of soot, and it must be accessible for such work.
Such devices should be used when constant control is possible, because firewood needs to be periodically added to them. It is good to make a foundation for them and cover them with brickwork.
The stove should not be placed close to flammable or unprepared materials, since metal parts become very hot and can cause ignition. The firewood used should not be damp.
Myths about long-burning stoves
Recently, marketers have begun to classify a special type of non-volatile heaters, designed for operation in smoldering mode, as this type. Example: stoves “Professor Butakov”, “Buleryan”, etc. Indeed, with a limited air supply through an adjustable throttle, the fuel smolders instead of burning and therefore the unit can work on one load for up to 8 hours.
But the unit has a number of disadvantages:
- fuel is consumed extremely irrationally: when smoldering, it does not burn completely and a significant part of it literally flies down the chimney;
- The heat release power in the smoldering mode is very low (the characteristics indicate the power in the combustion mode);
- The exhaust in smoldering mode is cold, so condensation forms abundantly in the chimney. The latter, due to incomplete combustion of fuel (smoke contains many heavy hydrocarbon radicals), is a toxic cocktail that is even prohibited from being poured into the ground near edible vegetation;
- The unit smokes heavily in smoldering mode.
Marketers call such furnaces pyrolysis, since their design includes a compartment for afterburning gases. This is a reason to call such a unit economical. But this is a fiction: at such temperatures there is practically no pyrolysis.
In general, such stoves are intended for field conditions where there is no power supply: they enable a team, for example, lumberjacks (Buleryan was created for them), to sleep at night without worrying about firewood. In greenhouses, if such stoves are used, it is in combustion mode, like an ordinary potbelly stove.
Gas heating boilers
Boilers using gas as fuel are considered the most convenient and economical. Installing them with your own hands is not difficult, and even the largest buildings can be heated using such a system.
Gas boilers can be:
- Single-circuit, designed to heat only air or soil;
- Double-circuit, capable of warming both the soil and the air to the required level.
For small rooms that are not used in winter, or those built in regions where there is no frost, a single-circuit gas stove will be sufficient, which will warm the soil or warm the air, extending the life of the greenhouse. Double-circuit systems are useful in large, capital buildings, in which the cultivation of fresh herbs does not stop all year round. If the greenhouse uses a double-circuit gas boiler, then one pipe, through which smoke from fuel combustion flows, is laid underground, and the second, with hot air, is laid along the top and walls of the greenhouse.
Depending on the size of the room, a direct draft or forced draft boiler can be installed in the greenhouse. The first type is based on air circulation inside the greenhouse itself, and the second is on the forced drawing in of air from outside and, accordingly, increasing the volume of air flow.
Infrared gas heaters are an excellent option for quickly raising and maintaining temperature for a short time if the main heating system in the greenhouse fails. The device consists of two parts - an infrared heater, with tubes in which gas burns, reflectors, and a small gas cylinder. Inside the tubes of the device, fuel burns and is converted into infrared radiation, which heats the soil, plants and walls of the greenhouse. It is irrational to constantly use such a device due to the relatively small power and fuel reserve, but in case of frost, turning on a gas IR heater will help save plants from the cold.
Gas boilers are considered the most popular in their class. Fuel for them is cheap and easy to buy, the system does not depend on the supply of electricity and does not consume it, and such a boiler can be installed even in a small greenhouse. But at the same time, the boiler is not considered fireproof, like any gas appliances, it has large dimensions and requires the installation of a chimney.
With the help of gas, not only air, but also water can be heated. Water in water boilers and heating systems is often heated with this type of fuel.
"Bubafonya"
“Bubafonya” is one of the best options for stoves for small greenhouses. Its design is simple and uncomplicated, but at the same time it allows you to heat the greenhouse very efficiently, spending a minimum of resources and effort. Making it yourself will not be difficult. The materials you can use are an old barrel and some metal, which is most likely found in the yard of every avid gardener, and various drawings of it can be easily found on the Internet. It’s worth understanding how a homemade “Bubafonya” is built.
Features and device
As mentioned earlier, the main feature of a potbelly stove is its increased efficiency and rare fuel loading. This effect was achieved thanks to the vertical supply of oxygen and the press, which helps to effectively distribute oxygen and remove the remains of burnt fuel.
Manufacturing
Although the Bubafoni device seems quite complicated, making it with your own hands is quite simple, especially if you have already dealt with metal blanks before. To create it you will need an iron barrel, a pipe slightly larger than the height of the barrel, a chimney pipe and a sheet of metal from which the press, doors and various small components will be made.
The following manufacturing instructions should be followed:
- first of all, you need to take the barrel and cut off its top; to save materials, you can also make a future lid from it;
- there should be no gaps in the lower part of the barrel, but if there are any, even small ones, then it is better to weld them;
- from a strong piece of metal you need to cut a pancake with a diameter 4 cm smaller than the diameter of the barrel, and then make a hole in its center that is suitable in size for the existing pipe;
- Corners or a metal profile should be attached to the bottom of the circle to create a gap between it and the fuel for free passage of air;
- you need to weld the pipe and the pancake to each other;
- make a hole in the lid for the barrel slightly larger than the diameter of the pipe, the gap between them should be minimal, but the pipe should slide freely;
- a hole is cut in the bottom of the barrel for the ash pan door;
- you should make an ash pit door, weld the canopies and secure it;
- make a hole on the side of the upper third of the barrel for the chimney and weld it to it;
- the stove must stand securely on the ground; if it does not want to do this on its own, then you can weld legs or supports to it.
About alternatives
There are, of course, alternatives:
Use other, less expensive types of fuel. If you have a resource base, solid fuels will be the cheapest: firewood, coal. Pellets make sense only if the plant for their production is located nearby. They are inexpensive, unlike other types of solid fuel, they allow you to fully automate the combustion process, but due to their low volumetric weight, delivery costs a pretty penny. The winning option is to find a source of supply of used technical oils. Natural gas is convenient and relatively inexpensive, but it looks like your yard is not gasified. Liquefied gas is unprofitable, especially taking into account the installation of a gas tank. Heating with petroleum heating oil (oil) is on the verge of profitability. Diesel fuel will definitely not pay for itself; you will end up at a serious disadvantage.
A wood stove is a troublesome, but the cheapest and most effective way to heat a greenhouse. For a more even distribution of heat, there is a fan nearby
Use renewable heat sources. A heat pump is unlikely to justify itself; operation is extremely cheap, but the equipment itself is very expensive. In many European countries, the state subsidizes such installations; we do not have such a practice.
Heat pump - environmentally friendly, economical to operate, but very expensive to install
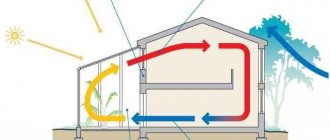
It makes sense to pay attention to the heating system of Ivanov’s vegetarian garden, which you can read about in the series of popular science books “Smart Garden” by Kurdyumov or on his website: https://kurdyumov.ru/knigi/teplica/teplica08.php. This cannot be said to be very effective, but still some kind of savings
Setting up a small greenhouse using all the elements of Ivanov’s solar vegetarian plant hardly makes sense. Solar panels and automatic gate control are unlikely to pay for themselves. But the location of the greenhouse on the southern slope, the blank insulated northern wall and the ground heat exchanger are sound ideas. And the gates can be turned manually. Thanks to the constant movement of air, the flow of which is created by fans, heat is accumulated in the ground during the day, and energy is released back at night. This solution will not increase the average daily temperature in the greenhouse, but will help level out the difference between daytime and nighttime temperatures. You can also use containers filled with stones or water as a heat exchanger
Ivanov's vegetarian device
If the greenhouse has not yet been built, it is worth using rational construction solutions that reduce heat loss and allow for more efficient use of solar radiation: correctly orient the greenhouse towards the sunny side; attach it to the south side of the house; make the northern side blank, insulate it well and line the inside with reflective material, foil; partially buried in the ground; provide for the possibility of installing an additional layer of greenhouse film during the cold period, etc.
A set of simple measures used during construction will reduce greenhouse heating costs by 1.5-2 times
Partial (0.5-1.5 m) deepening of the greenhouse into the ground is justified. Sunlight penetrates in sufficient quantities through the roof, the walls should be well insulated and lined with foil
The photo clearly shows additional rolls of film rolled up to the ridge of the greenhouse, which are unrolled in cold weather.
Use traditional methods of heating greenhouses, for example, a mixture of manure and straw laid in the fall lasts all winter, releasing a lot of heat.
The easiest way to have a beautiful front lawn
You've certainly seen the perfect lawn in a movie, on an alley, or perhaps on your neighbor's lawn. Those who have ever tried to grow a green area on their site will no doubt say that it is a huge amount of work. The lawn requires careful planting, care, fertilization, and watering. However, only inexperienced gardeners think this way; professionals have long known about the innovative product - liquid lawn AquaGrazz .
Features of heating greenhouse premises
The main factor in choosing a heating method for greenhouses is the price of maintaining the temperature. After all, most greenhouses have enormous heat loss. Ideally, for good plant growing, the greenhouse should be built from metal profiles and plastic, with hermetically sealed double-glazed windows.
But most vegetable growers and farmers cannot afford this method of construction, so most domestic greenhouses are covered with polyethylene or polycarbonate. These materials are transparent to sunlight, but also release a large percentage of heat into the surrounding space, so heating the room must be well thought out and powerful.
Boilers for greenhouses
After building the greenhouse, it is necessary to begin creating a heating system, the central element of which will be the boiler. The most commonly used:
- Electric ones are simple, easy to use and available wherever power lines are installed. But using such a boiler to heat a greenhouse will cost a pretty penny, and now rolling or emergency blackouts are common, and then young plants can die from the cold.
- Gas - a stable supply of natural gas ensures good heating of the room, but the price of this energy resource is also quite high. Although many farmers use gas boilers to heat greenhouses because they are easy and quick to maintain, you only need to pipe gas into the greenhouse once and connect the boiler - and the problems are solved. Regulating and maintaining the desired temperature is easy and simple, and the efficiency of gas heating has been proven for years. Often, greenhouses are heated with gas by those whose premises are located next to a gasified house.
Greenhouse heating methods
To maintain a temperature inside the greenhouse of at least 25 degrees Celsius, powerful equipment is required.
The peculiarity of its choice is that it requires heating a fairly large area - sometimes up to 1000-5000 square meters. m.
For this use:
- gas boilers;
- solid fuel stoves;
- electric boilers;
- diesel and combined models;
- IR heaters.
Reference. The most inexpensive option in terms of maintenance is gas boilers. By spending money once on the purchase of the device itself, in the future you will have lower utility bills for gas, maintenance and repairs.
Diesel fuel and electricity are costly ways to heat a large greenhouse area. Coal, firewood, sawdust, and briquettes are a little cheaper, however, they must be constantly purchased, delivered, and stacked manually.
The power of gas heaters for greenhouses with an area of up to 400-600 sq. m should be at least 40-60 kW. This is quite heavy equipment (from 100 kg), which is often controlled using automation.
Air
This heating method is usually used using solid fuel stoves. A “potbelly stove” can be used as a stove, which is installed outside the greenhouse and connected to a pipe for removing flue gases. To ensure uniform heating of the room, a horizontal chimney is made along the length of the greenhouse.
Photo 1. Air heating of the greenhouse: several convectors are installed around the perimeter of the room that heat the air.
For air heating use:
- electric, gas boiler, stove or regular outdoor fire;
- Heating elements/convectors;
- radiators and blowers.
Sometimes infrared heaters, which are mounted in the walls or ceiling of a building, are also classified as air heating. They are completely dependent on the electrical network, but are capable of heating a large area of the greenhouse.
Air heating with a heat pump (a temporary way to solve the problem), as well as heating with steam, which is supplied inside the table through external pipes and returns back to the boiler through other underground pipes, is also considered air heating.
Advantages: easy installation, volumetric air heating (bottom, top, side).
Disadvantages: low efficiency, sometimes dry air.
Water
It involves supplying water through radiators and pipes along the walls or in the center of the greenhouse. Due to this, a large area of the room is heated. This may be single-pipe wiring or other types of piping.
The heat source is a boiler (usually gas, electric or solid fuel), to which the pipes are connected.
For water heating use:
- chimney for waste disposal;
- system for automatically adding coolant (to maintain a constant temperature);
- external and internal pipelines, boiler.
Water heating can easily work due to the natural circulation of water. You can buy a pump and use it as needed.
Reference. It is best to choose cast iron radiators or bimetallic, aluminum devices that are easily connected to the heating system.
Advantages: the ability to install it yourself, warming up not only the air, but also the soil.
Disadvantages: not suitable for large areas.
Possible problems with a homemade device
- The most common problems when operating a homemade heating unit are:
- uneven heating of the internal space;
- excessive dry air.
Both factors negatively affect the condition of the plants in the greenhouse, so you should be especially careful when laying air pipes and providing additional air humidification. Undoubtedly, the selection and installation of technically complex, expensive equipment requires a considerable amount of time and effort to study the issue. However, these efforts can be attributed to a prolonged investment in a future rich harvest, which will delight you both morally and materially for more than one season.
DIY heating sources
Simple heating boilers for a greenhouse can be assembled and installed with your own hands. For implementation, you can use metal sheets, an old barrel or an empty gas cylinder.
Boiler for a greenhouse from a gas cylinder
Necessary materials:
- empty gas cylinder;
- metal grill;
- door latch;
- handles and hinges;
- U-shaped metal pipe – water circuit coil;
- steel plate and chimney pipe.
Step-by-step progress of work on manufacturing a heating boiler for a greenhouse:
- Cut the balloon in half. One hemisphere is the furnace body, the second is the ash tank.
- Prepare a grate that matches the size of the cylinder.
- Insert the grate into the body and secure it with welding - the grate should divide the space into 1/3 and 2/3 parts.
- Cut a circle from a steel plate, the diameter of which is equal to the cross-sectional size of the cylinder.
- Cut 1/3 off the circle. For the most part, prepare a rectangular hole. Weld fittings to the door (latch, hinges, handle).
- Make an ash pan door from the smaller segment of the circle.
- Cut the bottom of the ash pan from the second half of the cylinder and connect it to the end - the door.
- Inside the boiler, mark the location of the ash pan and drill two holes at the top of the body.
- Weld the coil to the inner surface of the furnace by threading the ends of the pipes through the holes. To secure the fastening, you can place a metal sheet.
- At the top of the boiler, cut a hole for the pipe and weld the pipe. The chimney should pass through the greenhouse at an angle of 20°, and the exit should be through the back wall. The height of the pipe is equal to the height of the greenhouse plus 1 m.
- Connect the chimney to the pipe using a coupling and sheet asbestos.
Connecting the chimney to the combustion chamber
When connecting the boiler, it is important to ensure reliable thermal insulation of the area where the chimney comes into contact with the roof of the building.
Video: greenhouse heating system
The proposed videos demonstrate the features of organizing and operating various methods of heating country greenhouses.
Option 1. Water circuit: connection through a Zhukovsky gas boiler, exhaust - galvanized pipe 15 mm, installation method - combined (at the top and bottom of the greenhouse). Coolant circulation is forced through a pump.
Video: Water system
Option 2. Stove heating. The use of two types of wood stoves in the greenhouse: brick and metal, the chimney is laid horizontally. Recommendations for choosing wood for kindling.
Video: Stove heating
Video: boilers for greenhouses
Video: Technology for assembling a pyrolysis boiler for a greenhouse, installation, connection and operation
Video: Transformation of a wood-burning stove into a water boiler
About heating greenhouses
The most effective way is to heat the soil. A do-it-yourself winter greenhouse can be created in several ways.
By laying the heating circuit in the ground, it is possible to provide acceptable conditions for the normal growth of plant roots and the supply of nutrients to them. Simply heating the air can also create comfortable conditions for most crops, especially in the climate zone in which the European part of Russia lies.
When heating greenhouses, there is a large flow of heat through the walls and soil. Therefore, it is customary to install 250 - 350 W of heating system power per 1 m2. Taking into account the different heights of greenhouses, you can use a different standard - 100 W per 1 m3.
The elements of a water heating system provide air heating by convection and should be located as low as possible. The air heating system is mounted on top, at a height of at least 2 m from the ground. The temperature of the air supplied through the air ducts should not be higher than 40°C.
Greenhouse on the garden plot
“Bubafonya” - what lies behind the name and how to build a miracle stove
Not long ago, the Internet literally exploded with a mysterious project called “Bubafonya”. What is this - a funny nickname or a complex abbreviation? The secret is out! “Bub” and “Afonya” are parts of the surname and first name of the author of this startup, Bubyakin Afanasy (affectionately, Afonya).
What is the difference between a homemade oven
- I added a valve that regulates the air supply and, accordingly, the intensity and duration of combustion of one bookmark.
- He simplified the design, making it accessible to any summer resident (the furnace is divided into two chambers thanks to a lowering/rising piston).
Afanasy himself, testing his own invention, achieved a burning duration of 61 hours! A very serious result.
The structure of the people's favorite "Bubafoni"
So, what and how to make this stove for a greenhouse with your own hands? To make the design you will need:
- an old gas cylinder or a piece of pipe with a diameter of 300–400 mm (for large greenhouses it is preferable to take a 200-liter iron barrel);
- from 2 to 5 meters of pipe 100–150 mm in diameter;
- sheets or scraps of metal, 2 mm thick;
- a pipe with a diameter of 30–40 mm (about 1 m long);
- gear and blades for the piston;
- welding machine, clay mortar and grinder.
Step-by-step manufacturing instructions and video
If you use an old gas cylinder for the stove, you need to work with it extremely carefully. First you need to unscrew the valve and rinse the container with water several times. After 2-3 washes, you should fill the container with water and only then start cutting with a grinder:
- Cut off the top of the cylinder and, if necessary, weld a piece of pipe on top (so that the total height of the structure reaches 850 mm).
- If the diameter of the cylinder is 300 mm, cut a circle of thick metal with a diameter of 270 mm. This will be the base of the piston.
- Cut a hole about 100 mm in the middle of the circle and weld a pipe of the same diameter with a length of 900–1000 mm to it.
- Install 6 curved blades on the inside of the piston and weld an old gear (90 mm in diameter with a 20 mm hole) on top. Our air control piston is ready!
- At the top of the cylinder on the side, cut a hole for a pipe 100–150 mm in diameter (smoke outlet). Weld a piece of pipe up to 400 mm long to it.
- Make a lid the diameter of the cylinder with a hole for the piston.
- Coat all joints with clay mortar.
- Connect the stove to a 4-meter chimney (it must be insulated, for example, with mineral wool, to avoid a large amount of condensation).
When making a stove for a greenhouse from an old barrel you will need:
- durable 200 liter barrel (better than the Soviet model);
- a long pipe with a diameter of 200 mm for a horizontal chimney (preferably galvanized);
- 1.5-inch pipe for the piston, 1 m long (with a larger size the combustion will be too strong);
- metal sheets for the cover and piston, blades.
To improve the heating system, you can add a “water jacket” to the Bubafon. Almost anything can be used to heat a homemade stove, with the exception of coal. Sawdust, flammable garbage, pine cones, firewood or chips - “Bubafonya” will accept everything.
A few secrets for effective work
In order for the furnace to operate with maximum efficiency, and its maintenance does not cause inconvenience, it is necessary to observe some subtleties of operation:
- After ignition, the valve must be raised for 30 seconds, otherwise the fire will go out.
- To speed up the ignition process, you can add a little used machine oil (about 100 g) into the firebox through the piston. However, in this case, the ash cannot be used to fertilize plants. It is unacceptable to use gasoline for these purposes - it is very explosive.
- To improve heat transfer around the horizontal chimney pipe, you can make a box (casing) of brickwork with a gap of 30–70 mm.
- At the point where the horizontal chimney is attached to the vertical one, it is necessary to provide a so-called “glass” for draining condensate.
Optimal choice
The best option for heating greenhouses is to install a potbelly stove, which is considered the most economical and easy to operate. The heater consists of a barrel with a door for the firebox, a chimney, a pipe for the heat to escape outside, and a jumper in the upper part.
Heating occurs due to the movement of smoke:
- Hot smoke moves through the pipe; the pipe is installed either on the sides of the greenhouse or in the center.
- The surface of the oven radiates heat.
- Warm air forms above the jumper and flows out through the pipe.
Waste lumber, coal or firewood can be used as fuel. The quality of combustion depends on the type of fuel and the penetration of air into the combustion chamber of the furnace. This heating method is suitable for those who can often control the combustion process. This is the only drawback of the stove.
For long-burning stoves, this disadvantage is an advantage: fuel can be added to them much less frequently. They also consume less fuel and reduce heating of the furnace walls without reducing heat output. They are very similar in characteristics to infrared heaters.
A long-burning furnace has two chambers, one of which completely burns the residual fuel, and the other burns only the main part. The access of oxygen to the chamber is limited, as a result of which the fuel does not burn immediately, but smolders for a long time, releasing a large amount of heat.
Various household waste can be used as fuel for long-burning stoves, but without harm to plants. Constant temperature in the greenhouse provides the necessary conditions for crop growth.
Factors for choosing a solid fuel boiler
Before equipping a room with a boiler, you should consider some points:
- Climate zone. Since the greenhouse is heated in the winter months, it is necessary to consider the statistics of previous years and clarify the average temperature in each month. This will allow you to see the extremes of temperature fluctuations and select the most profitable option for the boiler and fuel.
- Greenhouse material. If the main light-transmitting material is a simple film, then the plants will not survive extreme cold, no matter how actively the boiler works. If glass or polycarbonate is used, then the chances of getting a harvest are much greater.
- Fuel availability. If the nearest coal mine is hundreds of kilometers away, then using coal as the main fuel can be economically expensive. In addition to the cost of the product itself, logistics costs will come on top, and the price may be higher than that of gas and electricity.
- Room area. A large greenhouse (approximately 400 sq. m.) will require either one powerful boiler or two. If the partitions are transparent, then it is better to take two devices to optimally maintain the temperature on the outskirts.
About boiler power
Forgive me, but your post is akin to the question “I want to go for a walk, what clothes should I wear”? To recommend panties or a sheepskin coat, you need to know whether it’s winter or summer outside, hot or cold, sun or rain. It's the same with the greenhouse. Where do you live, in the Krasnodar region or in the Northern Urals? What type of cellular polycarbonate is used to cover the greenhouse? Is the cheapest 4 mm (thermal conductivity 3.8 W/(m K)) or 25 mm (1.6 W/(m K))? How are you going to heat it: just in the spring to drive out the seedlings or do you want to have fresh vegetables all year round? What temperature should be maintained? What is the average height of a greenhouse? After all, we heat not the area, but the volume? What are its proportions, the floor area does not matter, heat is lost through the external walls - it is their area that you need to know. How is the structure oriented to the cardinal points, does it receive direct sunlight in winter? Since we don’t know any of this, we can’t give you any advice on boiler power.
About agricultural economics
Heating a greenhouse with electricity is by no means a cheap thing. Such solutions are not used in the agro-industrial sector; they are unprofitable. You are not the first to come up with such an idea, but if you are interested in the economic side of the issue, calculate the costs and compare with the possible benefits. All your predecessors abandoned the idea of heating greenhouses with electricity; it is much cheaper to buy vegetables and fruits.
For comparison - a comparison of the cost of installing heating equipment using different energy sources, using different energy sources
And operating costs. The data is given for the Moscow region; in a particular area, the cost of solid fuel can be much lower. Electric heating with low initial costs is extremely expensive to use