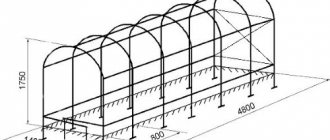
Types of greenhouses made of reinforcement
The main thing is that it is reliable and does not require a lot of money, time, or energy for the installation process. The structure will help you have a lot of fun with minimal strain on your physical and mental strength, which will undoubtedly benefit your health. To do this, it is enough to set aside weekends.
There are only two types:
- The classic version based on steel reinforcement.
- Modern version made of plastic reinforcement based on composite material.
Any option has pros and cons. Let's take a closer look at the advantages:
- A frame of any shape and size can be created without much effort. Quick dismantling possible;
- Moderate cost of materials.
The disadvantages are significant, but surmountable:
- It is not profitable to store materials because they occupy a large area and quickly deteriorate. But, thanks to regular priming, the appearance of rust can be suppressed;
- It is advantageous to use plastic material to create a small greenhouse.
If you use the fittings correctly, then the greenhouse will last a long time and will become a reliable shelter for obtaining a decent harvest.
Required tools and materials
To build a lightweight structure that will protect garden crops from adverse external factors on an area of 1.5x3 m, you will need the following materials and tools:
Installation diagram of arcs for covering with greenhouse film.
- 9 m of wooden blocks (section from 25x40 mm to 50x50 mm);
- 4 bolts, screws or studs M8 or M10 with washers and nuts (the length of the fasteners must exceed twice the thickness of the wooden block);
- 5 m of polyethylene film with a density of at least 100 microns (the standard width of a folded sheet is 1.5 m);
- 16-17 m of composite rod with a cross section of 8-10 mm;
- drill;
- hacksaw or jigsaw;
- sander;
- square;
- roulette;
- tools for tightening fasteners;
- construction stapler with staples type 53.
Foundation for a greenhouse made of reinforcement
Yes! A greenhouse made of reinforcement is mounted on a foundation, since heavy weight will lead to shrinkage into the ground. This is not a problem, but gradually cracks in the film and disruption of the integrity of the frame are possible, even to the point of collapse.
The foundation is created based on reinforcement with steel rods with a diameter of 12 mm. A cross section of 8 mm is used for the frame. But for a small greenhouse, what about a large structure?
Differences between the foundation for a large greenhouse:
- In this case, a strip foundation is used;
- Depth of at least 0.8 - 1 meter. The minimum width is 20 cm. This will save approximately 10% of the heat;
- In the northern regions, the depth is calculated based on the maximum freezing of the soil;
- For insulation, the trench is lined with sheets of foam plastic.
A simple method of foundation in stages:
- A trench with the required dimensions is prepared;
- Formwork is made with a height of 10 - 15 cm. Suitable: plywood, chipboard sheets or boards with a thickness of 25 mm. The upper part is leveled;
- Reinforcing mesh and frame sections are installed;
- The first layer of concrete with a thickness of 20 - 25 cm is poured. 2 - 3 pours are required. To avoid voids, each approach is carefully compacted.
Important: In this case, it is not profitable to send stones or crushed bricks into the trench, as this will reduce the strength of the foundation.
It doesn't look easy. Let's assume we've dealt with this, what to do next. The foundation is the most difficult, but important stage, since this will help avoid the fate of a thatched house. The rest of the work on constructing a greenhouse from rebar with your own hands is much easier.
Greenhouse 6 by 3 m with net for cucumbers
This greenhouse has impressive dimensions: 6 by 3 m. It is quite high - 2 m, and has a built-in net for cucumbers. It is made of 8 mm reinforcement and reinforced with a beam for strength. The greenhouse covering is made of agrotextile, which is secured with boards that imitate formwork.
You can do it yourself using a simple and understandable scheme:
- Assemble the base from the slats. It is better to fasten it with overlapping bolts. The base can be made according to the sample dimensions: 3 by 6 m, or according to dimensions convenient for your site.
- Cut the reinforcement into pieces. 6-10 pieces of 4.5-5 meters each are enough.
- Drill holes in the base and insert reinforcement.
- Reinforce the arches on top with a pipe or beam.
- Cover the arches with netting if you plan to grow cucumbers.
The greenhouse frame is ready. All that remains is to cover it with agrotextile. You can use any other material, for example, film.
Frame for a greenhouse made of reinforcement
Finally, we are approaching completion and obtaining the finished state of the greenhouse. To fasten the reinforcement and form a durable frame, you can weld rods or use knitting wire. To avoid damaging your legs, it is worth installing further from the foundation.
Stages of work:
- Arches are assembled using reinforcing bars. The depth of the foundation and bearing capacity are taken into account. The required height is determined. Depends on the height of the owners. Less is more profitable, but bending down is not very good for your back and health. That’s why we create comfortable working conditions;
- The finished structure can be transferred to the foundation. Welding is performed on the basis of horizontal crossbars;
- The distance between the arches is maintained at 40 - 50 cm.
If it’s too difficult, you can watch a video example based on the master’s work. Many incomprehensible moments will become simple.
How to choose a profile pipe
Profiles are coated with polymer paint or zinc. The first option is cheaper in cost, but over time the top layer may peel off. This will not only deprive the greenhouse of its neat appearance, but will also lead to corrosion.
Thanks to the galvanized coating, the pipes will not rust and are not afraid of sudden temperature changes. That is why, when choosing profiles for a greenhouse or greenhouse, it is recommended to give preference to them.
Range of steel profiles
Sheathing the frame (step by step)
This is an equally important issue, since it directly affects the microclimate inside the greenhouse. As a rule, simple models use film, polymer or cellular plastic.
But after it went on sale, cellular polycarbonate began to be perceived as an excellent alternative to expensive glass. This material transmits sunlight well, is resistant to moisture and mechanical stress, and will last at least 20 years.
What is holding back the popularity of cellular polycarbonate:
- When exposed to intense heat or fire, it is subject to melting and rapid deformation. The material deteriorates and the greenhouse is unsuitable for use;
- The increased cost in comparison with other suitable materials is deterrent.
Therefore, film is more often used, since it is easier to install and attracts an affordable cost.
Film types:
- Unstabilized version. It can transmit around 80% of the heat of our star. But the reduced strength will require annual replacement.
- Hydrophilic membrane transparent film. Excellent transmission of solar energy, strength, elasticity and impact resistance. Due to the peculiarity of the material, drops of condensate flow down the side, which promotes the development of plants. The material retains heat well.
- Heat-retaining polyethylene. Excellently maintains a temperature increased by 1-3 degrees. Provides an increase in harvest volume by 20-30%. But the minimum strength will require replacement after 9 months.
- Reinforced polyethylene. Virtually no deformation. Therefore, it can be used for 2 seasons. But it blocks the sun's rays.
- Polyvinyl chloride film. It is resistant to external influences. Serves up to 6 years.
Greenhouse operating modes
First mode
when it is completely closed. It is usually used in early spring, after planting seedlings, and also at the beginning of summer in cold times, during frosts or strong winds.
Second mode
- for ventilation. We remove the end walls. We use it in warmer times. And also during hardening and adaptation of seedlings to sunlight.
Sowing and early growing of plants is usually done at home. Most apartments have three- to five-layer plastic windows, which do not allow all ultraviolet rays to pass through. And not all people have windows facing the sunny side.
If you immediately put the plants outside, you can burn them. Therefore, it is better to adapt seedlings to street lighting gradually. By opening one or both side walls, we provide good ventilation, hardening and at the same time protection from direct sunlight
Third mode
. We lift the covering material from one, usually the shadow side.
If desired, you can open the greenhouse from the sunny or shady side, from the windy or leeward side. To do this, we screw the covering material onto the pipe inserted from below and place it on the protruding ends of the stop reinforcement. Can be twisted directly with ropes.
It is usually used for shading plants in the spring, when it is hot during the day and the seedlings are not yet adapted to direct sunlight. In this case, we open only the shadow side. And there will be more light in the garden bed and it won’t burn the plants.
Fourth mode
- both sides are open. The top remains closed.
Used for shading in hot weather in summer or when there is a risk of hail.
Fifth mode.
The covering material is rolled up and lies on the supports. It is used in good weather, when the plants are sufficiently mature and acclimatized to external environmental conditions.
To close the greenhouse, the twist is pulled out beyond the stops and unfolds itself under the weight of the pipes. Loops of ropes on both sides are put on screws. The greenhouse is covered and strengthened.
This takes a maximum of 2 minutes. I usually only use 5 - 6 ropes. This is enough to reliably protect plants even in moderately strong winds.
Thus, the greenhouse operates throughout the growing season, from early spring to late autumn. It is designed in height for medium-sized plants. Last year tomatoes were grown here. They reaped a good harvest. The fruits in the greenhouse ripened successfully even in October.
For the winter, I put the reinforcement and covering material in the garage. The design can be disassembled quickly. We cut off the wire twists of the reinforcement. When you pull the ends of the arcs out of the boards, they straighten on their own.
We tie all the reinforcement into a bundle. We twist the covering material together with the inserted pipes and ropes into a roll. So the design does not take up much space when disassembled.
In the spring, too, much time for installation is not required. The recesses for the arches are already drilled and the screws on the bed are already screwed in. We stuck the reinforcement into the top boards of the bed, tied it with wire, and unrolled the covering material. The ropes are already in place. Place their ends on screws. All is ready!
On our site, the beds are standardized. Therefore, the structure can be easily placed on any other bed. This allows for crop rotation. That is, tomatoes can be grown in the same greenhouse on another bed where, for example, carrots grew in the previous season.
Covering a greenhouse with film
To do this, they rely on two main methods. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at how this is done.
Clips
For this purpose, special places are made in the greenhouse. The clamps are made from bent sheet steel. A rubber gasket is suitable for fixation, as this will increase the service life of the film.
Coarse mesh
Can be stretched both inside and outside the greenhouse. In fact, the film ends up between two meshes. Therefore, it is a reliable and durable option.
- Based on the strength of the reinforcement frame and properly selected film, you can get a good harvest at any time of the year.
- As we understand, installation is easy, the main thing is to make a foundation.
- All that remains is the installation of a door to enter the interior space and ventilation, supplying electricity for lighting and automation of watering.
Now we understand what types of greenhouses made of reinforcement are and what the foundation is used for. We looked at the stages of creating and covering the frame.
All that remains is to choose a cultivated plant to grow. But it’s worth staying in one direction, since any combination is not beneficial.
Making a frame arched greenhouse with your own hands
The decision to make a greenhouse with our own hands from fiberglass reinforcement was preceded by the construction of raised beds. In the spring, high soil moisture remained for a long time on the plot. Plants had to be planted late, which affected the harvest.
We live in Siberia. There are late spring and early autumn frosts here. In the summer it sometimes hails. The climate is sharply continental and the temperature difference during the day can reach more than 20 degrees. There is also strong wind.
There are two greenhouses, but they are difficult to heat. A greenhouse is preferable because it has a smaller volume of enclosed space and does not require heating. A positive temperature inside during the cold season can be maintained due to the earth heated during the day or the processes of rotting of plant residues occurring.
Greenhouse design requirements
There are many greenhouse designs. There are permanent and temporary ones. Coated with polycarbonate, glass frames and polyethylene film. Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages.
I needed a greenhouse that would meet the following requirements.
- It can be used throughout the growing season and it should not interfere with grown plants.
- The covering should be easy to remove, and at the same time the bed can be quickly covered in case of threat of hail or frost.
- High stability in strong winds. It should not tear off the coating or destroy the structure.
- It should be quickly assembled and disassembled, and easily moved to another area or bed.
- Do not take up much space during winter storage.
- Do not interfere with plant care.
- The frame must be made of fiberglass reinforcement.
- Covering made of film or covering material.
Taking into account all these requirements, the greenhouse design described below was developed. Fiberglass reinforcement was chosen because it has a number of useful qualities:
- it is flexible and at the same time durable;
- after use it returns to its straight position, so it takes up little space when stored in winter;
- not subject to corrosion and rotting;
- has a nice color, can be painted if desired, looks good and neat on the site;
- has a long service life.
Required tools and materials
In our garden plot there are six-meter and three-meter beds with a height of 45 cm and a width of 70 cm. Below is a calculation of materials for six-meter greenhouses. It is assembled from two 3-meter ones.
I chose this option as it is more difficult to use. The photographs and video show how the covering material is joined, the speed of opening and closing the greenhouse even on such long beds.
To make it, you will need a regular tool that every gardener has. I partially bought the necessary materials, and some came in handy from the remnants of previous works.
To work you will need the following tools and materials
- A hacksaw or grinder for cutting fiberglass reinforcement.
- A screwdriver or drill with a drill bit with a diameter of 6 - 7 mm.
- Roulette.
- Household scissors for cutting wire and cord.
- Self-tapping screws 50 mm, 26 pcs. in total.
- Cord diameter 5mm, total 32m.
- Soft wire for twisting reinforcement joints with a diameter of 1 - 2 mm, only 6 m. You can take it from an old electric reel. Easy to cut with utility scissors.
- Fiberglass reinforcement with a diameter of 6 mm, only 46 m. Pay attention to the quality. In low-quality reinforcement with a weak polymer coating, the fiberglass quickly begins to “fluff”. When touched with a bare hand, it is easy to get small glass splinters, like from glass wool. And you shouldn’t take large-diameter fittings. It will be difficult to bend.
- Covering material or polyethylene film 215 cm wide, total 6.3 m. I used what I had on hand - packaging film with pimples. But she is not persistent. It wears out quickly and deteriorates in the sun. Nevertheless, we had enough for the season. The next year I repaired it with transparent tape and used it again. Last year I used covering material.
- Dense material 8cm wide, 13m in total. You can use thick fabric or some synthetics. Will be hemmed to the covering material for insertion into it for the weight of pipes or a metal rod.
- Polyethylene or polypropylene pipes, 2 - 2.5 cm in diameter, total -13 m. Can be replaced with rods or fittings.
Prices for 6 mm fiberglass reinforcement in our city are about 18 rubles per meter. Sold twisted into reels of 50 - 100 m. A polypropylene pipe, 20 mm in diameter and 2 m long, costs about 100 rubles. Covering material spunbond white 30 g/m2, width 3.2 m from 45 rubles per linear meter. Cord from 2 rubles per meter.