A greenhouse is an indispensable attribute of any personal plot. In greenhouses, vegetables and fruits grow much faster and receive the necessary humidity, heat and light. The greenhouse protects against temperature changes and pests. Previously, summer residents used glass to cover greenhouses, but modern technologies make it possible to use a stronger and more durable material - polycarbonate. A DIY greenhouse made from this material is more durable, protects plants from ultraviolet rays, and the roof can withstand a large volume of snow.
Arched polycarbonate greenhouse with window
In addition, due to their ability to retain heat, polycarbonate greenhouses allow you to harvest crops all year round. In sunny weather in winter, the temperature inside such a greenhouse can rise to +35˚.
What is polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is an artificial polymer made from carbonic acid and dihydric alcohols; it belongs to the group of thermoplastics. The first polycarbonate compound was invented by Hermann Schnell back in 1953. He worked as a specialist in the laboratory of a well-known pharmaceutical company. It was thanks to this scientist that the world received plastic jars for medicines and transparent blisters for tablets.
Diabetes medicine in a plastic jar
Medicines in blisters
In the same year, the first polymer compound received a patent and the name “Makrolone”. It was 200 times stronger than glass, did not allow moisture to pass through, and remained virtually unchanged under the influence of both low and high temperatures.
The polymer later found use in the production of eyeglass lenses, computer parts, compact discs, LED lamps and car headlights. The material is widely used in the creation of protective equipment for hockey players, motorcyclists, and is also used for the manufacture of construction helmets. Comes in different colors.
Colored polycarbonate Colored cellular polycarbonate
Summer residents associate polycarbonate with dense sheets of transparent plastic, which are sold wound on large reels.
Types of polycarbonate
In Russia, according to GOST, polycarbonate panels are categorized as “Safety glasses”. They have a high degree of transparency, which does not reduce their strength and durability. Sheet polycarbonate is available in two types - solid and cellular. The latter has a complex structure, which increases its ability to retain heat.
IMPORTANT ADDENDUM!
The thicker the polycarbonate sheet, the softer the light and the lower the light conductivity.
For greenhouses, cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of 4 to 8 millimeters is usually used. These types of polycarbonate have, on the one hand, high strength and lightness, on the other hand, they transmit light well and retain heat.
Cellular polycarbonate Cellular polycarbonate in section
Types of cellular polycarbonate: diagram
In addition, cellular polycarbonate sheets are impregnated with a special protective layer that does not transmit ultraviolet rays. Solid polycarbonate, also called monolithic, is used for making shop windows, canopies and partitions in public places. Externally, it is indistinguishable from ordinary glass.
Solid polycarbonate
But, unlike its fragile predecessor, it is several times lighter and 250 times stronger. In this indicator, it even surpasses plexiglass.
INTERESTING FACT!
Polycarbonate, along with gold, platinum and silver, was chosen as the material for the medals of the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi.
The game organizers felt that this material was better suited than others for two reasons. Firstly, this type of plastic does not change under the influence of both low and high temperatures. And secondly, you can easily apply any design to it. So, for the first time in the world, the Russians came up with a medal with almost real “ice”.
Medal of the Olympic Games in Sochi
Durable and lightweight. Polycarbonate sheets are used to create display cases, partitions in banks, and canopies. Strong “glass” cannot be broken even with a hammer.
Equipment with protected glass made of monolithic polycarbonate
Canopy made of colored monolithic polycarbonate
Features of polycarbonate installation
After completing the construction of the foundation and frame of the greenhouse, you should begin installing polycarbonate sheets.
The following tools may come in handy:
- perforated and sealing tapes;
- marker;
- polycarbonate sheets;
- special self-tapping screws with thermal washers;
- drill;
- hand circular saw.
To make the greenhouse look beautiful and aesthetically pleasing, it is necessary to cut the polycarbonate sheets as evenly as possible. A hand-held circular saw is best suited for such purposes. The cut is smooth and straight.
Cutting polycarbonate with a jigsaw
After preparing all structural elements, it is worth additionally processing the ends of the polycarbonate. To prevent the penetration of dust and moisture, one of the ends should be carefully sealed with sealing tape. If this is not done, the polymer may darken prematurely, which will negatively affect the amount of sunlight the plants receive. It is better to glue the opposite end with perforated tape. This will help avoid the formation of condensation and will also effectively protect against dust and debris.
Perforated tape
To secure the cut pieces of polycarbonate to the greenhouse frame, it is worth purchasing special self-tapping screws with thermal washers.
Plastic thermal washers for polycarbonate
The thermal washer, on the one hand, will help not to overtighten the self-tapping screw, which is a very important point for cellular polycarbonate. An overtightened self-tapping screw will lead to creasing of the honeycomb structure of the sheet, which can cause cracks and reduce the service life of the material. On the other hand, if the self-tapping screw is loosely tightened, the contact of the polymer sheet with the frame will be loose, the sheet will vibrate and may prematurely collapse at the point of contact.
Scheme of fastening polycarbonate sheets to a metal frame
In addition, the thermal washer will help provide the necessary clearance at the mounting location. This is necessary for thermal compression or expansion of the material when the seasons change. If you neglect the use of thermal washers, in cold or hot weather the polycarbonate sheets may be subject to deformation, which will significantly worsen the appearance of the greenhouse and reduce its service life.
Polycarbonate butterfly greenhouse
Greenhouse "Snowdrop"
The Snowdrop greenhouse is a universal design that, like any other similar device, will allow you to successfully grow various crops. Read more here.
Prices for thermal washers
thermal washers
Technical characteristics of polycarbonate
Despite its popularity, the properties and characteristics of polycarbonate are not known to everyone. Let's look at some of them.
Strength
This indicator depends on the thickness of the panel. Modern honeycomb sheets are available in different thicknesses: 4, 6, 8, 10, 16, 20 and 25 millimeters. Moreover, each of these blocks has its own internal structure. The table shows linear dimensions, specific gravity, maximum permissible bending radius and other linear dimensions that may be useful for working with the material.
Linear dimensions of cellular polycarbonate sheets
The type of internal "grip" affects strength. Thanks to their “layered” structure, such panels can withstand heavy loads.
Indicators of mechanical strength of polycarbonate
If installed correctly and using the recommended fasteners without changing the structure, a polycarbonate greenhouse can last at least 5 years.
How does polycarbonate behave depending on temperature?
Most polycarbonate panels are resistant to high and low temperatures. The thermal expansion index changes slightly. Maximum expansion when heated is 1 mm per 1 m2.
Change in the linear dimensions of a honeycomb polymer with temperature changes
Permissible temperature range: from −4 to +130˚C, but there are also particularly frost-resistant thermoplastics. They do not lose their properties even at extreme temperatures - minus 100˚C.
UV resistance
Polycarbonate sheets transmit light differently. The thicker and more complex its structure, the more scattered the light. Unpainted panels have high light conductivity, above 85%, colored panels - no more than 65%. Each polycarbonate panel has a protective coating on the outside that prevents dangerous ultraviolet rays from entering the greenhouse.
Protective properties of polycarbonate Polycarbonate in a roll with a protective layer
When installing the polymer, you should pay attention to the markings and lay the sheets with the protective side up. There is no need to be afraid that the coating will lose its properties; the varnish is “fused” into the polymer, which allows you to maintain the protective function for at least 10 years.
Chemical protection
Polypropylene is resistant to alkali and ammonia-based sealants. However, it is easy to clean with alcohol solutions or neutral, non-alkaline liquid cleaning agents.
Summer veranda made of polycarbonate
Dries well and does not lose its appearance. Such coatings can be watered with water from a regular hose.
Moisture resistance
Polycarbonate sheets do not allow or absorb water. This makes them an indispensable material for roofing work - such canopies are used in summer cafes, for the construction of gazebos and verandas.
Polycarbonate gazebo Dome for a polycarbonate pool
Anti-vandal telephone booths are made from polycarbonate; canopies at public transport stops are made from it, as well as advertising signs.
Thermal insulation characteristics
In terms of heat retention characteristics, polycarbonate is the best material. It is indispensable for glazing greenhouses. Photos of greenhouses made of cellular polycarbonate on the Internet prove the popularity of this material among summer residents.
Polycarbonate greenhouse: inside view
The viscous structure of plastic is much denser than film, glass and other similar materials. The heat transfer coefficient depends on the thickness and structure of the sheet. Average values are 4.1 W/(m² K) (for 4 mm) to 1.4 W/(m² K) (for 32 mm).
Noise insulation
A polycarbonate greenhouse is the best place for secret negotiations. Multilayer panels will provide reliable noise suppression. The panels are 16 millimeters thick and can absorb sound vibrations up to 21 dB. Therefore, it is often used to build fences - such a wall can muffle street noise.
Polycarbonate fence
Remember that for building fences it is better to take polycarbonate sheets with a thickness of at least 16 mm. This will ensure the durability of the structure and protect it from damage. The service life of such a fence is at least 15 years.
Fire resistance
Polycarbonate is a highly flammable material. In the European classification it is classified as category B1 - this means that the material does not burn. Its structure is such that when exposed to a point of fire, it “melts” and contracts, holes appear on the plastic, which prevents further spread of fire. An important feature: when melted, polycarbonate does not release caustic or toxic substances. And the combustion products immediately “evaporate” through the resulting holes.
Cons to consider
Speaking of disadvantages, it should be noted that polycarbonate is less protected from external influences than glass, although it reflects ultraviolet radiation, thereby protecting plants from drying out in the sun.
However, here are the design disadvantages of cellular polycarbonate:
- the edges of the material should not be open, as moisture or insects can penetrate its internal “honeycombs”, which will lead to the appearance of mold or other fungi, as well as deterioration in performance properties and the circulation of greenhouse gases;
- it is necessary to very carefully clean the sheets from which the greenhouse is made from dust and dirt with soft cloths and neutral cleaning agents;
- products containing salt, alkaline, ether and chloride components should not interact with polycarbonate;
- It is strictly prohibited to use abrasive materials and sharp objects to avoid damaging the ultraviolet protection layer.
Advantages and disadvantages of polycarbonate greenhouses
All of the above qualities of thermoplastic really make it one of the most popular materials for the construction of greenhouses. That is why for many, the question of what to build a greenhouse from is no longer perplexing.
Greenhouse – stage of laying polycarbonate
Advantages of polycarbonate:
- Durability . If assembled correctly, a polycarbonate greenhouse can last faithfully for at least 10 years. On average, the operation of such a structure reaches 20 years or more.
- Acceptable weight. The material is 16 times lighter than glass.
- Possibility of choosing panels of any structure and size, depending on financial capabilities.
- It is easy to process , fits well, and does not burst at sub-zero temperatures. It can be glued and drilled, and can even be cut with scissors or a knife. You can cut out windows, doors, vents.
- The panels are transparent and evenly diffuse sunlight. In such a greenhouse, the harvest can be obtained all year round.
- Polycarbonate is easy to care for and easy to clean.
- The material does not allow moisture to pass through and cannot be “chewed”. This means that your beds will be protected from pests, provided, of course, that there is a good foundation under the greenhouse.
Don’t let the apparent high cost scare you; the sizes and prices of polycarbonate are fully consistent with the stated characteristics, provided that you buy from trusted suppliers.
Greenhouse-droplet made of polycarbonate. The disadvantages include:
- Large greenhouses will require large expenses. About half the cost of the entire structure will be taken away by polycarbonate.
- If the sheets are positioned incorrectly, for example, with the protective layer inward, the service life will be reduced to three years.
- When in contact with sand, cement or any other abrasive material, scratches appear, which can lead to clouding of the canvas and a decrease in light transmittance.
What is the difference between a greenhouse and a greenhouse
Many people completely identify these concepts, but a greenhouse and a greenhouse are still different designs. The main differences are as follows:
- Greenhouse - to maintain the required temperature, this structure requires sunlight or the use of additional energy sources. Such a structure is large in size and an adult can move freely inside.
Classic greenhouse Source mastervdome.com
- A greenhouse is an energetically self-sufficient system. The influx of heat occurs due to reactions occurring in organic compounds and the greenhouse effect under the influence of the sun. There are no doors in greenhouses; to provide access to the plantings, removal of the upper structural elements is provided.
Greenhouses are equipped with convenient covers that are removed or set aside Source spb-teplichka.com
The greenhouse will be convenient for seedlings or low-growing crops. Adult tall plants are placed in greenhouses.
Determining the correct location of the greenhouse on the site
The right place for a greenhouse will save nerves, time and money in the future. First of all, you need to find out which areas of your garden may be flooded. To do this, you need to make test measurements in the spring using a drill and an ordinary thread with a pebble. This procedure is familiar to all summer residents.
It also happens that there are no other options for constructing a greenhouse. In this case, the structure must be equipped with a strong foundation. It can be installed on slabs or piles. Drainage ditches must be installed along the greenhouse.
Scheme of the site with a functioning drainage system
The place under the greenhouse should have maximum light during the day. This is usually the south side of the site. We immediately discard buildings that potentially create a shadow in the future.
Forbidden places for a greenhouse
It is best that there are no trees or tall bushes around the greenhouse. The entire space is cleared of weeds and debris. The type of soil is of great importance. The best option is when the soil is sandy. Clay or silt soil must be prepared in advance. Usually, a pit is dug at the site of the future greenhouse and covered with gravel. The next layer is sand, and the last layer is fertile soil.
Dumping a strip foundation
Low-lying places with strong wind blowing are not suitable for us. It is permissible to install a greenhouse with a slope, but only on a cement foundation on stilts. Such flower beds got their name - vegetarians. By type it is a wall-mounted greenhouse, but built in a certain way.
Vegetarian scheme and operating principle
Such greenhouses are very common in Holland and China. If the former use vegetarian gardens for flower beds, then our Chinese neighbors use them for vegetable crops. After we have determined the location, we need to select the shape of the greenhouse and make a drawing. This will help you calculate the costs of materials in advance.
What you shouldn't forget
Growing in a greenhouse is not much different from growing outdoors, but there are some significant differences.
First of all, the roof of the greenhouse, in addition to protecting against cold and rain, limits air circulation. This means that you must manually ensure proper watering, maintain the required level of humidity, and properly ventilate the internal space to circulate greenhouse gases in the most favorable manner for the growing crop.
In summer, very high temperatures can arise inside the greenhouse; in this case, growing plants is only possible if the structure opens on the sides.
Despite the coating protecting them from damage from excess ultraviolet light, during the hottest times of the year it may be advisable to cover the greenhouse roof with shade netting in the event of particularly strong sunlight.
Choosing the right greenhouse shape
How to choose the shape of a polycarbonate greenhouse? The choice of design for a future greenhouse depends on two main factors - monetary and climatic. The more snow and precipitation falls in winter, the narrower the vertical of the cone. Pyramid greenhouses are built in places where it is difficult to reach the greenhouse due to heavy snow.
Original pyramid-shaped greenhouse
Such greenhouses do not need to be cleaned; the snow itself will fall under its own weight. The disadvantage of such a greenhouse is obvious - in the upper part of the vaults the space is eaten up. The area, which is fully used in arched structures of smoother shapes, remains unclaimed in triangular ones. Typically, this type of construction is used not for greenhouses, but for greenhouses. More popular among gardeners are arched structures and greenhouse houses.
Greenhouse-arch Flower garden-tent Greenhouse-house
Arch-shaped greenhouses are the most economical option. Their installation does not require a large amount of materials. To cover the span from base to base, one standard size polycarbonate sheet is enough.
FOR REFERENCE,
Standard size of polycarbonate sheet: 2.10 m×6.12 cm.
Arched greenhouses are used for planting small plants: tomato seedlings or flowers.
Arched greenhouse frame
And the remaining material can always be used in such a mini-greenhouse.
Arched mini-greenhouse
Advantages of arched greenhouses:
- Easy installation.
- Saving money.
- It can be placed on a lightweight foundation made of timber or bricks without cement.
- A spherical or arched roof has better aerodynamic performance. From such roofs the wind will not tear off the slab even during a hurricane.
Disadvantages of the greenhouse-arch:
- Limited space in the outer beds.
- Low functionality.
Greenhouse houses. The most common option is gable greenhouses made of polycarbonate or greenhouses with a straight roof. Thanks to their universal structure, such greenhouses can be built in different sizes and heights. You can increase the space due to additional sections and side rows.
Greenhouse-house made of metal profile Greenhouse-house with a two-level roof
Greenhouse-house
There are other options for greenhouses: drop-shaped, tunnel-shaped, two-part, etc. Some of them can be seen in this photo.
Schematic representation of frame options of different shapes
Polycarbonate greenhouses: drawing
Before purchasing materials for constructing a greenhouse, you need to make a design or schematic drawing of it. It will save time on thinking about design details in the process and will allow you to purchase the necessary material in advance in the quantity that will be needed. Typically, the diagram indicates the number and type of supports for the foundation, the volume of required fill material, reinforcement and reinforcing materials for the base, as well as the number of polycarbonate sheets and arched blocks. Be sure to indicate the dimensions - this will help you correctly calculate all the necessary materials.
Greenhouse-house: drawing Drawing indicating connecting elements Schematic representation of the foundation with brickwork
The calculations should include elements such as:
- The number of windows, doors, vents, their sizes, as well as the number of fittings.
- Materials for covering the base: cement, perhaps sheets of plasterboard or even plastic bottles. Don't forget about the piles themselves. By the way, galvanized pipes can cope with this role.
- The length of the frame arcs should be 3,4,6,12 meters. This will help to better hide the joints of the sheets.
- When purchasing polycarbonate, you must take into account that the honeycombs run along the slope.
- On the drawing it is better to indicate the size of the doorway, its height, as well as materials for arranging the paths.
Features of small greenhouses
In modern times, the presence of a greenhouse on the plot of a country house or private house is not surprising. Such structures are used frequently and densely and can have the most unusual configurations.
- On large plots of land, structures of large dimensions are often installed; large volumes of different plants can be grown in them.
- When there is little soil and owners do not need a lot of plantings, then mini models of greenhouse buildings are used.
Making a small greenhouse is not too difficult. Many summer residents will take on the work process, trying to reduce costs so as not to contact experienced specialists who produce these structures to order.
If everything is done correctly, then the end result will be a long-term, effective structure in which many plantings will begin to grow.
Area and dimensions
The dimensions of a polycarbonate greenhouse depend on many factors. After we have decided on the location, we need to look at the site and decide how much margin we need on the sides. It is important that the greenhouse does not clutter up the space, and that it is convenient to walk around it even with a garden wheelbarrow.
IMPORTANT
Leave space for paths around the greenhouse - at least 1 meter.
If we talk about height, it depends on the height of the person who will work in it most of the time. He should be comfortable being in the greenhouse at full height. It is also necessary to consider what specific plants will be in this greenhouse. If you plan to grow grapes, then the height of the greenhouse should be at least 3.5 m. And for growing medium-sized crops, greenhouses with a height of two and a half meters are usually used. Of course, we proceed from the capabilities of the person and the dimensions of the site. If a person decides to spend money on a good-quality greenhouse, then it is better to make it more spacious.
GOOD TO KNOW!
The smaller the volume of the greenhouse, the greater the chance of overheating the plant!
The choice of greenhouse area and its size should be approached as seriously as possible - this is a structure for more than one season. If the technology is followed, such a greenhouse can last at least 20 years. A standard greenhouse is usually 6 meters in length. To build such a structure, you need about 4 sheets of polycarbonate.
Greenhouse "Ministar"
The Ministar greenhouse () differs from other small-sized greenhouses. Firstly, the distance between the arcs of the Ministar is not 1 m, but less - 0.67 m. Consequently, the supporting structure can withstand a greater load. So, the layer of dry snow that will not cause harm to the greenhouse is 50-55 cm (for other considered options it is up to 30-35 cm).
Secondly, the shape of the greenhouse is not arched, but has a gable roof.
Thirdly, it has strictly fixed dimensions: length – 3.3 m, width – 2 m, height – 2.1 m.
And finally, even the design of the doors at Ministar differs from other greenhouses. The doors are not solid, but consist of two equal parts that can be opened together - if you need to go inside, or only one half - if you only need to ventilate the greenhouse.
The price of a greenhouse with Economy polycarbonate is from 15,500 rubles.
Choosing a foundation option for a polycarbonate greenhouse
Let’s make a reservation right away: if you plan to use a polycarbonate greenhouse only in the summer season, and especially if your site does not suffer from drafts, then there is no need to worry about a monolithic foundation. Arranging mobile greenhouses is enough. They can be moved from place to place or simply disassembled.
Mobile greenhouses made of polycarbonate Mobile greenhouse made of polypropylene pipes
Such greenhouses are easy to make with your own hands; they can be used anywhere on your site. However, if you are planning a structure that will last forever, then a solid foundation is simply necessary. It will protect the building from winds and also retain heat. In addition, such a greenhouse is not afraid of pests. And the plants will be reliably protected from temperature changes in the soil and frost.
What to install a polycarbonate greenhouse on? The choice of foundation depends on the soil on which you plan to build the greenhouse. The proximity of groundwater is of primary importance here.
Tape
This type of foundation is usually installed under greenhouses that are located in lowlands or wet soils. This foundation is made in two versions: block and brick. Its peculiarity is that it covers the entire perimeter. To do this, you need to dig a trench 25 cm wide, 50 cm deep and make a special formwork.
Expert advice
Example of a strip foundation Formwork for a strip foundation
The strip foundation can be made of bricks or blocks. This is the most cost-effective option for constructing a solid foundation for a greenhouse.
Strip foundation made of blocks
If the greenhouse is not very large, blocks or bricks can be replaced with wooden beams impregnated with bitumen varnish or mastic. Moreover, the base can be either flush with the ground or protrude, forming a small side.
Spot
The foundation is in the ground only to the depth of the supports. These can be piles, pipes filled with concrete, or bricks. The peculiarity is that such piles are not located along the entire perimeter, but at some points.
Columnar foundation for a frame house Point foundation made of bricks
The length of the “step” depends on the massiveness of the structure. The lighter it is, the fewer columns. Typically, this type of foundation involves the use of timber as a base. The wood is processed, sawn, joined and fastened around the perimeter.
Wooden beam
The most budget option for installing a greenhouse. The beam is fastened with staples around the perimeter and installed on a sand bed. Even cobblestones or bricks are placed under the corners. This foundation can only support small polycarbonate greenhouses.
Foundation on a sand cushion made of wooden beams The main task of the foundation in this case is to raise the structure above ground level in order to protect the wood from the harmful effects of moisture. It is better to treat the timber with an antiseptic.
REMEMBER!
Such a lightweight foundation can be used for greenhouses with a size not exceeding 8x3 meters. Otherwise, it is better to use a strip foundation with wood frame.
Pile
Used on soils with unstable stability - peat and clay, rich in sandy loam or prone to flooding. It is considered the strongest and most durable, but also the most expensive. A monolithic base will keep the structure in its original condition. Large polycarbonate greenhouses are installed on such piles. They are usually placed on a hill, creating a cushion of air that can slightly lower the temperature in the greenhouse.
Greenhouse on stilts Metal base on stilts
To create this type of foundation, it is necessary to drill wells, pour crushed stone and sand with concrete at a distance of no more than 70 centimeters from each other. The piles are fixed with wooden formwork.
Pouring a pile foundation
This type of foundation is used to build houses. Such structures are considered the most durable and durable.
Do you need to build a foundation?
To ensure that the greenhouse is not blown away by a strong gust of wind, and that the entire structure is sufficiently rigid and stable, it is necessary to make a foundation. This will take very little time and will allow you to easily move the greenhouse to a new location if necessary.
Here, as you can see, the greenhouse is installed on a wooden foundation
Here is a simple set of materials that will be required to build a foundation:
- wooden beam 12x12 mm;
- roofing felt;
- wood screws;
- hacksaw;
- roulette;
- antiseptic;
- shovel.
A trench is dug along the perimeter of the structure being erected, its width and depth exceeding the timber by 5-7 mm. Roofing felt is laid in the trench. Next, pieces of timber of the required length are prepared and treated with an antiseptic composition. After this, the timber is laid in the trench, and the edges of the roofing material are wrapped towards the foundation (if necessary, the roofing material can be secured to the timber with a construction stapler). All that remains is to securely fasten the beams with self-tapping screws - the foundation is ready.
Example of a foundation for a greenhouse
Prices for roofing material
roofing felt
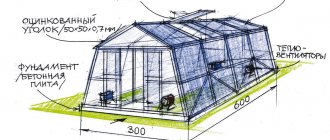
Polycarbonate greenhouse frame materials
The choice of material from which to build a greenhouse depends on many factors. Let's list some of them:
- Winter or summer greenhouse.
- Shape of the building.
- Shelter material.
- Financial opportunities.
Three materials are most often used to construct greenhouse frames. Each has disadvantages and advantages.
Metal carcass
Metal is most often used in the manufacture of frames for greenhouses. The advantages are obvious: strength, the ability to create different shapes and dimensions. Stability of the structure.
Greenhouse design with metal frame
To weld the frame, it is better to use a galvanized profile pipe. It is not afraid of corrosion, durable and strong. This frame will withstand both storms and snowfall. Both pipes and galvanized drywall profiles are used. The second type is suitable for temporary seasonal structures.
Metal profile greenhouse frame
You need to pay attention to the quality of the seams. Incorrectly processed joints can damage polycarbonate. Conditional disadvantages include the complexity of bending the structure when making a frame with your own hands. (We'll tell you how to solve this problem a little later). The frame of a greenhouse made from a profile pipe is considered the strongest.
Wooden frame
Wood is one of the cheapest options for building a greenhouse. This material does not require any special skills to operate. Any boy, remembering his labor lessons, will be able to connect the parts.
Greenhouse with wooden frame
A wooden greenhouse is round in shape. However, a wooden greenhouse made of polycarbonate may not survive the coating material:
- Wood is a short-lived material, especially in combination with high humidity and possible parasites. Such greenhouses will not last very long, no more than three years.
- It is difficult to create a greenhouse of the required shape - wood does not bend. It can only be used in buildings of classical forms.
- Wood, even painted, “heaves” and swells. Be prepared that your greenhouse will not close and open tightly, which means the heat will quickly leave the room.
Frame made of polypropylene pipes
Plastic is an excellent solution for mobile and seasonal greenhouses. It is easy to assemble, you can choose a convenient shape, and it is quite durable. It cannot be used in winter - the material will burst at the first frost. Among the advantages are relative cheapness, the ability to replace any element, ease of assembly, and water resistance.
Plastic greenhouse: diagram
Greenhouse made of polypropylene pipes
There are limitations to using plastic pipes in combination with polycarbonate. Plastic can “creep” under the weight of the shelter. It is better to cover such greenhouses with film.
Frame made of aluminum profiles
A fairly good option for creating a stable frame. A greenhouse made from an aluminum corner made by yourself will serve for at least 35 years. Aluminum does not corrode, is easy to assemble, and is strong enough to withstand even glass lining.
Greenhouse made of aluminum structures and options for its fastening
The only negative is the thickness of the profile. Polycarbonate is too wide for aluminum to hold it, you need to use additional fasteners.
Ready-made or self-assembled
Of course, ordering and assembling a small greenhouse according to the instructions is easier than understanding how to prepare the materials to create a new home for future plants, arrange them correctly, organize a suitable climate inside, and not make mistakes in the calculations.
It’s especially disappointing if the greenhouse, made with your own hands and with love for the crops grown, failed and the plants died.
In the ready-made version, there is much less chance of such a situation arising, although if the instructions are not followed correctly, the green pets being raised can die even in the most expensive ready-made greenhouse.
Attentiveness, a calculator and as much information as possible, now available on the Internet - then the decision to build a small greenhouse will be justified, and a transparent house for plants, assembled with your own hands, will become their cozy refuge in the cold or hot season.
Interior arrangement of the greenhouse
The internal structure of a polycarbonate greenhouse depends entirely on the wishes of the person. The average Russian summer resident tries not to use a greenhouse in the winter. Others also use it during the cold season.
Moreover, it is not necessary to use a central heating system. Modern infrared heaters or heat guns are suitable. Some summer residents who spend the winter on their plots often create winter greenhouses here. In this case, the greenhouse must be heated with your own hands.
96.Greenhouse in winter.
The price of a polycarbonate greenhouse in the catalogs of leading manufacturers
The most popular models are presented in the table. The price of polycarbonate greenhouses today is on average 10% lower than the seasonal price. You can save from 1.5 to 2 thousand rubles on your purchase. We invite you to familiarize yourself with the average prices now in order to meet the new summer season fully armed.
| Photo | Manufacturer | Average price, rub. |
| LLC "Greenhouse Center" | 9 500 | |
| LLC "New Forms" | 19 700 | |
| 14 500 |